The document presents SQL Server query tuning strategies, emphasizing the importance of identifying and optimizing queries that contribute most to performance issues. It outlines various techniques including monitoring wait states, analyzing execution plans, and employing Response Time Analysis (RTA) to diagnose and prioritize optimization efforts. The document also advises a collaborative approach between developers and DBAs to ensure effective tuning and highlights the value of indexing and query rewriting in improving database performance.



















![2/12/2013 Confidential - Internal Use Only 21
Execution Plan
Recommendation from SSMS
CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX [<Name of Missing Index>]
ON [dbo].[registration] ([cancelled],[signup_date])
INCLUDE ([student_id],[class_id])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/querytuning-getitrightthefirsttime-sqlserver-130606173507-phpapp01/85/SQL-Server-Query-Tuning-Tips-Get-it-Right-the-First-Time-21-320.jpg)




![2/12/2013 Confidential - Internal Use Only 27
SSMS Plan
CREATE INDEX reg_can ON registration(cancelled, signup_date)
INCLUDE (class_id, student_id)
Execution Stats – 595 Logical Reads
CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX [<Name of Missing Index>]
ON [dbo].[registration] ([class_id],[cancelled],[signup_date])
INCLUDE ([student_id])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/querytuning-getitrightthefirsttime-sqlserver-130606173507-phpapp01/85/SQL-Server-Query-Tuning-Tips-Get-it-Right-the-First-Time-27-320.jpg)
![2/12/2013 Confidential - Internal Use Only 28
SQL Statement 2
• Lookup order status for caller
SELECT o.OrderID, c.LastName, p.ProductID, p.Description,
sd.ActualShipDate, sd.ShipStatus, sd.ExpectedShipDate
FROM [Order] o
INNER JOIN Item i ON i.OrderID = o.OrderID
INNER JOIN Customer c ON c.CustomerID = o.CustomerID
INNER JOIN ShipmentDetails sd ON sd.ShipmentID = i.ShipmentID
LEFT OUTER JOIN Product p ON p.ProductID = i.ProductID
LEFT OUTER JOIN Address a ON a.AddressID = sd.AddressID
WHERE c.LastName LIKE ISNULL(@LastName,'') + '%'
--AND c.FirstName LIKE ISNULL(@FirstName,'') + '%'
AND o.OrderDate >= DATEADD(day, -30, CURRENT_TIMESTAMP)
AND sd.ShipStatus <> 'C'
• Execution Stats – 10,159 Logical Reads](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/querytuning-getitrightthefirsttime-sqlserver-130606173507-phpapp01/85/SQL-Server-Query-Tuning-Tips-Get-it-Right-the-First-Time-28-320.jpg)


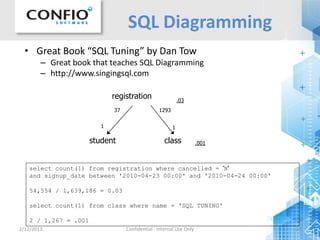
![2/12/2013 Confidential - Internal Use Only 31
SQL Diagramming
o .08
.03
SELECT COUNT(1)*1.0/(SELECT COUNT(1) FROM Customer) FROM Customer
WHERE LastName LIKE 'SMI%'
.03
SELECT COUNT(1)*1.0/(SELECT COUNT(1) FROM [Order]) FROM [Order]
WHERE OrderDate >= DATEADD(day, -30, CURRENT_TIMESTAMP)
.08
SELECT COUNT(1)*1.0/(SELECT COUNT(1) FROM [Order]) FROM [Order]
WHERE OrderStatus <> 'C'
.005
-- Combined
.005
i c
psd
a
.005](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/querytuning-getitrightthefirsttime-sqlserver-130606173507-phpapp01/85/SQL-Server-Query-Tuning-Tips-Get-it-Right-the-First-Time-31-320.jpg)
![2/12/2013 Confidential - Internal Use Only 32
Data Skew
• Only 0.5% of rows are <> ‘C’
• How about changing the query?
– AND o.OrderStatus = 'I'
• Add an Index on ShipStatus
SELECT OrderStatus, COUNT(1)
FROM [Order]
GROUP BY OrderStatus](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/querytuning-getitrightthefirsttime-sqlserver-130606173507-phpapp01/85/SQL-Server-Query-Tuning-Tips-Get-it-Right-the-First-Time-32-320.jpg)
![2/12/2013 Confidential - Internal Use Only 33
New Plan
CREATE INDEX IX2_OrderStatus ON [Order] (OrderStatus)
INCLUDE (OrderID,CustomerID)
Execution Stats – 3,052 Logical Reads](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/querytuning-getitrightthefirsttime-sqlserver-130606173507-phpapp01/85/SQL-Server-Query-Tuning-Tips-Get-it-Right-the-First-Time-33-320.jpg)

