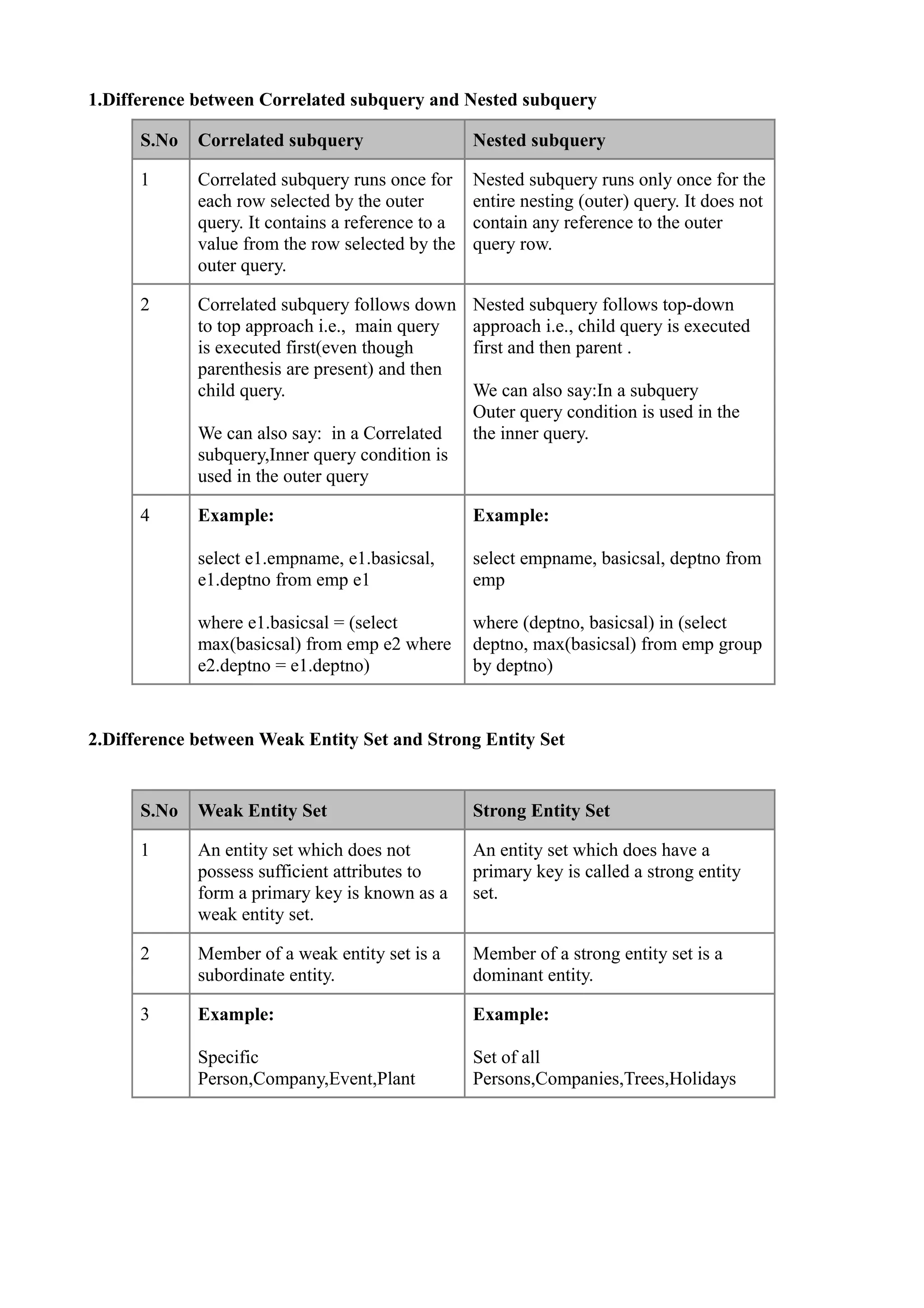
The document compares differences between correlated and nested subqueries, weak and strong entity sets, char and varchar data types in SQL Server, and SQL Server 2005 and 2008. A correlated subquery runs once for each outer query row and references the outer row, while a nested subquery runs once and does not reference the outer row. A weak entity set lacks a primary key while a strong entity set has one. Char occupies a fixed length while varchar occupies variable length plus 2 bytes for the length. SQL Server 2005 introduced XML datatype while 2008 encrypted entire databases and separated date and time datatypes.