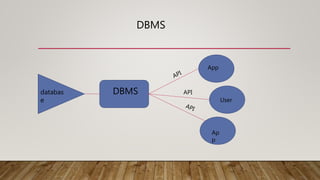
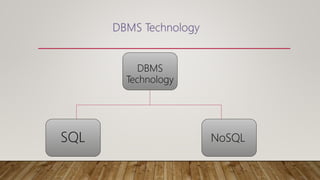
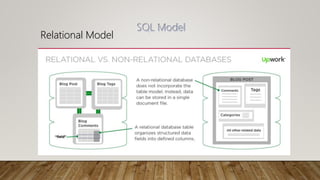
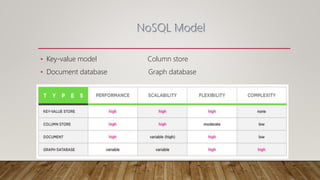
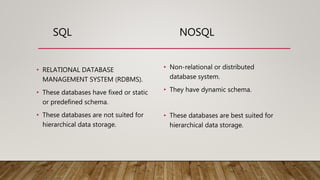
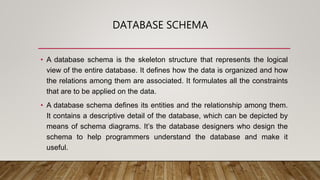
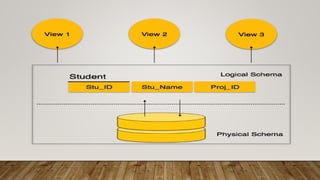
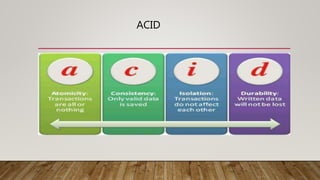
The document compares SQL and NoSQL databases, highlighting their distinct characteristics and use cases. SQL databases are structured and best for complex queries with fixed schemas, while NoSQL databases offer greater flexibility and are suited for unstructured data and dynamic schema. Key topics covered include database management systems, data manipulation languages, and the importance of database schemas.