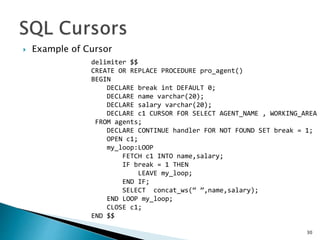
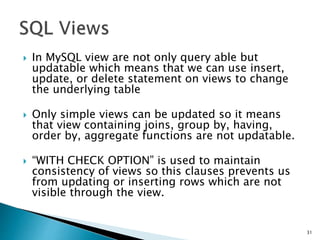
This document provides an overview of SQL (Structured Query Language) in 3 sentences or less:
SQL is a standard language for storing, manipulating and retrieving data in relational database systems. The document outlines various SQL commands, clauses, and functions for working with data types, tables, queries, procedures, indexes and more. Examples are provided to illustrate how to use SQL statements to define schemas, insert, update, select and manipulate data in relational database tables.











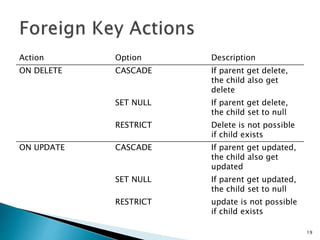
![ Foreign key is used to maintain referential integrity between two
tables it points to the primary key of another table
Foreign key constrain denoted a parent child relationship . A
child can’t be exist and parent can’t delete if child is exists.
Foreign key can be set to NULL
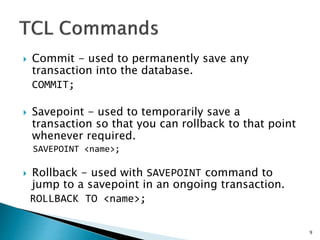
To Create Foreign Key
ALTER TABLE <table> ADD FOREIGN KEY <col_name>
REFERENCES <p_table>(<p_col>) [on_delete_action]
[on_update_action] ;
To Delete Foreign Key
ALTER TABLE <table> DROP FOREIGN KEY;
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlnotes-210201145734/85/SQL-Sort-Notes-18-320.jpg)


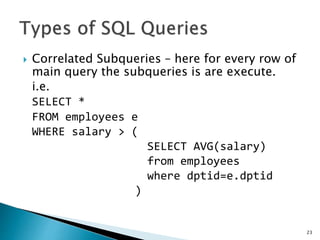


![ A stored procedures is a segment of declarative
SQL statements stored inside the database
catalog.
Stored procedures performance, reduce network
traffic, provide code reusability & Security.
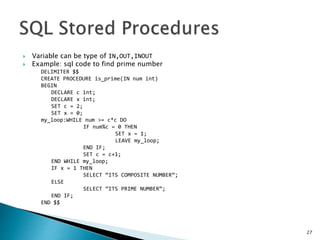
Stored Procedure are create using
CREATE PROCEDURE <prs_name> (<paramenters>)
BEGIN
[variable declaration]
[perform some operations]
END
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlnotes-210201145734/85/SQL-Sort-Notes-26-320.jpg)
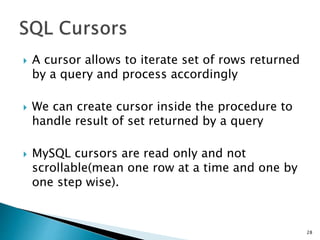
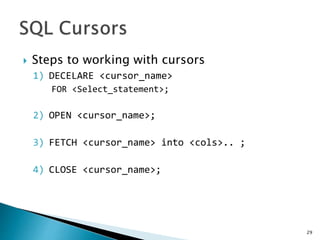

![ A Trigger is a set of SQL statements stored in the database
catalog which executed or fired when the some event
associated with table.
Trigger are special kind of stored procedure that are
executed automatically on firing of some event
We use “FOR EACH ROW” if there is bulk row operation in
Triggers
Triggers are created using
CREATE TRIGGER <trigger_name> <trigger_time> <trigger_event>
ON <table_name>
BEGIN
[process]
END
To delete Trigger
DROP TRIGGER <name>;
33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlnotes-210201145734/85/SQL-Sort-Notes-33-320.jpg)

