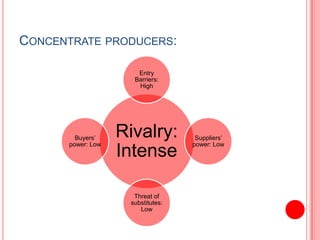
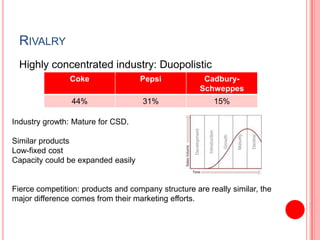
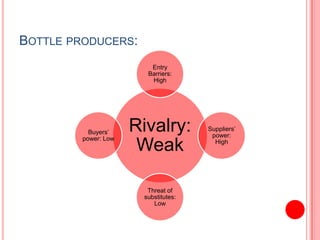
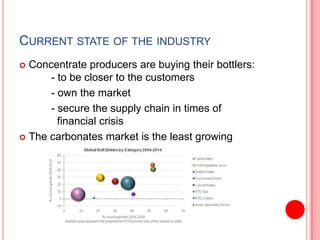
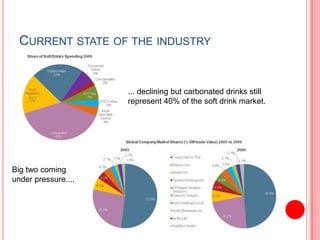
This document analyzes the Coca-Cola and PepsiCo concentrate producer and bottler industries using Porter's Five Forces framework. It finds that the concentrate producer industry exhibits a duopoly between Coca-Cola and PepsiCo, with high barriers to entry. The bottler industry has consolidated considerably and bottlers have weak bargaining power against concentrate producers. Both industries face challenges from stagnating carbonated soft drink consumption and increasing costs, driving both to diversify into new products and markets like Asia to maintain profitability.