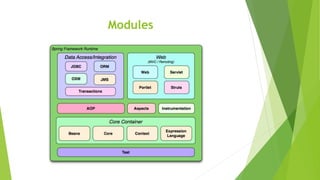
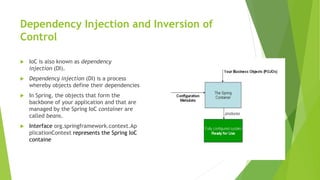
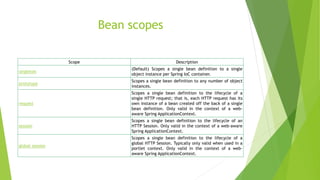
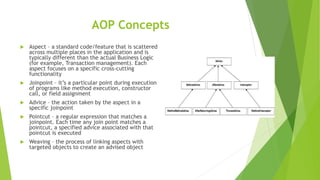
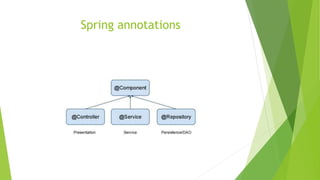
This document provides an overview of key concepts in the Spring Framework including dependency injection, modules, beans, and annotations. It explains that Spring handles infrastructure and configuration so developers can focus on the application. It also describes concepts like the singleton scope, autowiring, AOP, and the Spring Expression Language.