There are several key differences between identity and sequence in SQL Server 2012. Identity is dependent on and a property of a table, while sequence is independent and an object. Identity requires inserting a new record to generate a new ID, while sequence allows directly viewing the next ID. Sequence allows for cycling, caching, and defining a maximum value, which identity does not support.
The main differences between temp tables and table variables are that temp tables are stored in tempdb and can be used by multiple users, while table variables are stored in memory and only available to the current user. Temp tables support all DDL operations like indexes, while table variables only support clustered indexes. Temp tables also support transactions and functions cannot use table variables.
![1.Difference between Identity and Sequence in SQL Server 2012
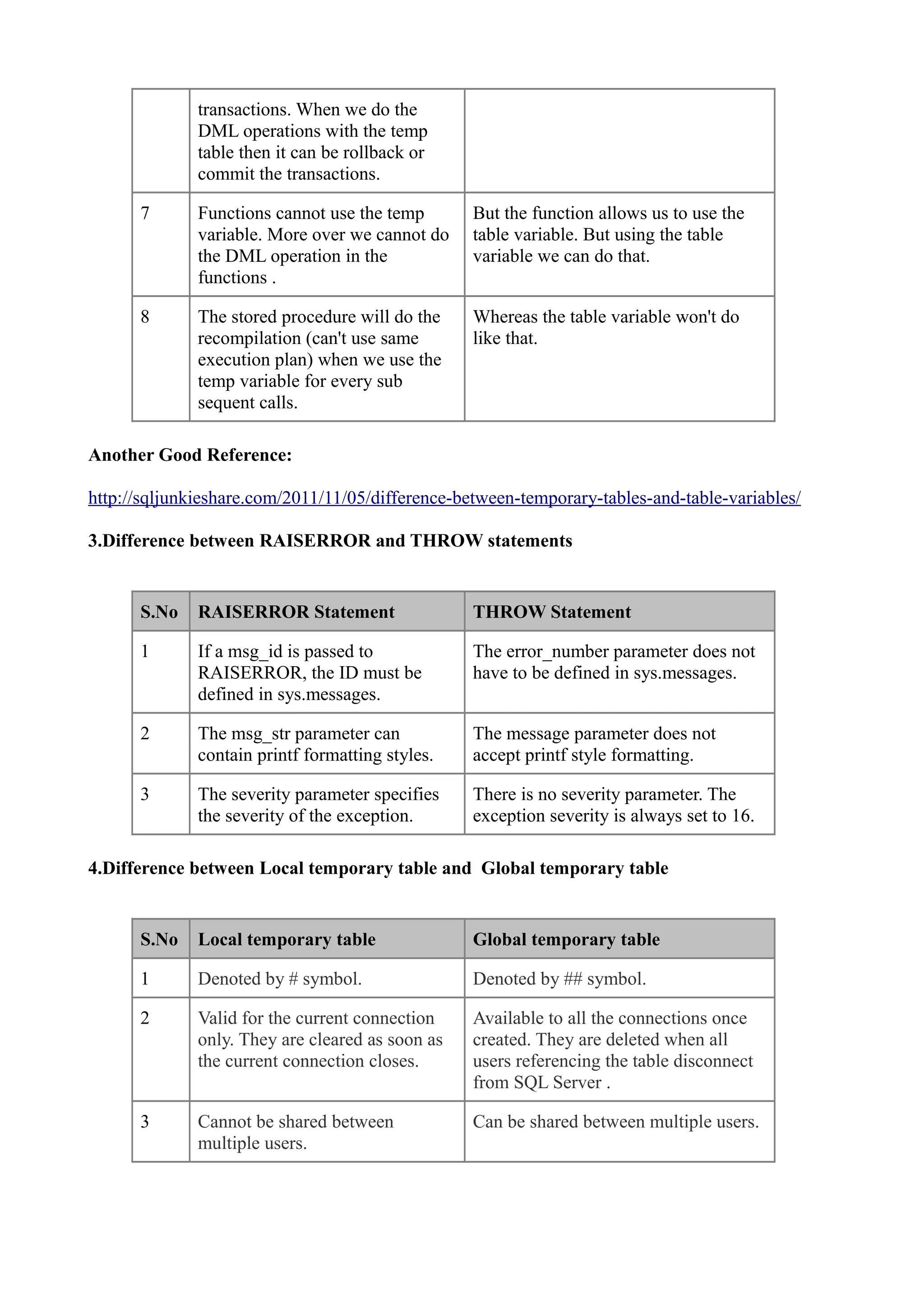
S.No Identity Sequence
1 Dependant on table. Independent from table.
2 Identity is a property in a table. Sequence is an object.
Example : Example :
CREATE TABLE Table CREATE SEQUENCE [dbo].
test_Identity [Sequence_ID]
( AS [int]
[ID] int Identity (1,1), START WITH 1
[Product Name] varchar(50) INCREMENT BY 1
) MINVALUE 1
MAXVALUE 1000
NO CYCLE
NO CACHE
3 If we need a new ID from an In the sequence, we do not need to
identity column we need to insert new ID, we can view the new ID
insert and then get new ID. directly.
Example : Example :
Insert into [test_Identity] Values SELECT NEXT VALUE
(‘SQL Server’) FOR dbo.[Sequence_ID]
GO
SELECT @@IDENTITY AS
‘Identity’
–OR
Select SCOPE_IDENTITY() AS
‘Identity’
4 We cannot perform a cycle in In the sequence, we can simply add
identity column. Meaning, we one property to make it a cycle.
cannot restart the counter after a
particular interval. Example :
ALTER SEQUENCE [dbo].
[Sequence_ID]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlserverdifferencefaqs-3-120726045720-phpapp02/75/Sql-server-difference-faqs-3-1-2048.jpg)
![CYCLE;
5 We cannot cache Identity column Sequence can be easily cached by just
property. setting cache property of
sequence. It also improves the
performance.
Example :
ALTER SEQUENCE [dbo].
[Sequence_ID]
CACHE 3;
6 We cannot remove the identity The sequence is not table dependent so
column from the table directly. we can easily remove it
Example :
Create table dbo.[test_Sequence]
(
[ID] int,
[Product Name] varchar(50)
)
GO
–First Insert With Sequence object
INSERT INTO dbo.test_Sequence
([ID],[Product Name]) VALUES
(NEXT VALUE FOR [Ticket] ,
‘MICROSOFT SQL SERVER 2008′)
GO
–Second Insert without Sequence
INSERT INTO dbo.test_Sequence
([ID],[Product Name]) VALUES (2 ,
‘MICROSOFT SQL SERVER 2012′)
7 We cannot define the maximum Here we can set up its maximum
value in identity column it is value.
based on the data type limit.
Example :](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlserverdifferencefaqs-3-120726045720-phpapp02/75/Sql-server-difference-faqs-3-2-2048.jpg)
![ALTER SEQUENCE [dbo].
[Sequence_ID]
MAXVALUE 2000;
8 We can reseed it but cannot We can reseed as well as change the
change the step size. step size.
Example : Example :
DBCC CHECKIDENT ALTER SEQUENCE [dbo].
(test_Identity, RESEED, 4) [Sequence_ID]
RESTART WITH 7
INCREMENT BY 2;
9 We cannot generate range from We can generate a range of sequence
identity. values from a sequence object with the
help of sp_sequence_get_range.
2.Difference between Temp table and Table variable
S.No Temp table Table variable
1 A Temp table is easy to create and But the table variable involves the
back up data. effort when we usually create the
normal tables.
2 Temp table result can be used by But the table variable can be used by
multiple users. the current user only.
3 Temp table will be stored in the But a table variable will store in the
tempdb. It will make network physical memory for some of the data,
traffic. When we have large data then later when the size increases it
in the temp table then it has to will be moved to the tempdb.
work across the database. A
Performance issue will exist.
4 Temp table can do all the DDL Whereas table variable won't allow
operations. It allows creating the doing the DDL operations. But the
indexes, dropping, altering, etc.., table variable allows us to create the
clustered index only.
5 Temp table can be used for the But the table variable can be used up
current session or global. So that a to that program. (Stored procedure)
multiple user session can utilize
the results in the table.
6 Temp variable cannot use the But we cannot do it for table variable.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlserverdifferencefaqs-3-120726045720-phpapp02/75/Sql-server-difference-faqs-3-3-2048.jpg)