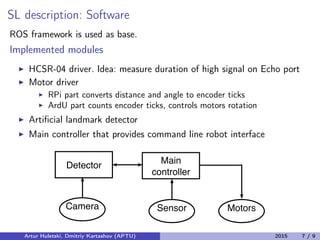
The document outlines the design and implementation of a mobile robot using a Raspberry Pi and Arduino for research in robotics. It covers the hardware components, including various sensors and motors, as well as the software framework utilized for functions and communication between components. The authors also discuss future improvements, such as merging circuit components and enhancing motor communication.



![Hardware scheme
Raspberry Pi B
Arduino Uno
L298-based PCB
JGA25-375
JGA25-375
HCSR-04 Camera
UBEC
3:2 Voltage Divider
3:2 Voltage Divider
11.1V battery
11.1V
5V
5V
5V
Motors On/Off
11.1V
11.1V
Encoder Data
Trig request
5V response
3V response
5V
5V
5V
USB
5V ping
3V ping
[I2C]
Movement
request
Artur Huletski, Dmitriy Kartashov (APTU) 2015 5 / 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/huletskirpirobot-150503020855-conversion-gate02/85/Raspberry-Pi-robot-with-ROS-5-320.jpg)