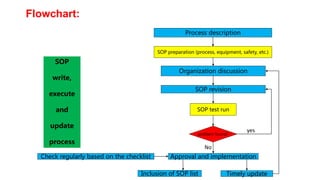
Standard operating procedures (SOPs) are written instructions that document routine processes and activities. This document discusses what SOPs are, who needs them, when and where they are used, why they are important, and how to write them. It provides guidelines for writing SOPs, including describing processes, preparing the documentation, obtaining approvals, and regularly updating and testing SOPs. Key elements that should be included are the process steps, equipment details, safety measures, common issues, and emergency procedures. SOPs are important for training, consistency, quality control, and regulatory compliance.