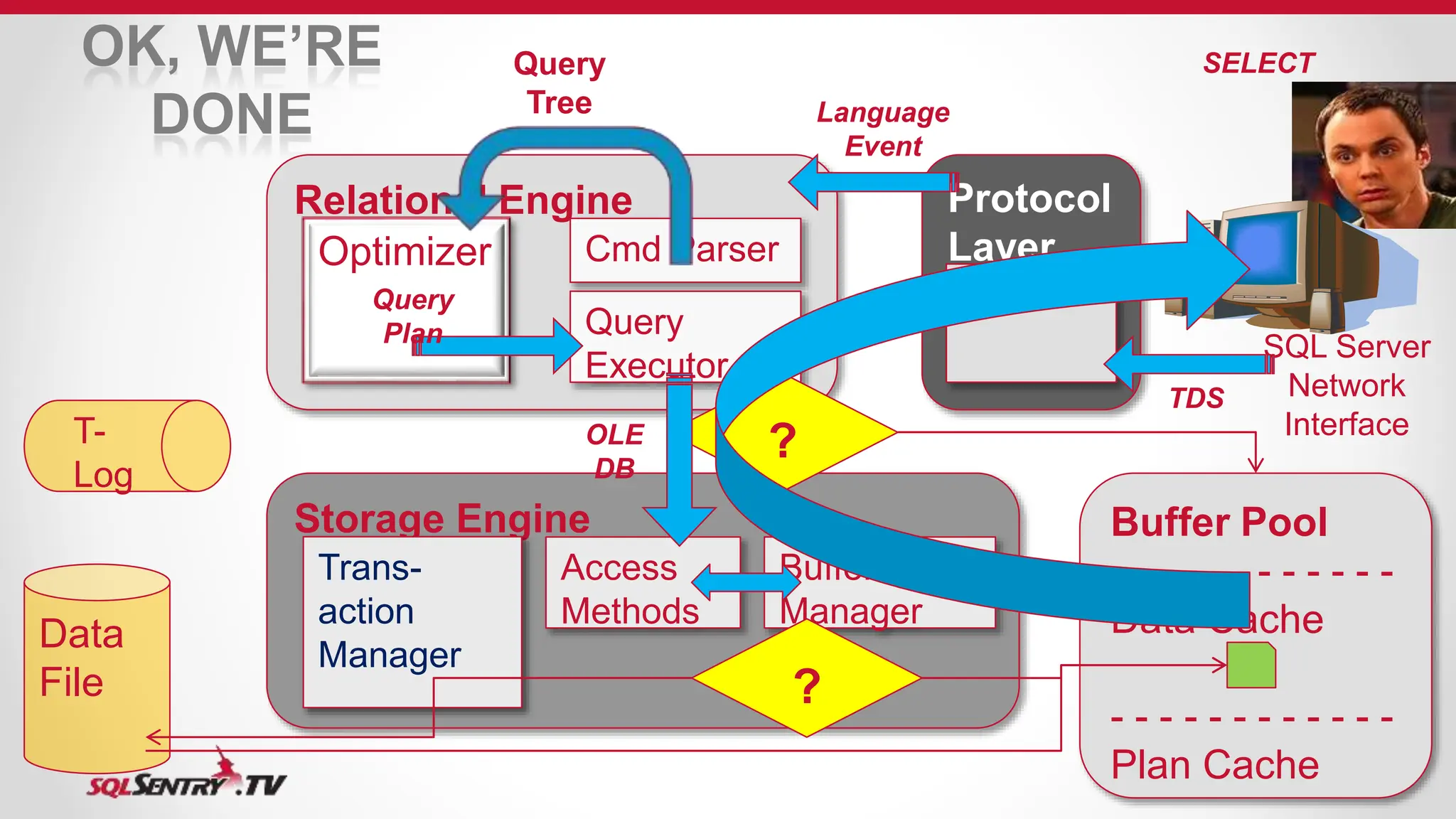
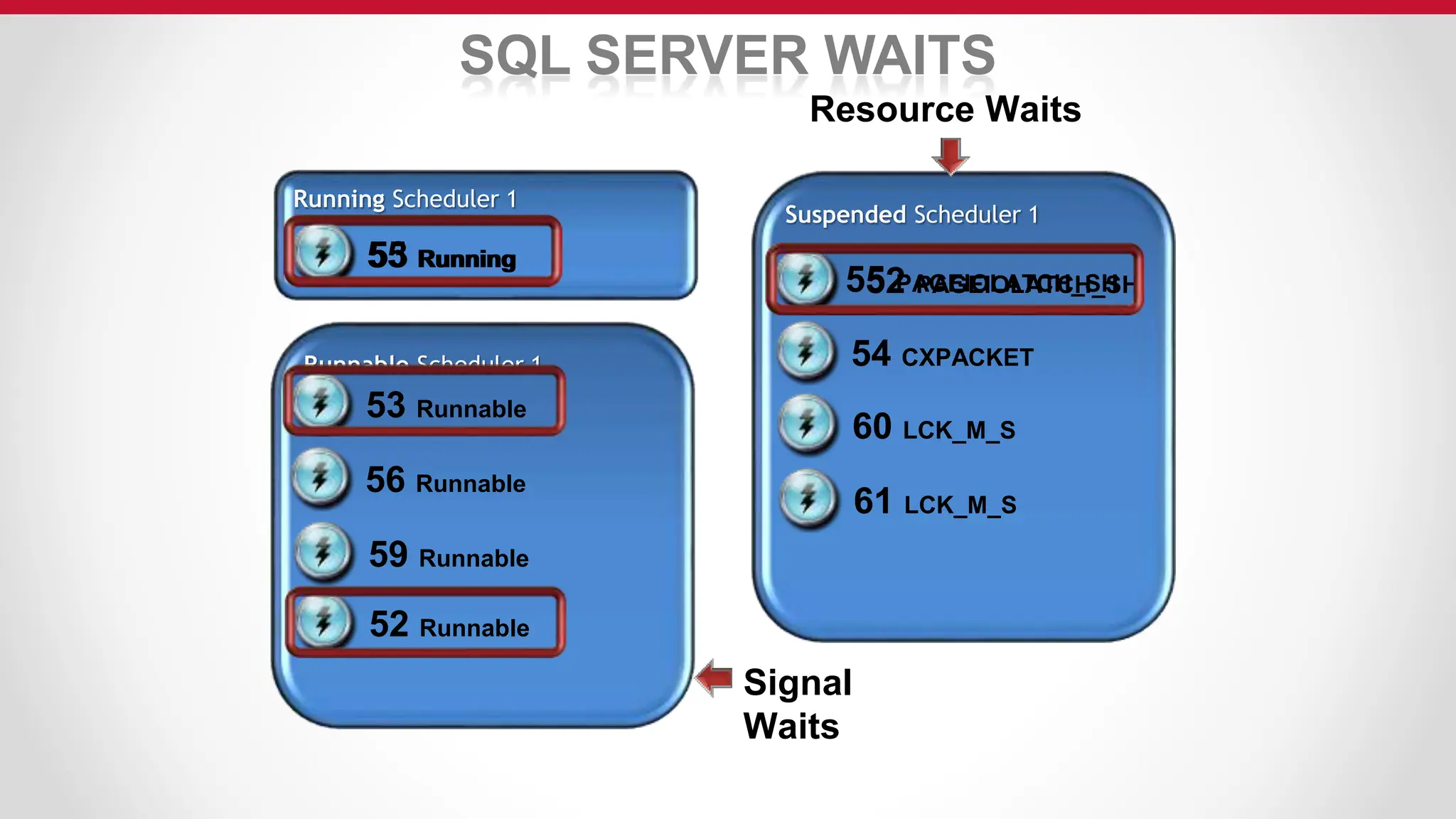
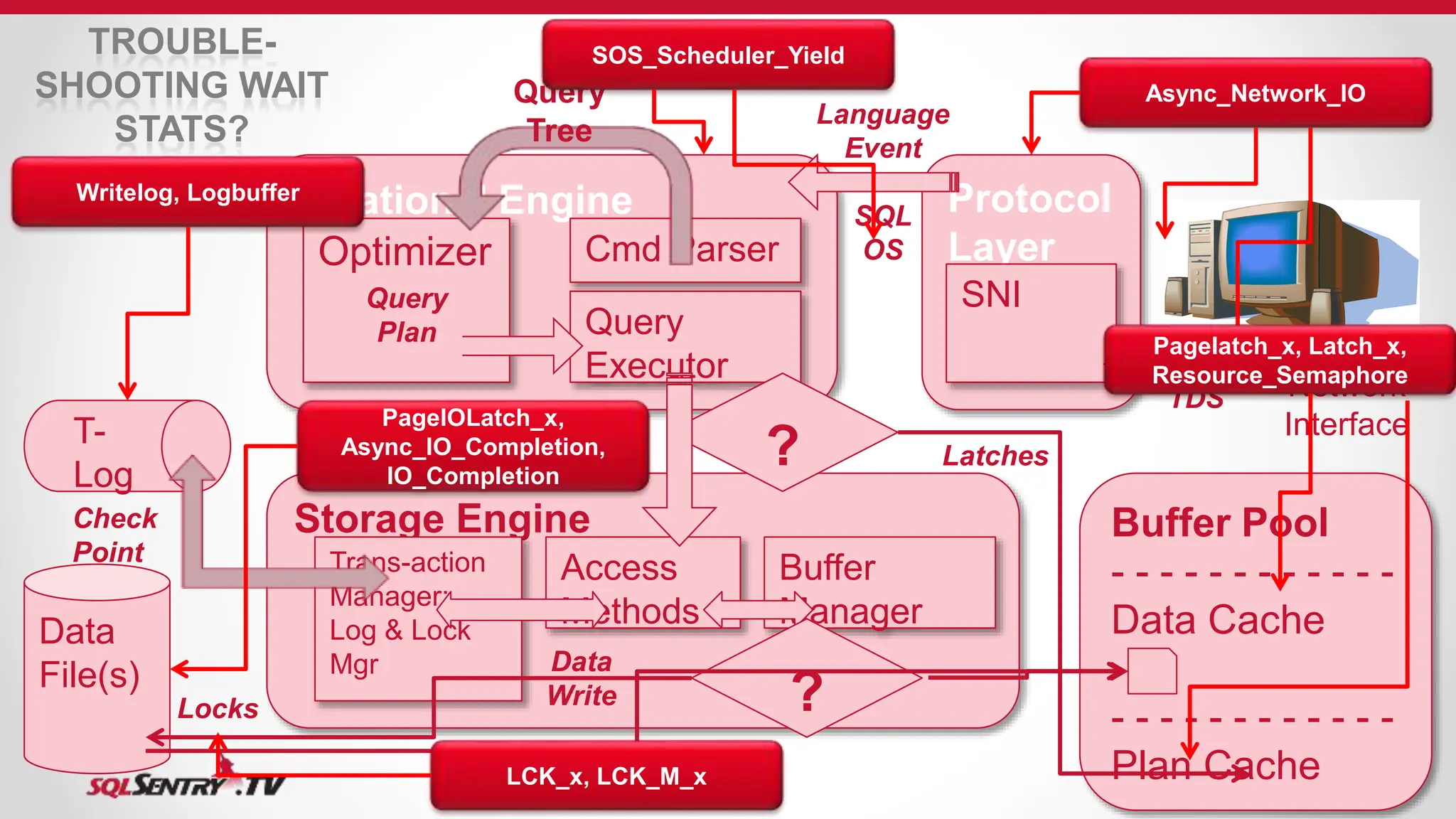
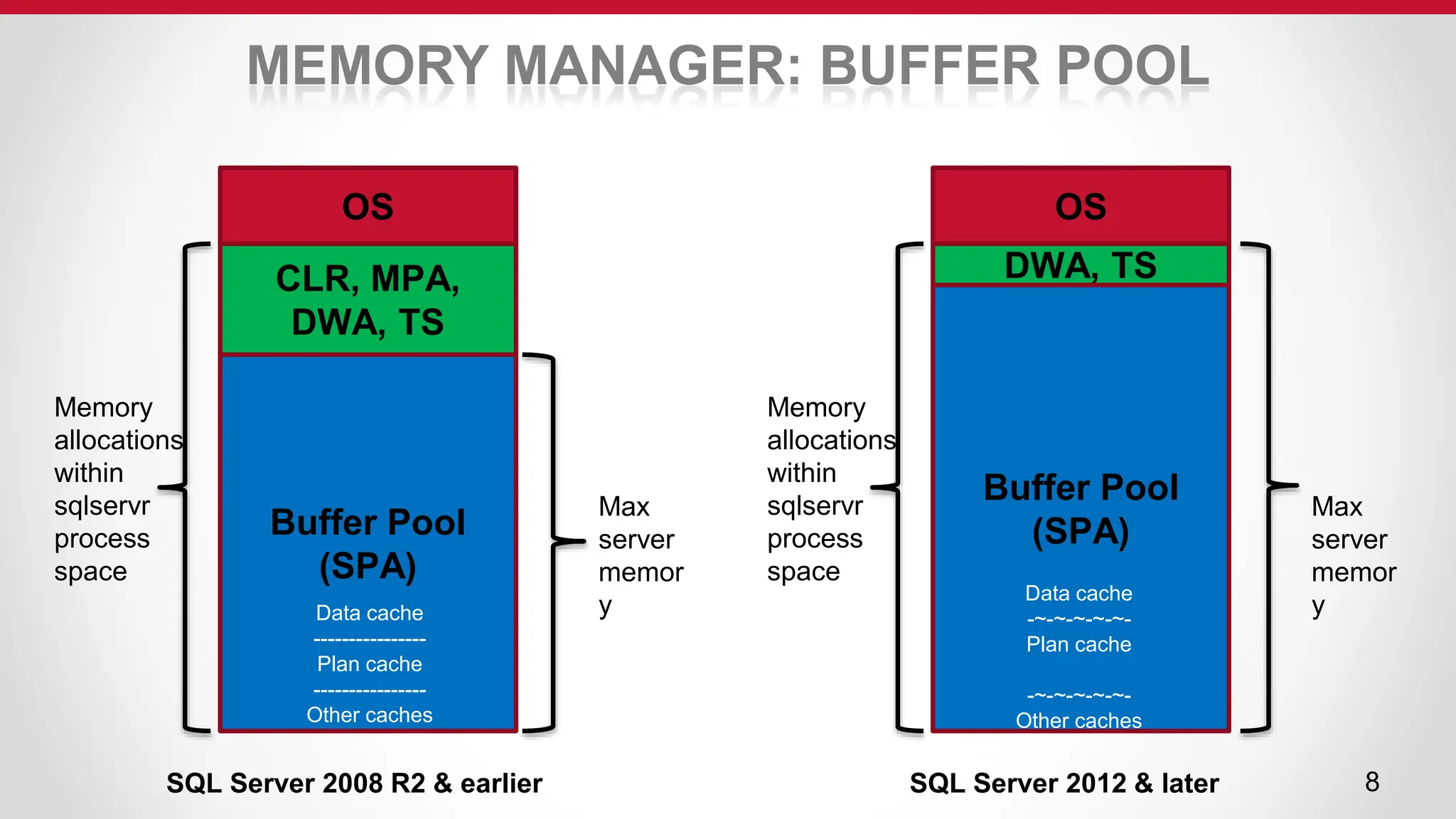
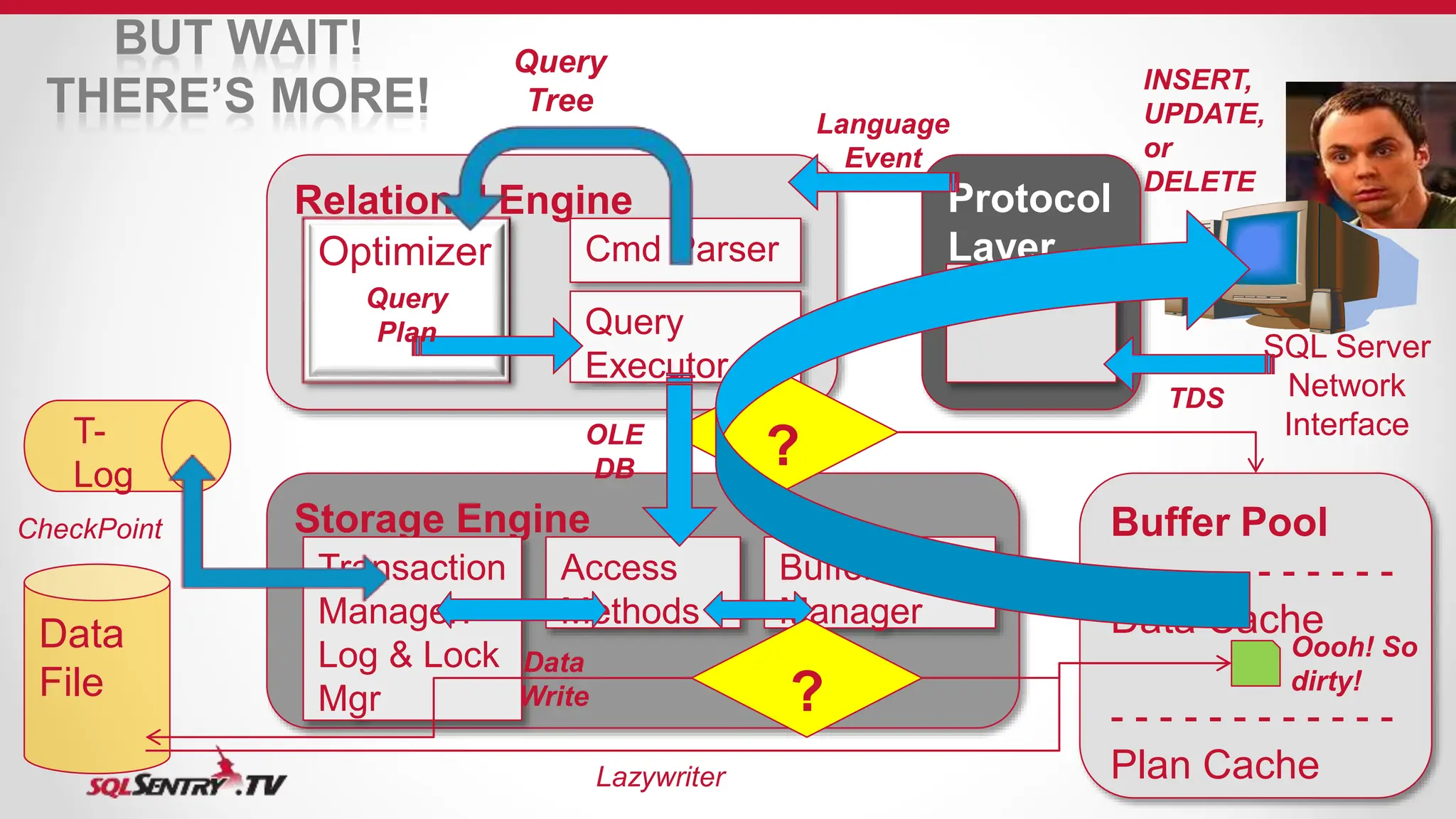
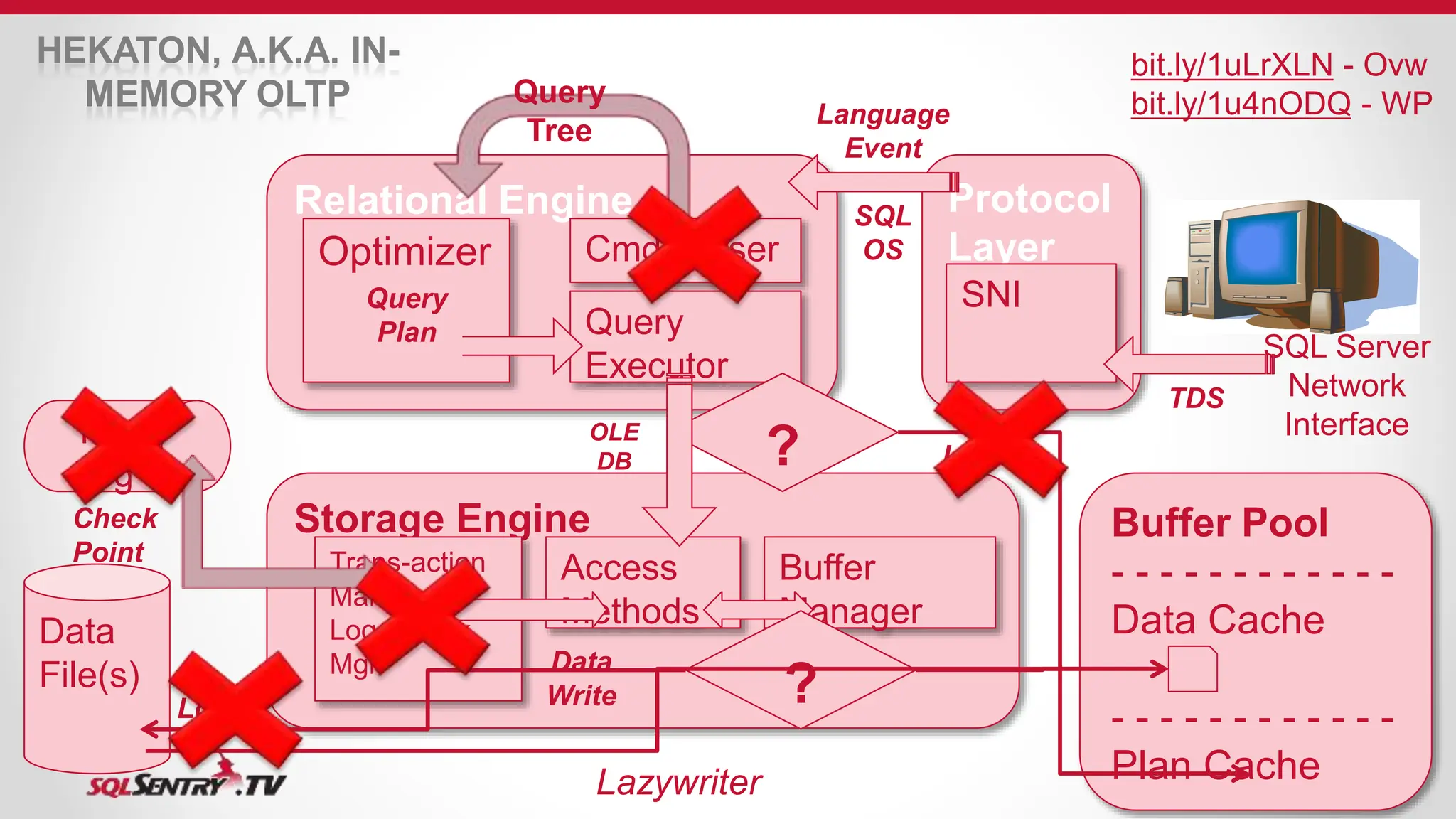
SQL Server uses an optimizer to generate efficient query execution plans. It considers factors like estimated costs and hardware capabilities to maximize performance. The relational engine parses queries and hands them to the optimizer, which generates plans for the query executor. Caches like the buffer pool and plan cache improve performance by storing frequently accessed data and plans in memory using algorithms like LRU for cache aging. Transactions are managed to maintain ACID properties using techniques such as logging, locking, and latching.