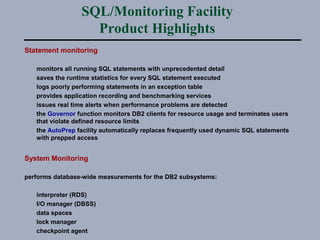
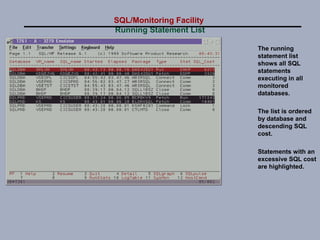
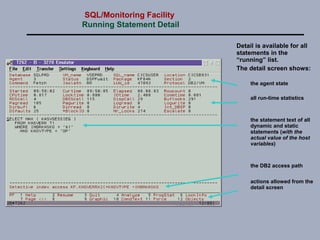
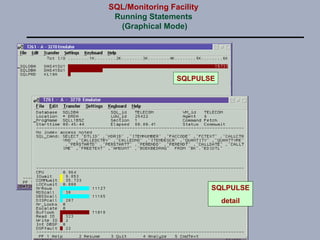
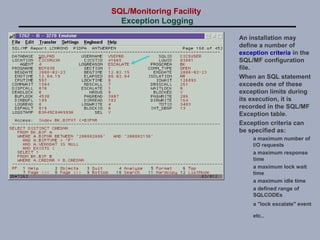
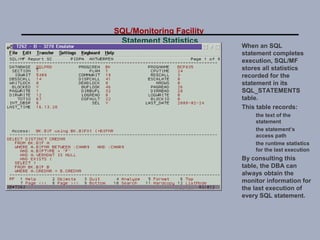
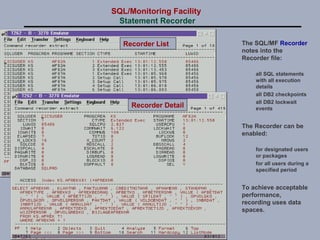
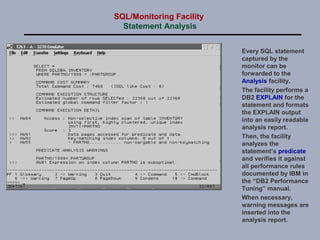
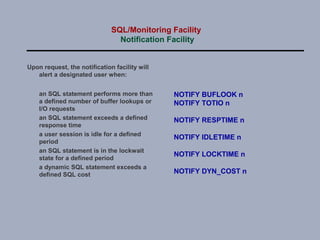
SQL/Monitoring Facility is an execution-time monitor for DB2 that provides monitoring at the database and SQL statement levels. It monitors resource usage, records execution statistics for every SQL statement, and controls resource consumption through a governor function. It also optimizes dynamic SQL statements with an auto-prep facility.