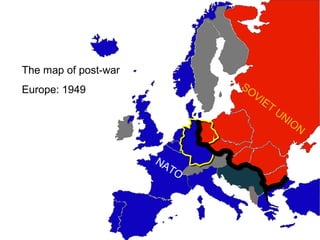
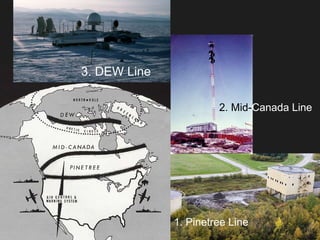
The document discusses the effects of the Cold War on Canada’s autonomy, highlighting key events such as the Berlin Blockade and the Cuban Missile Crisis. It examines Canada’s military commitments within NATO and NORAD, reflecting on the trade-offs made in terms of national sovereignty for security. Additionally, it questions the impact of post-war defense issues on Canadian autonomy, considering Canada's willingness to align with U.S. military strategies.