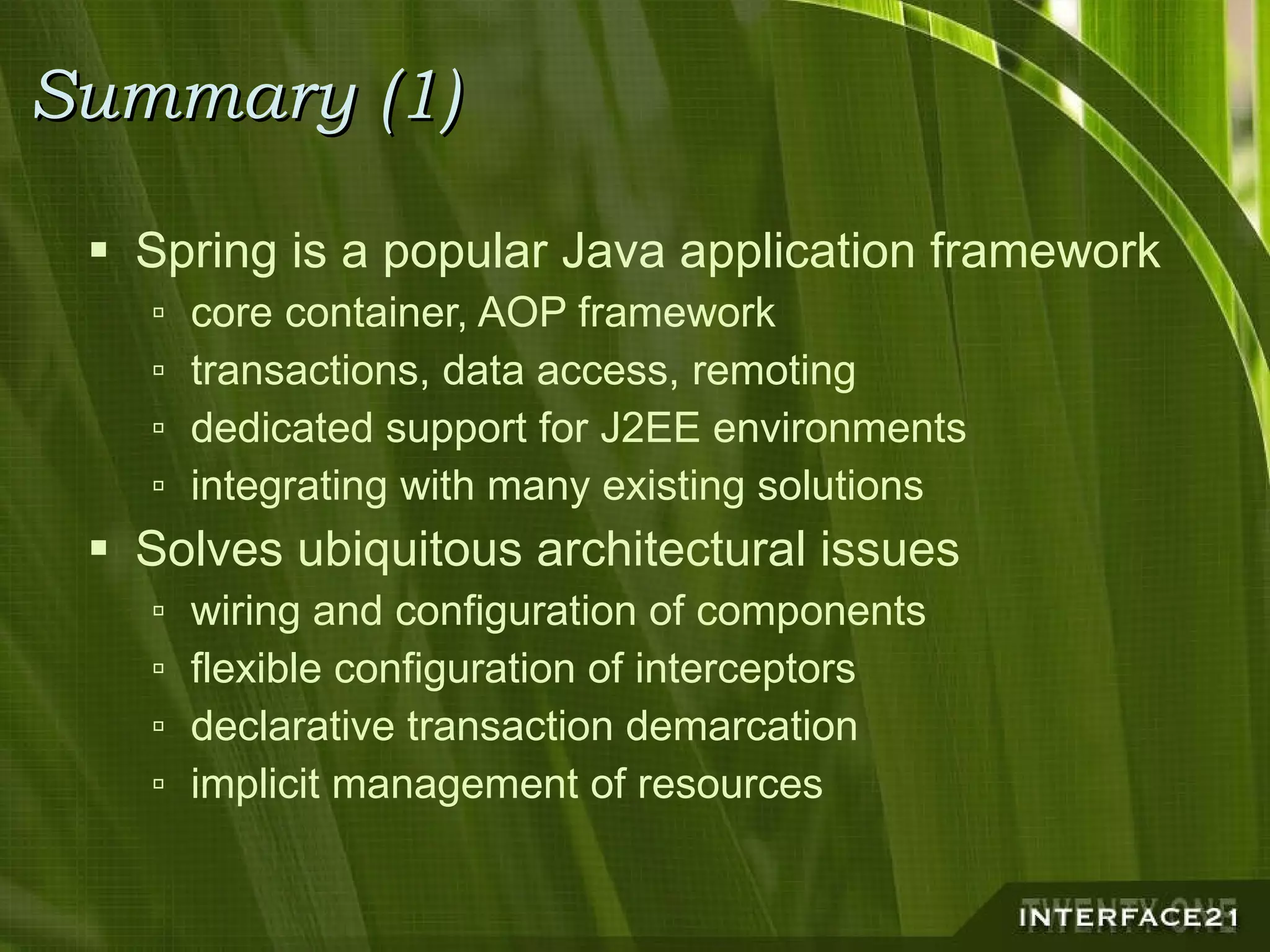
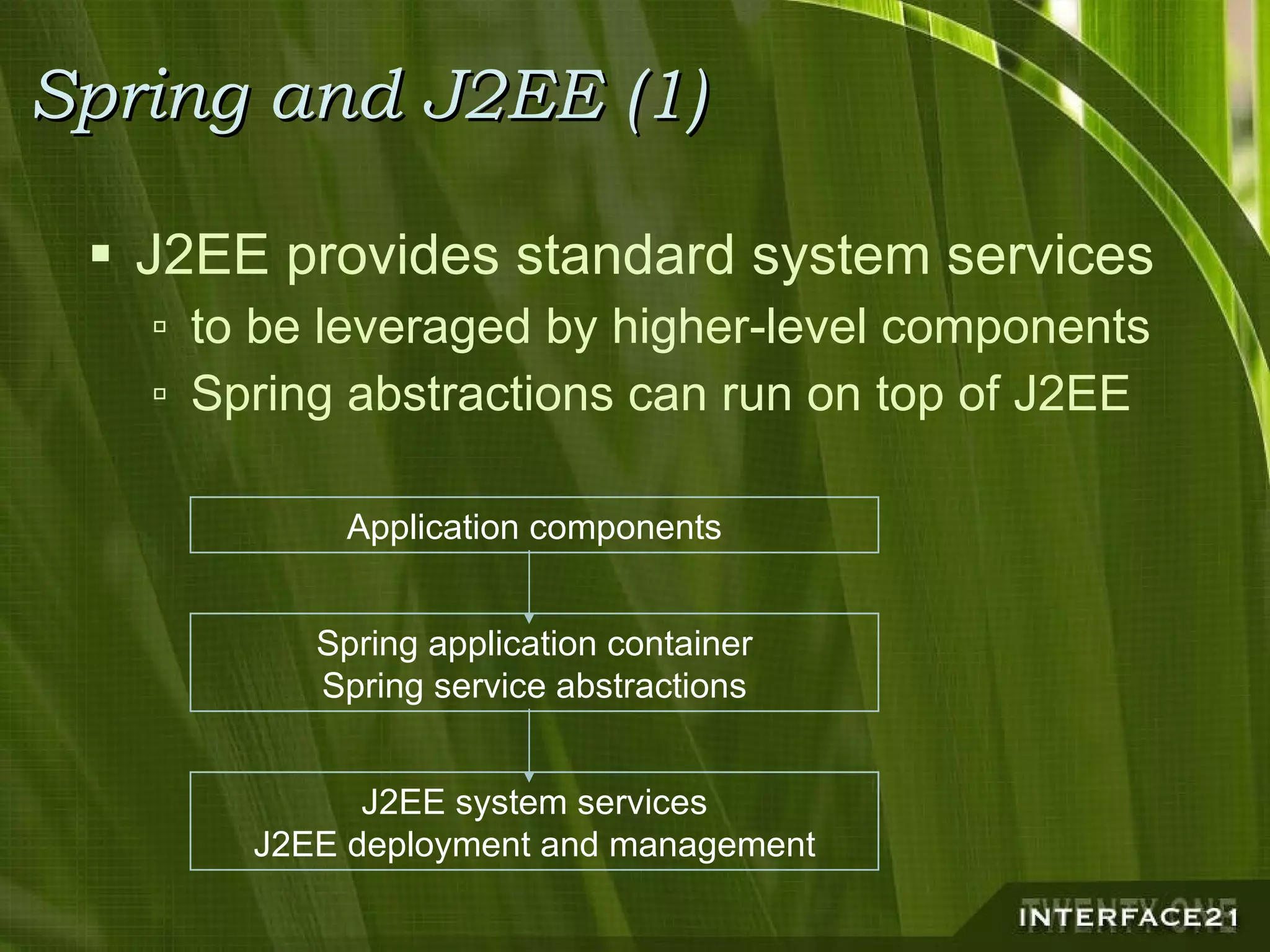
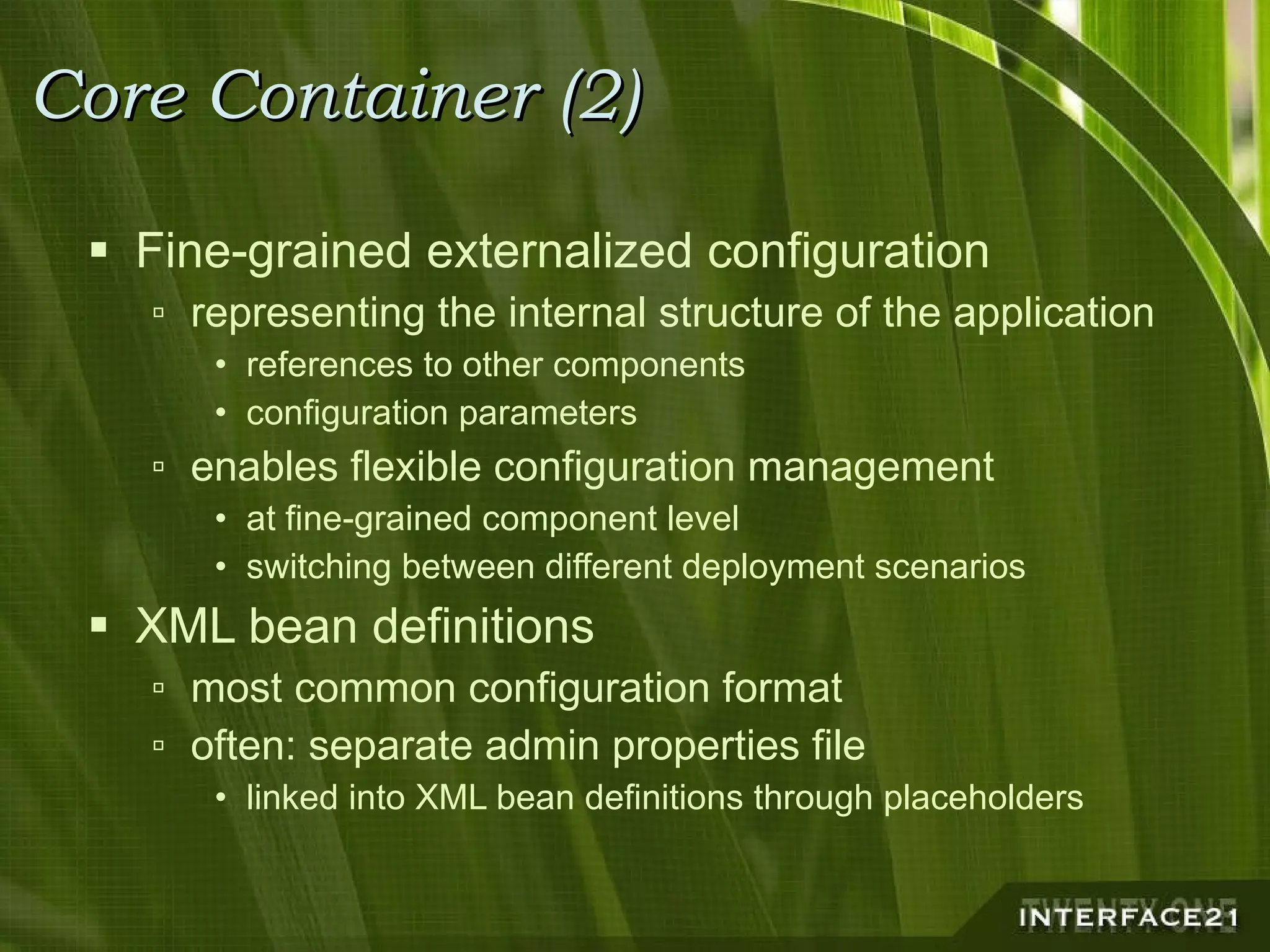
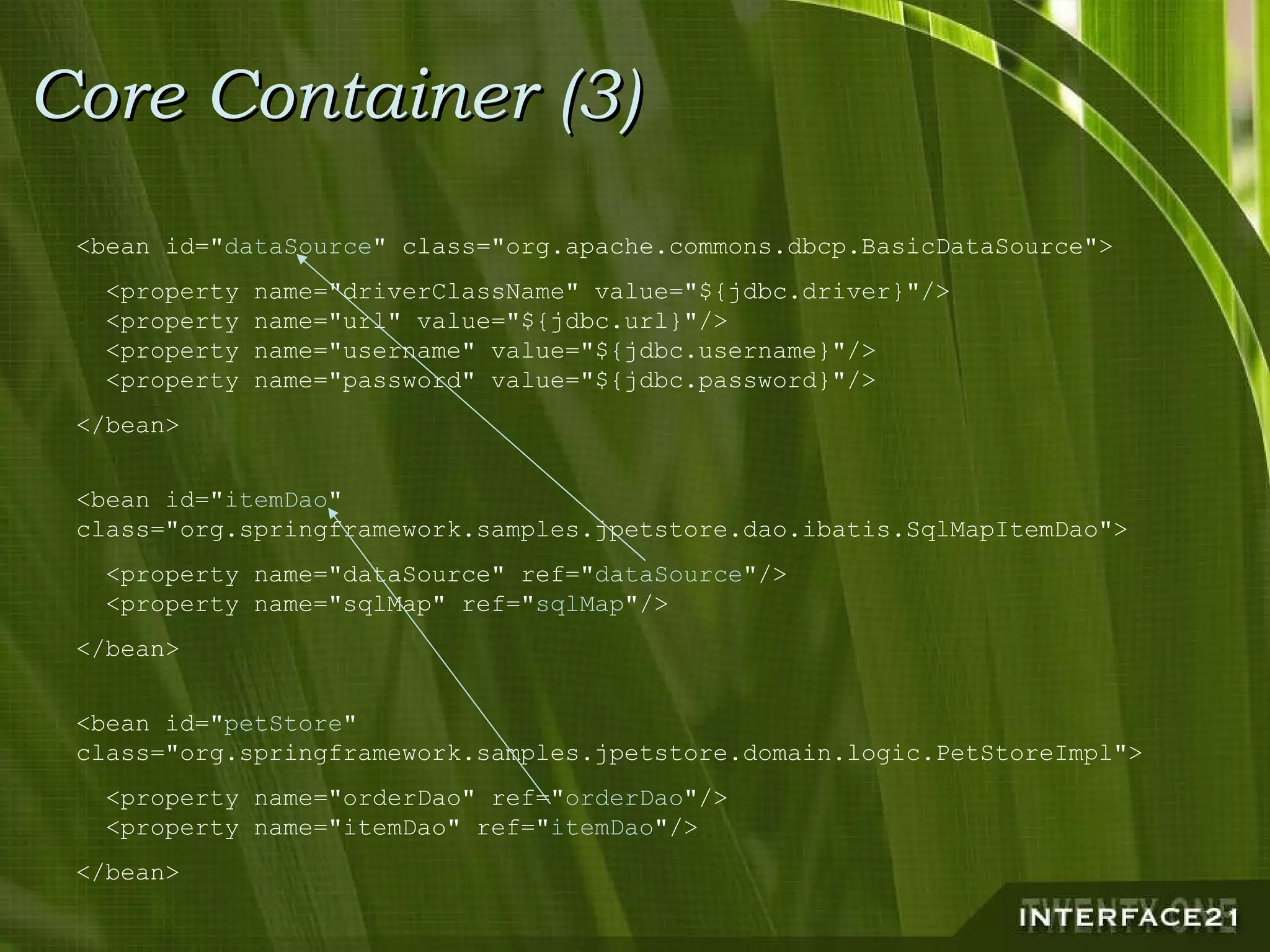
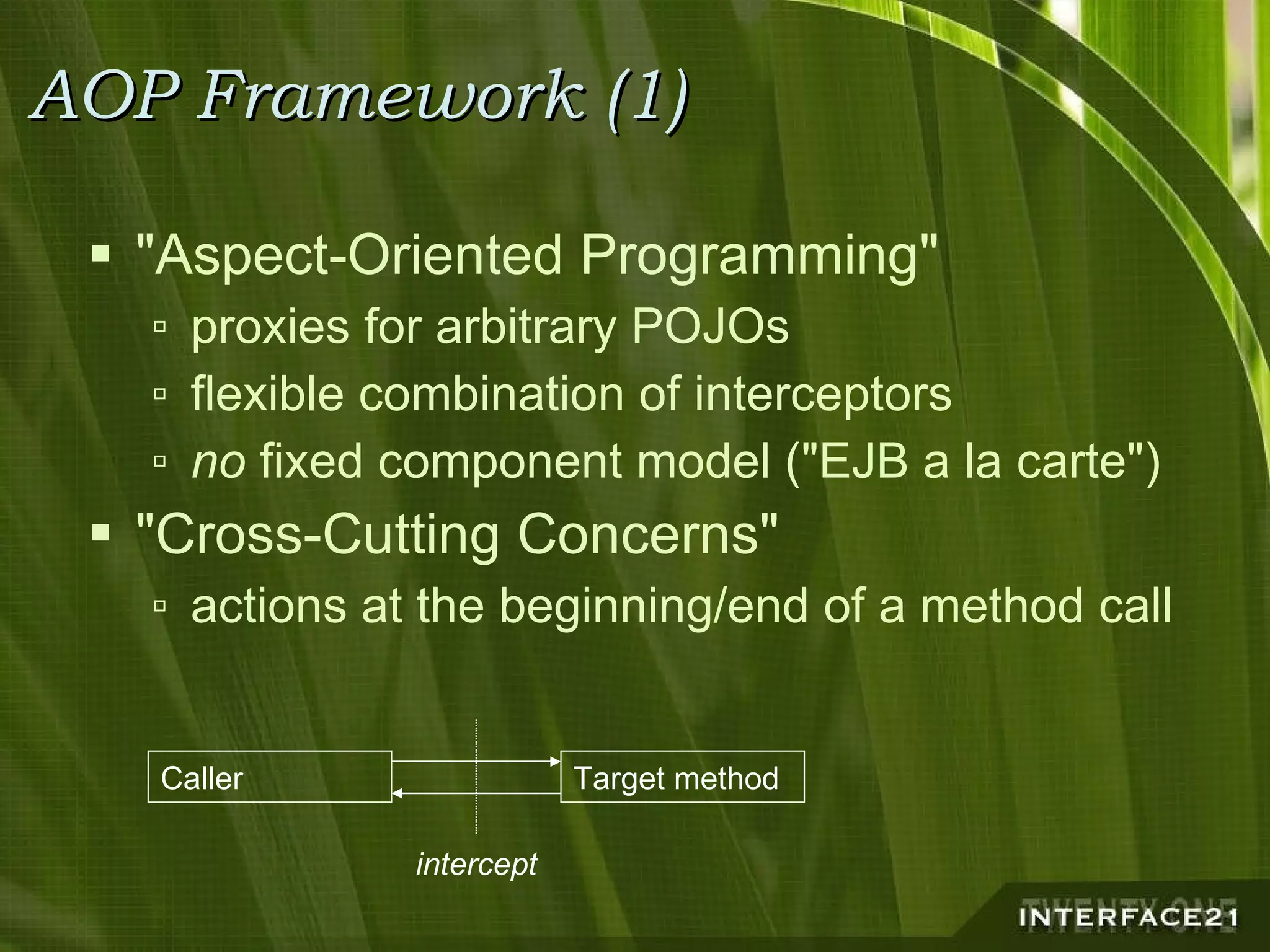
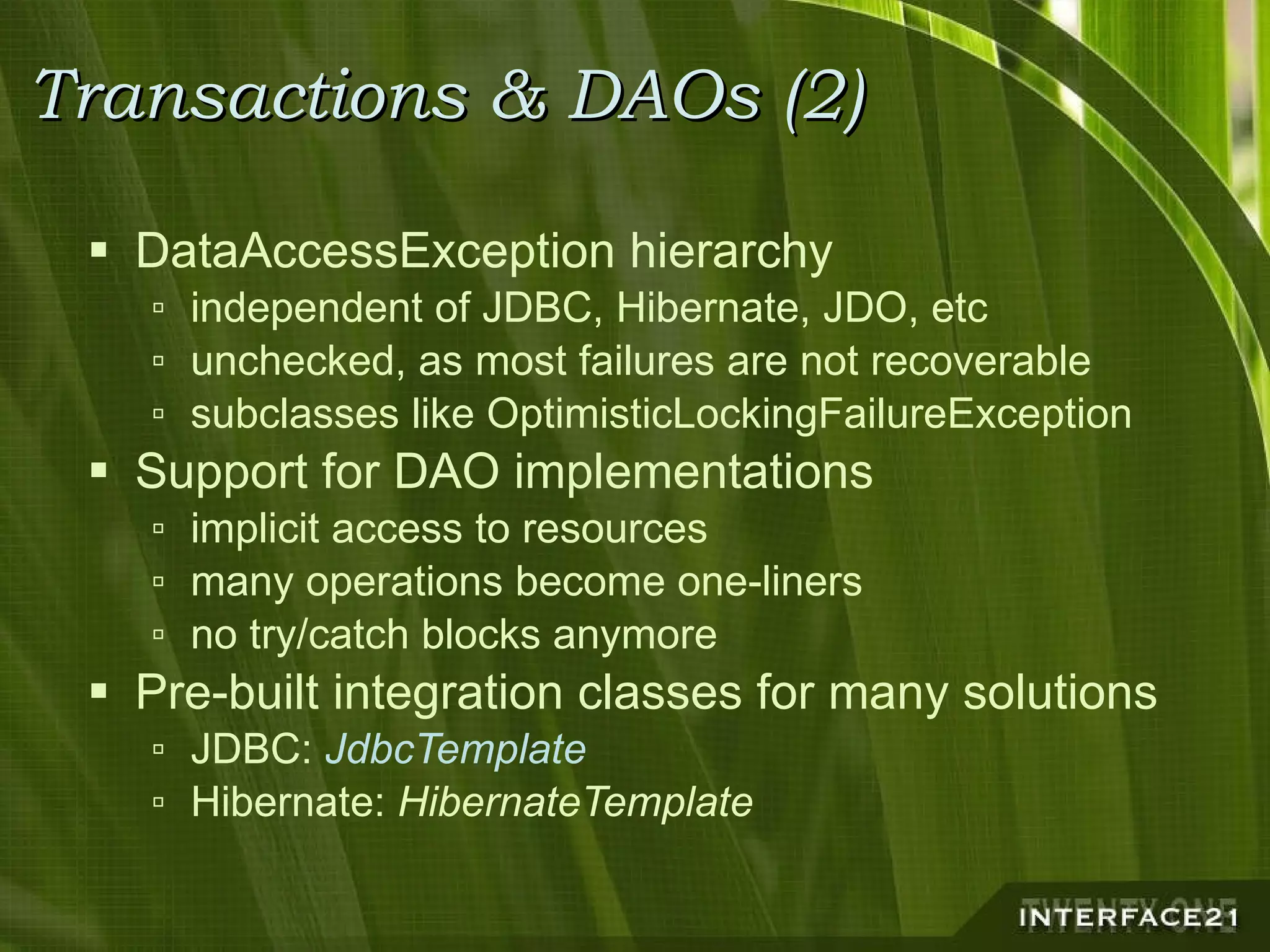
The Spring Framework is a popular Java application framework that provides solutions for common architectural issues like wiring and configuring components. It includes a core container, AOP framework, and support for transactions, data access, and remoting. Spring works in any environment and with many existing solutions. It allows flexible configuration of interceptors and declarative transaction demarcation while providing implicit management of resources. Spring is not tied to J2EE but can leverage J2EE services and works for any application type from rich clients to web applications to standalone applications.
![The Spring Framework J2EE without EJB Jürgen Höller http://www.springframework.com [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tu11-5l-120118023001-phpapp01/75/Tu1-1-5l-1-2048.jpg)










![Transactions & DAOs (3) Example for a JDBC-based DAO public class ExampleJdbcDao extends JdbcDaoSupport { public void clearDatabase() throws DataAccessException { getJdbcTemplate() .update("DELETE FROM imagedb"); } public void deleteImage(int imageId) throws DataAccessException { getJdbcTemplate() .update("DELETE FROM imagedb WHERE id=?", new Object[] {new Integer(imageId)}); } public int getNrOfImages() throws DataAccessException { return getJdbcTemplate() .queryForInt( "SELECT COUNT(*) FROM imagedb"); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tu11-5l-120118023001-phpapp01/75/Tu1-1-5l-19-2048.jpg)