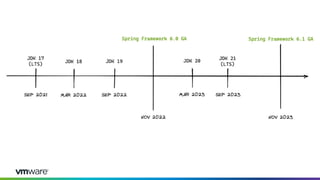
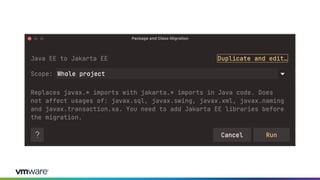
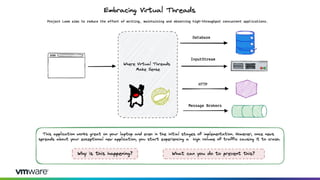
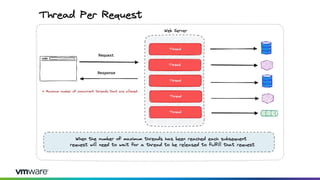
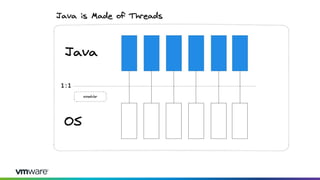
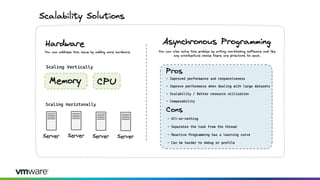
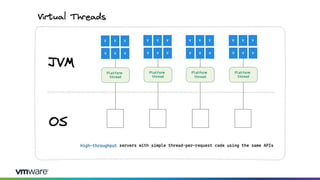
This document discusses new features and capabilities in Spring Boot 3 and beyond, including support for JDK 17 and Jakarta EE 9/10, ahead-of-time compilation, virtual threads, improved observability, and more. Spring Boot 3.1 RC1 has been released with features like using Testcontainers for development, building Docker images, and dependency upgrades. The speaker demonstrated Spring Boot 3 and discussed upcoming releases of Spring Framework 6.0 and 6.1 as foundations for new Spring Boot versions.