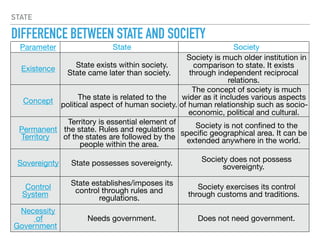
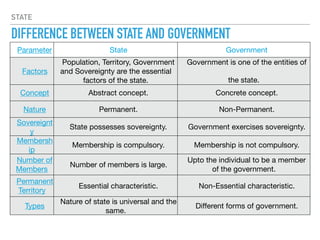
The document discusses the concept of the state within political science, highlighting its aspects, origins, and essential factors including population, territory, government, and sovereignty. It differentiates between the state and society, noting that the state is a political organization while society encompasses broader social relationships. The state requires a government for enforcement and regulation, while society operates through customs and traditions without the need for formal governance.