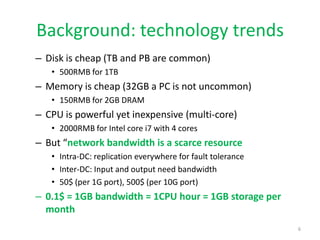
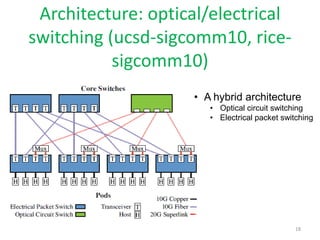
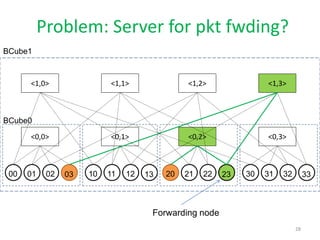
The document discusses the current state and future opportunities in data center networks (DCN), outlining challenges related to scalability, performance, and fault tolerance. It emphasizes the need for innovative designs and protocols to enhance network efficiency, given the growing demands of cloud computing and the inherent limitations of bandwidth. A modular DCN design is proposed as a potential solution to these challenges, along with a focus on the importance of research in this area.