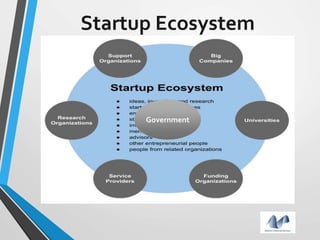
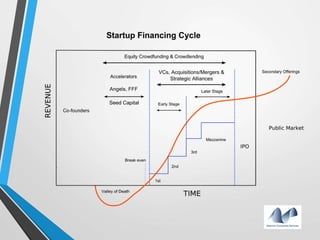
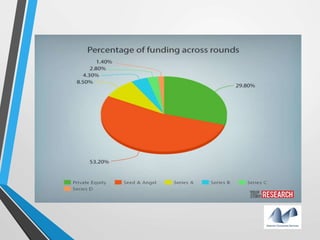
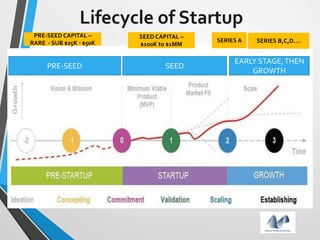
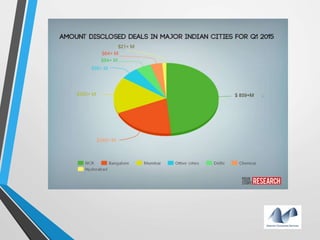
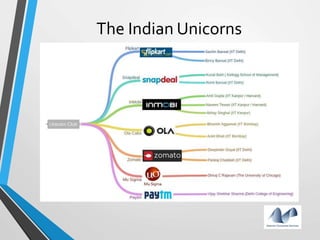
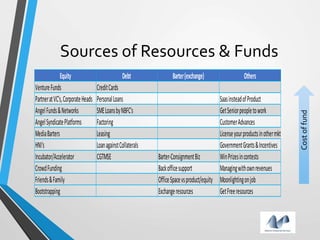
The document provides an overview of startups in India, including what defines a startup, the startup culture and ecosystem. It discusses the types of problems faced by startups as well as common entity types. The document also outlines several government initiatives to support startups, such as the Startup India program, tax exemptions, and sources of funding. It notes that the biggest question facing startups is fundraising and provides tips on valuation, dilution, finding investors, and structuring the fundraising process.