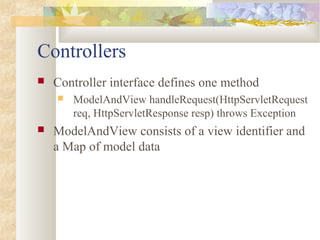
The document provides an overview of the Spring Framework, detailing its lightweight container, dependency injection, and the modularity it offers for building applications. It discusses various concepts such as inversion of control, different types of bean creation and lifecycle management, and the support for aspect-oriented programming (AOP) to manage cross-cutting concerns. The document also highlights the framework's capabilities for data access and transaction management, making it a powerful tool for Java development.
























![Pointcuts (cont'd)
public interface MethodMatcher {
boolean matches(Method m, Class targetClass);
boolean isRuntime();
boolean matches(Method m, Class targetClass, Object[] args);
}
Pointcut may be statically or dynamically
evaluated based on isRuntime()
Abstract class StaticMethodMatcherPointcut
requires override of 1st
method only
Only called if isRuntime() == true](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springtalk111204-150502051742-conversion-gate01/85/Spring-talk111204-28-320.jpg)


![Spring Advice
MethodBeforeAdvice
void before(Method m, Object[] args, Object target)
Cannot alter return type
ThrowsAdvice
Marker interface
Implementors define methods of form:
afterThrowing([Method], [args], [target], subclassOfThrowable)
AfterReturningAdvice
void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method, m,
Object[] args, Object target)
Cannot modify return value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springtalk111204-150502051742-conversion-gate01/85/Spring-talk111204-31-320.jpg)














![Hibernate DAO (cont’d)
public Reservation[] findReservations(Room room) {
List list = getHibernateTemplate().find(
"from Reservation reservation “ +
“ where reservation.resource =? “ +
“ order by reservation.start",
instrument);
return (Reservation[]) list.toArray(new Reservation[list.size()]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springtalk111204-150502051742-conversion-gate01/85/Spring-talk111204-47-320.jpg)
![Hibernate DAO (cont’d)
public Reservation[] findReservations(final DateRange range) {
final HibernateTemplate template = getHibernateTemplate();
List list = (List) template.execute(new HibernateCallback() {
public Object doInHibernate(Session session) {
Query query = session.createQuery(
"from Reservation r “ +
“ where r.start > :rangeStart and r.start < :rangeEnd “);
query.setDate("rangeStart", range.getStartDate()
query.setDate("rangeEnd", range.getEndDate())
return query.list();
}
});
return (Reservation[]) list.toArray(new Reservation[list.size()]);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springtalk111204-150502051742-conversion-gate01/85/Spring-talk111204-48-320.jpg)


![DispatcherServlet
The DispatcherServlet is the Spring Front
Controller
Initializes WebApplicationContext
Uses /WEB-INF/[servlet-name]-servlet.xml by
default
WebApplicationContext is bound into
ServletContext](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springtalk111204-150502051742-conversion-gate01/85/Spring-talk111204-52-320.jpg)