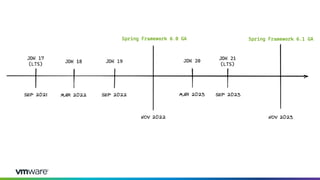
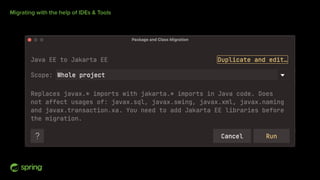
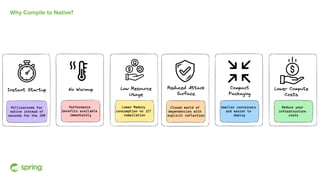
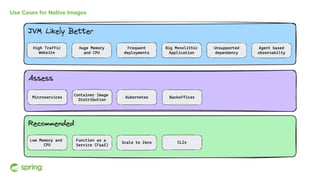
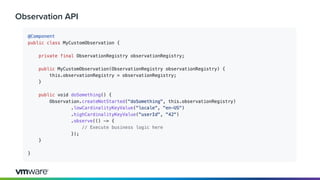
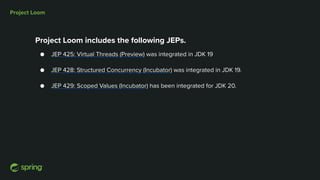
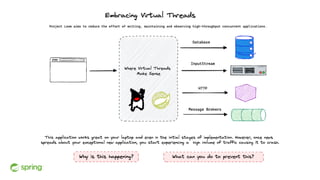
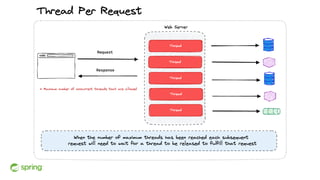
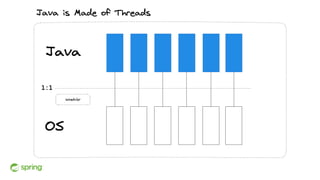
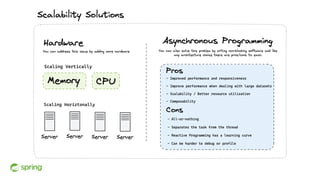
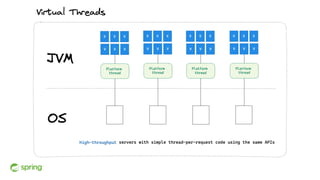
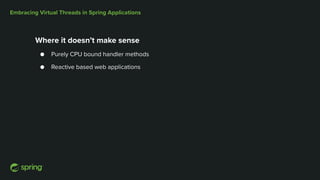
Dan Vega discussed new features and capabilities in Spring Boot 3 and beyond, including support for JDK 17, Jakarta EE 9, ahead-of-time compilation, observability with Micrometer, Docker Compose integration, and initial support for Project Loom's virtual threads in Spring Boot 3.2 to improve scalability. He provided an overview of each new feature and explained how they can help Spring applications.