The document provides an overview of the Spring Framework, including its core features such as dependency injection, aspect-oriented programming, transaction management, and web frameworks. It discusses how Spring promotes loose coupling, simplifies configuration, and provides abstractions that insulate applications from implementation details. Specific topics covered include DI/IoC, AOP, transactions, data access with Hibernate, and use of the DispatcherServlet web framework.






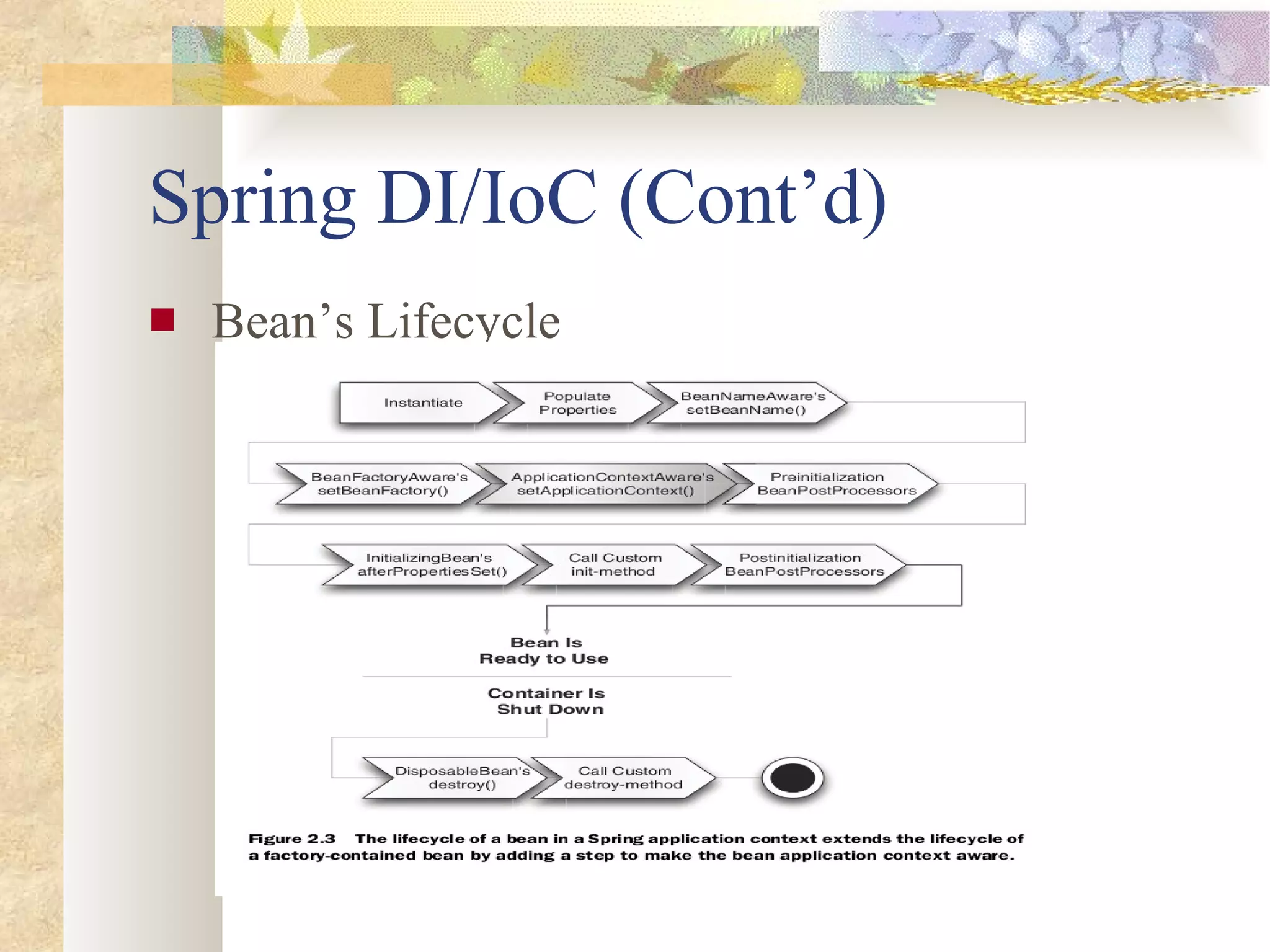
![Spring DI/IoC (Cont’d) Ways to instantiate container/working with application context ClassPathXmlApplicationContext FileSystemXmlApplicationContext XmlWebApplicationContext Syntax ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[] { "cfg/applicationContext.xml"}); Variations on dependency injection Constructor-based (PicoContainer, Spring) Setter-based (Spring) Interface based (Avalon)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springoverview-120105110704-phpapp01/75/Spring-overview-8-2048.jpg)















![Hibernate DAO (cont’d) public Reservation[] findReservations(Room room) { List list = getHibernateTemplate().find( "from Reservation reservation “ + “ where reservation.resource =? “ + “ order by reservation.start", instrument); return (Reservation[]) list.toArray(new Reservation[list.size()]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springoverview-120105110704-phpapp01/75/Spring-overview-28-2048.jpg)
![Hibernate DAO (cont’d) public Reservation[] findReservations(final DateRange range) { final HibernateTemplate template = getHibernateTemplate(); List list = (List) template.execute(new HibernateCallback() { public Object doInHibernate(Session session) { Query query = session.createQuery( "from Reservation r “ + “ where r.start > :rangeStart and r.start < :rangeEnd “); query.setDate("rangeStart", range.getStartDate() query.setDate("rangeEnd", range.getEndDate()) return query.list(); } }); return (Reservation[]) list.toArray(new Reservation[list.size()]); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springoverview-120105110704-phpapp01/75/Spring-overview-29-2048.jpg)


![DispatcherServlet The DispatcherServlet is the Spring Front Controller Initializes WebApplicationContext Uses /WEB-INF/[servlet-name]-servlet.xml by default WebApplicationContext is bound into ServletContext](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springoverview-120105110704-phpapp01/75/Spring-overview-33-2048.jpg)