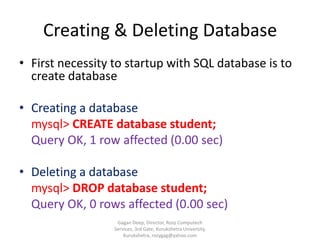
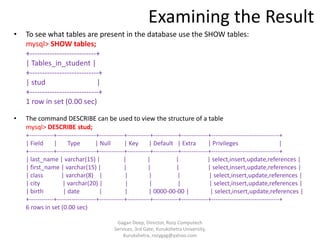
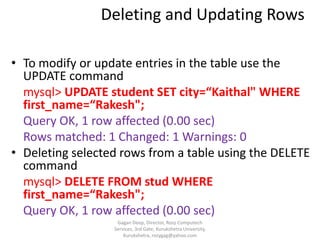
The document provides an overview of SQL and its characteristics. It discusses that SQL is a standard language for relational database management systems and provides a high-level declarative interface. The document also describes the different components of SQL including data definition language, data manipulation language, and data control language. It provides examples of creating tables and databases, inserting and querying data, and other SQL statements.