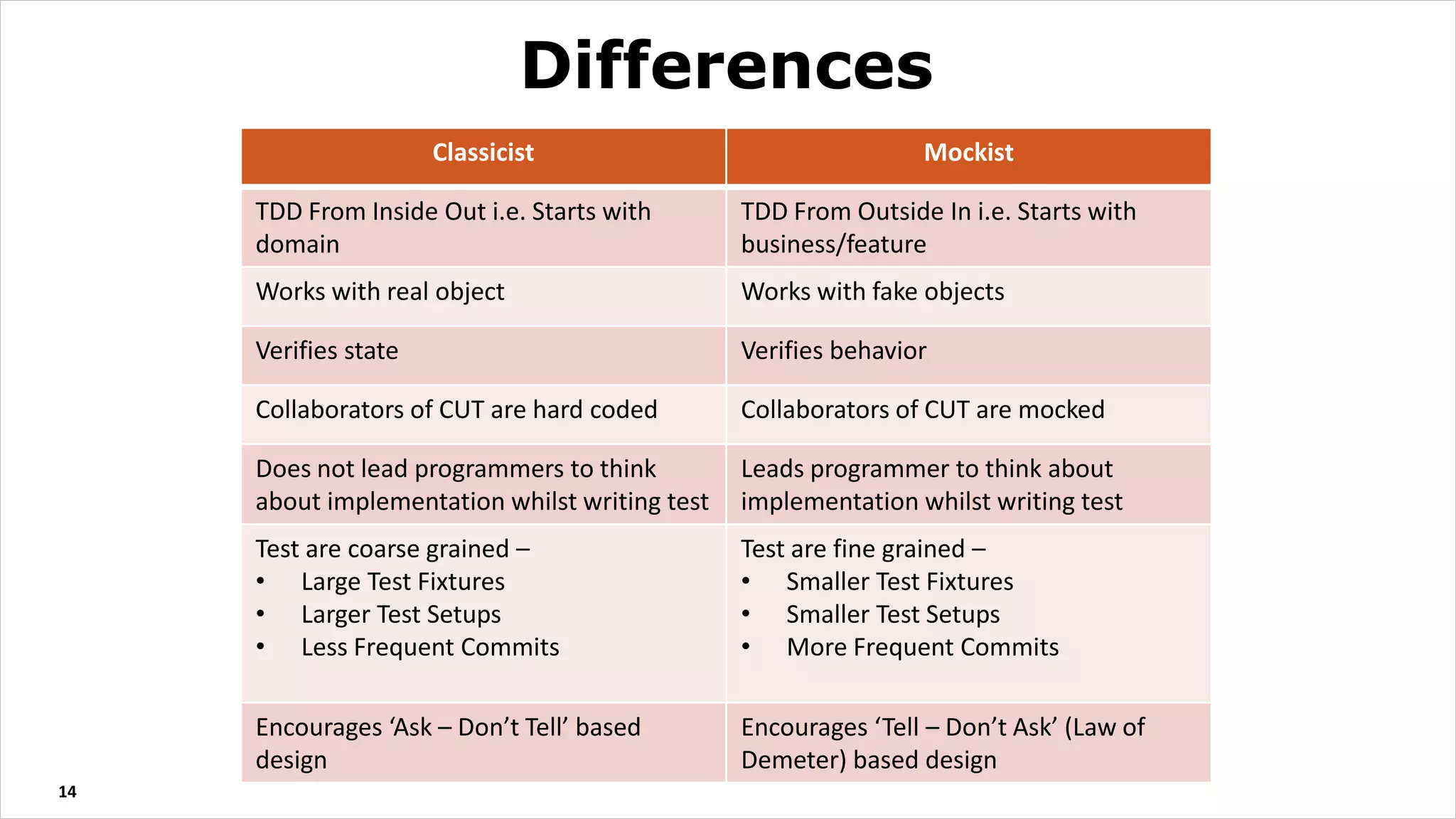
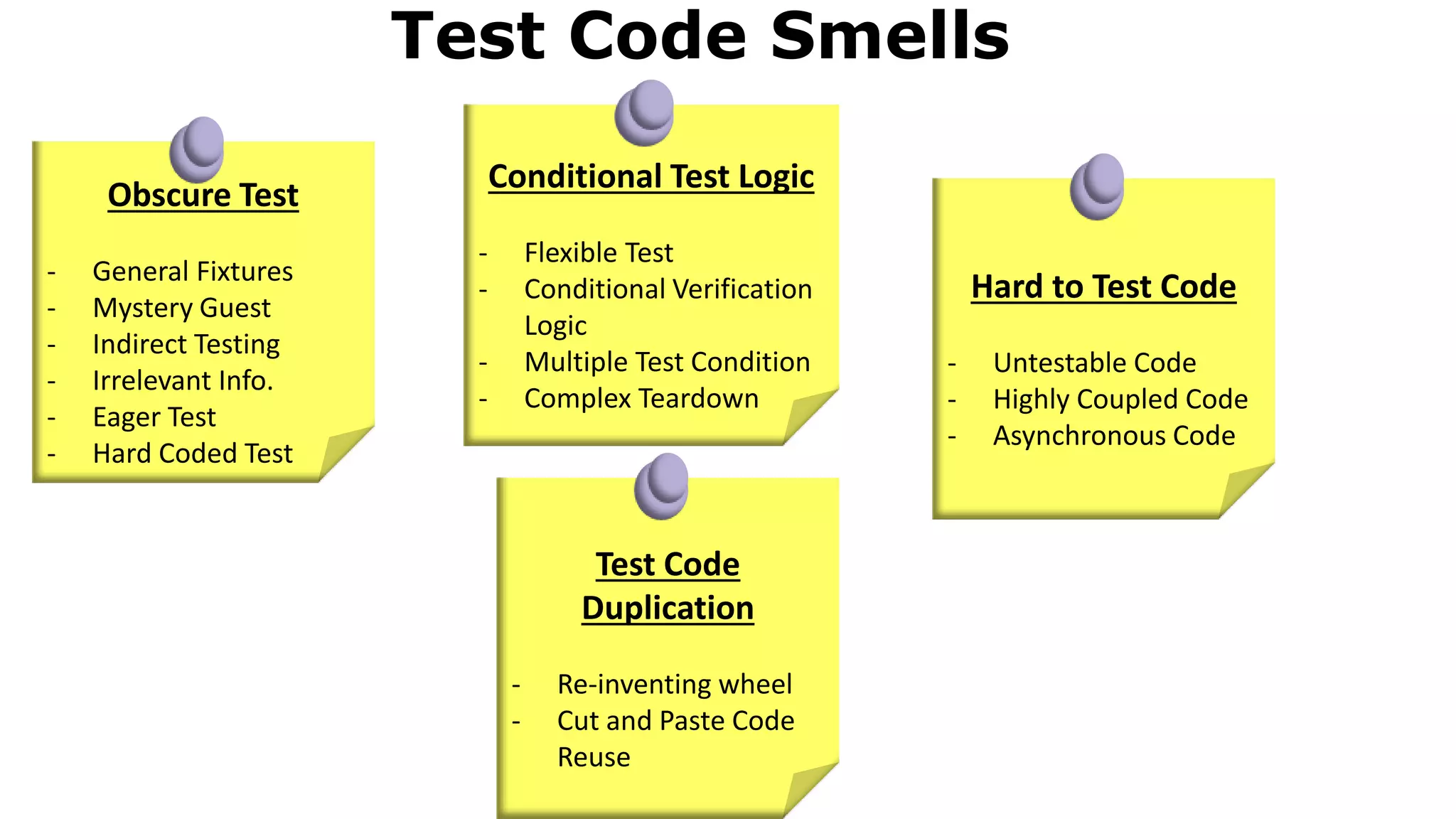
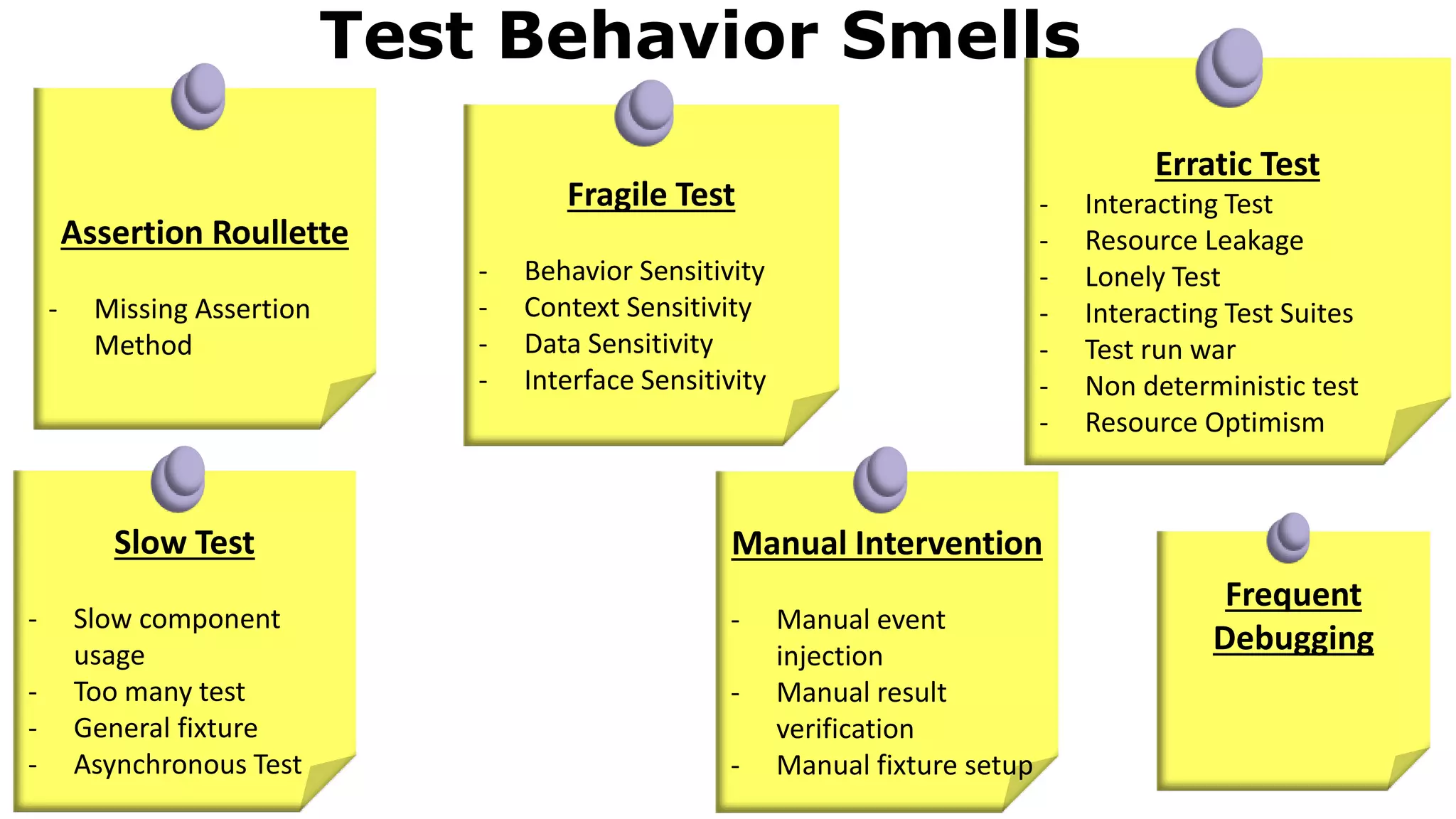
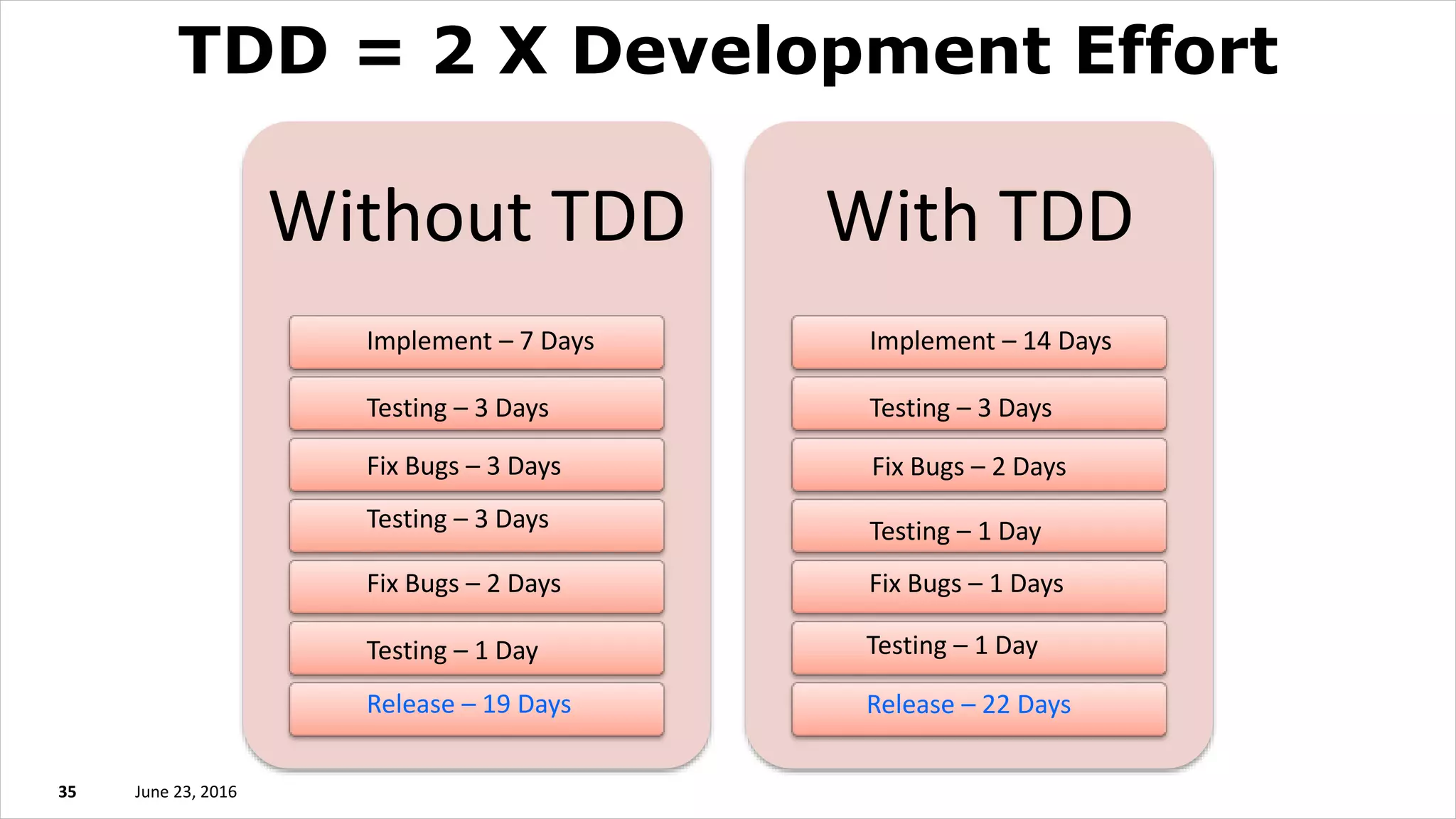
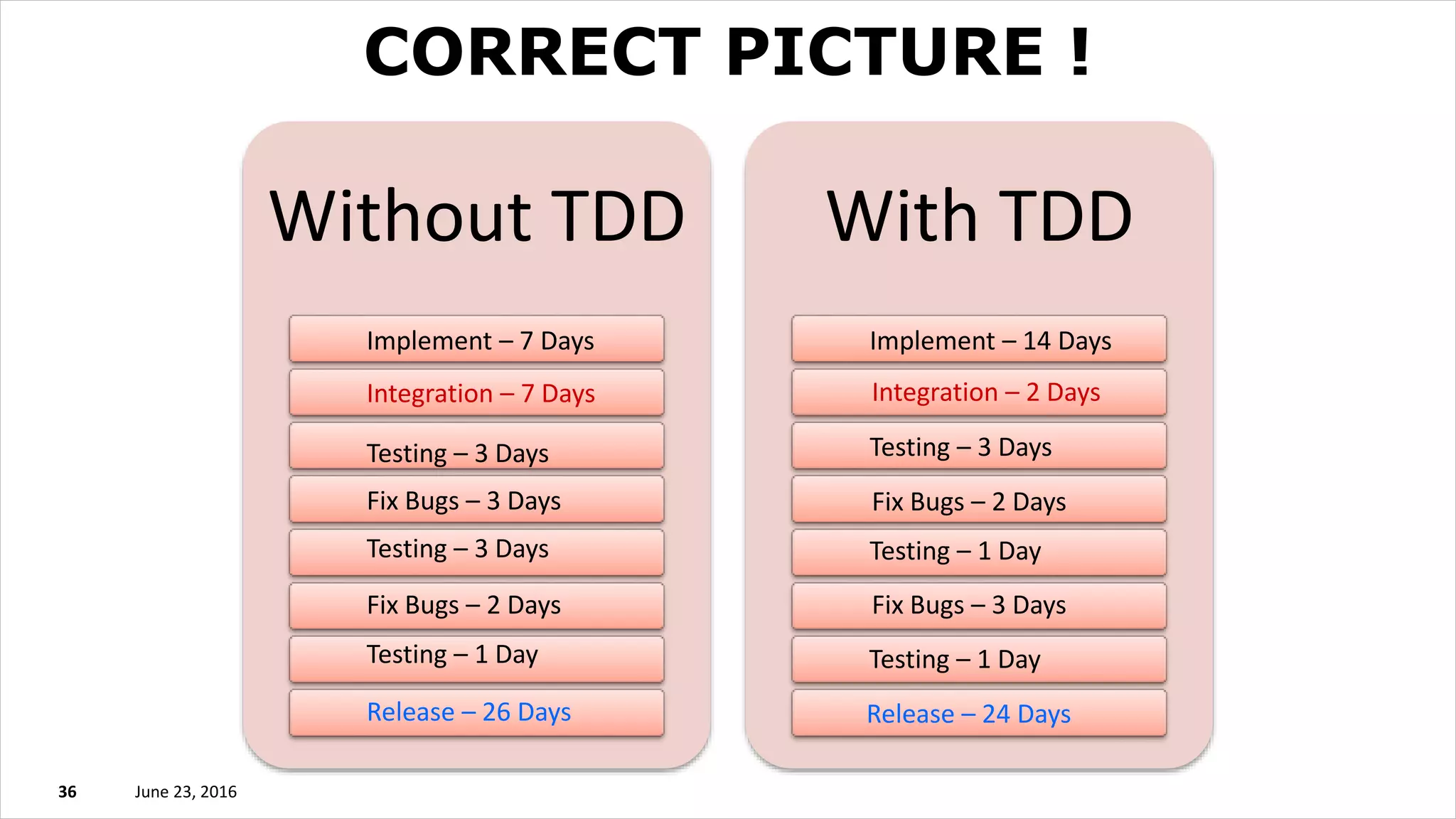
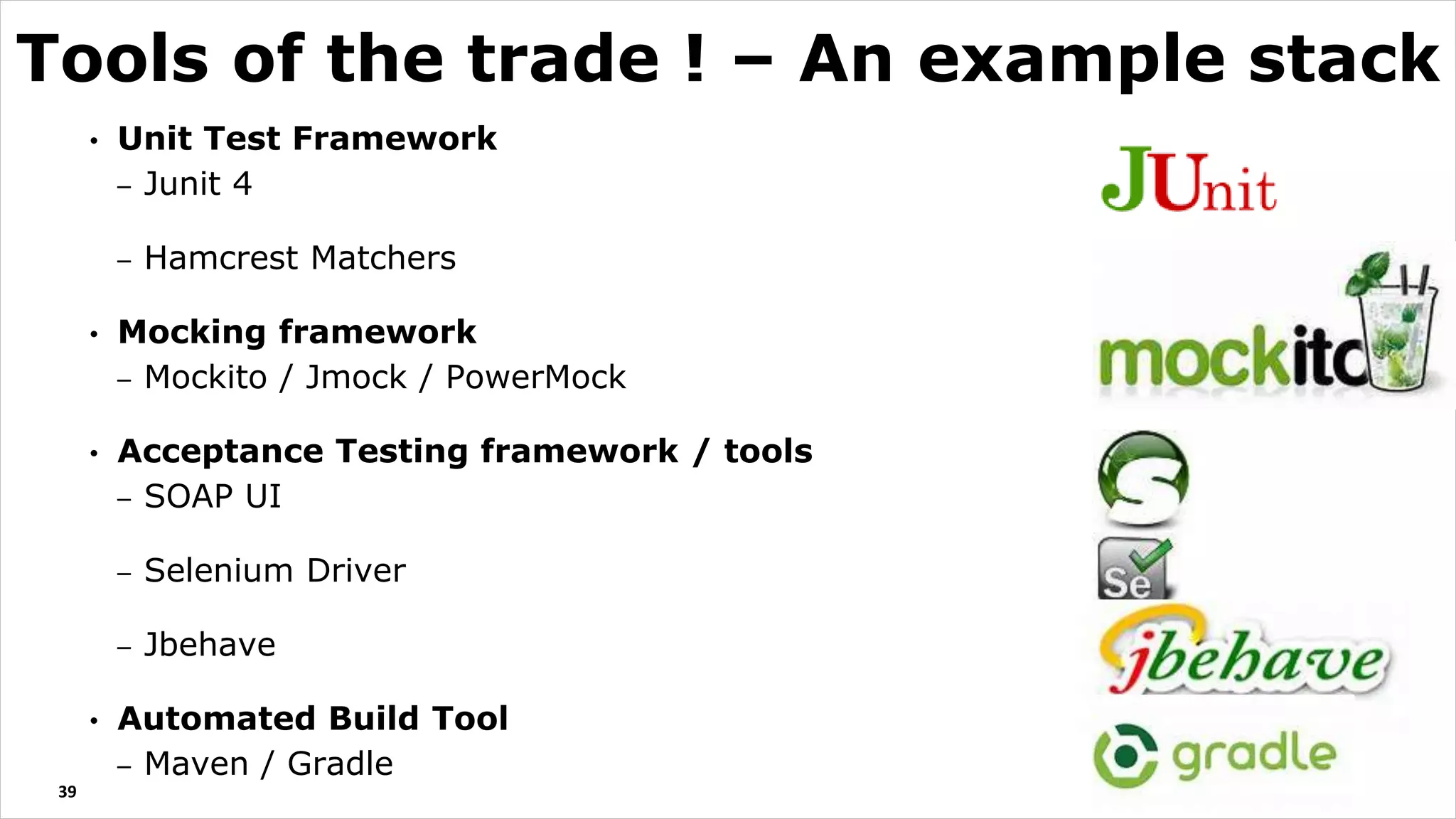
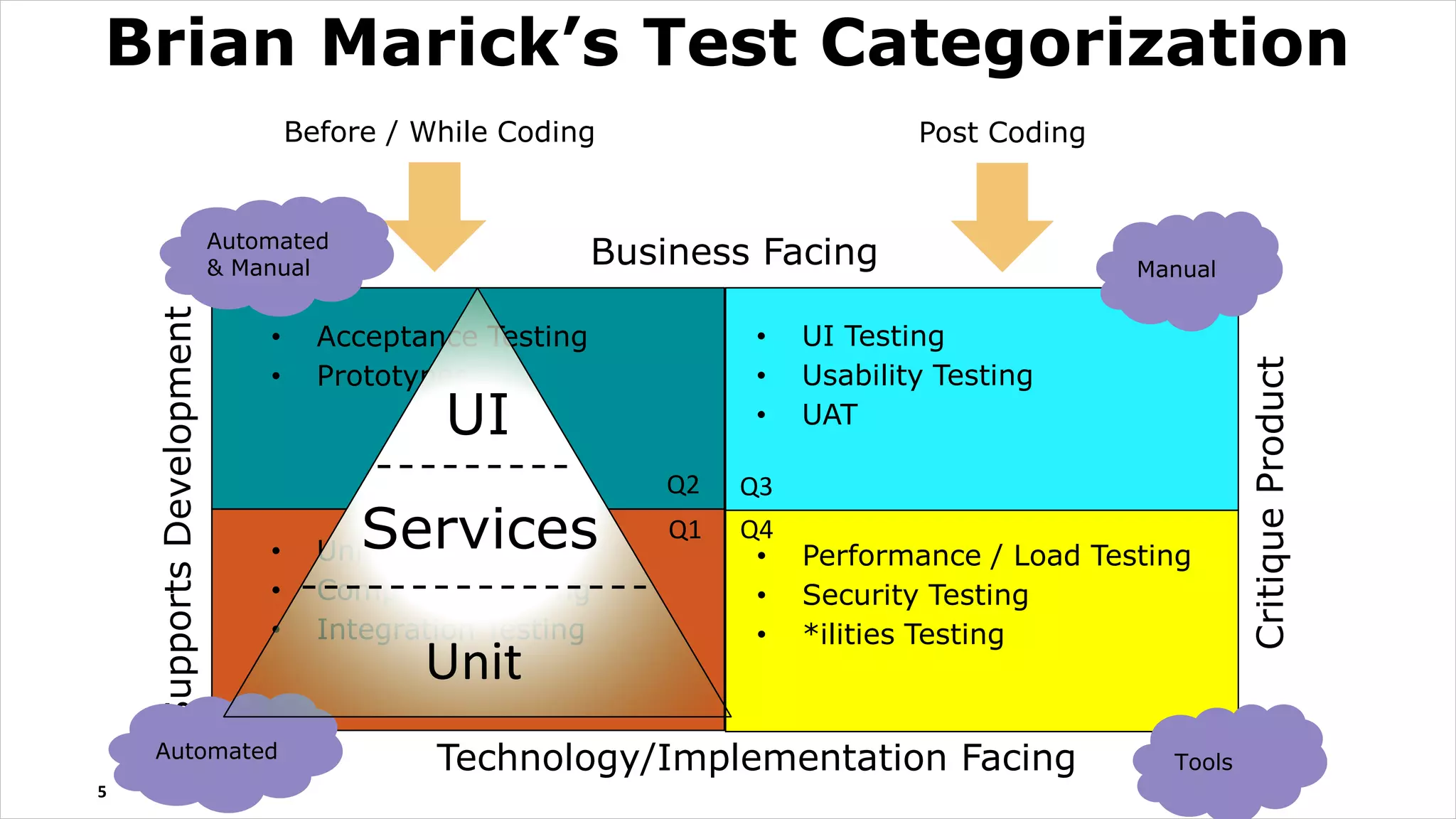
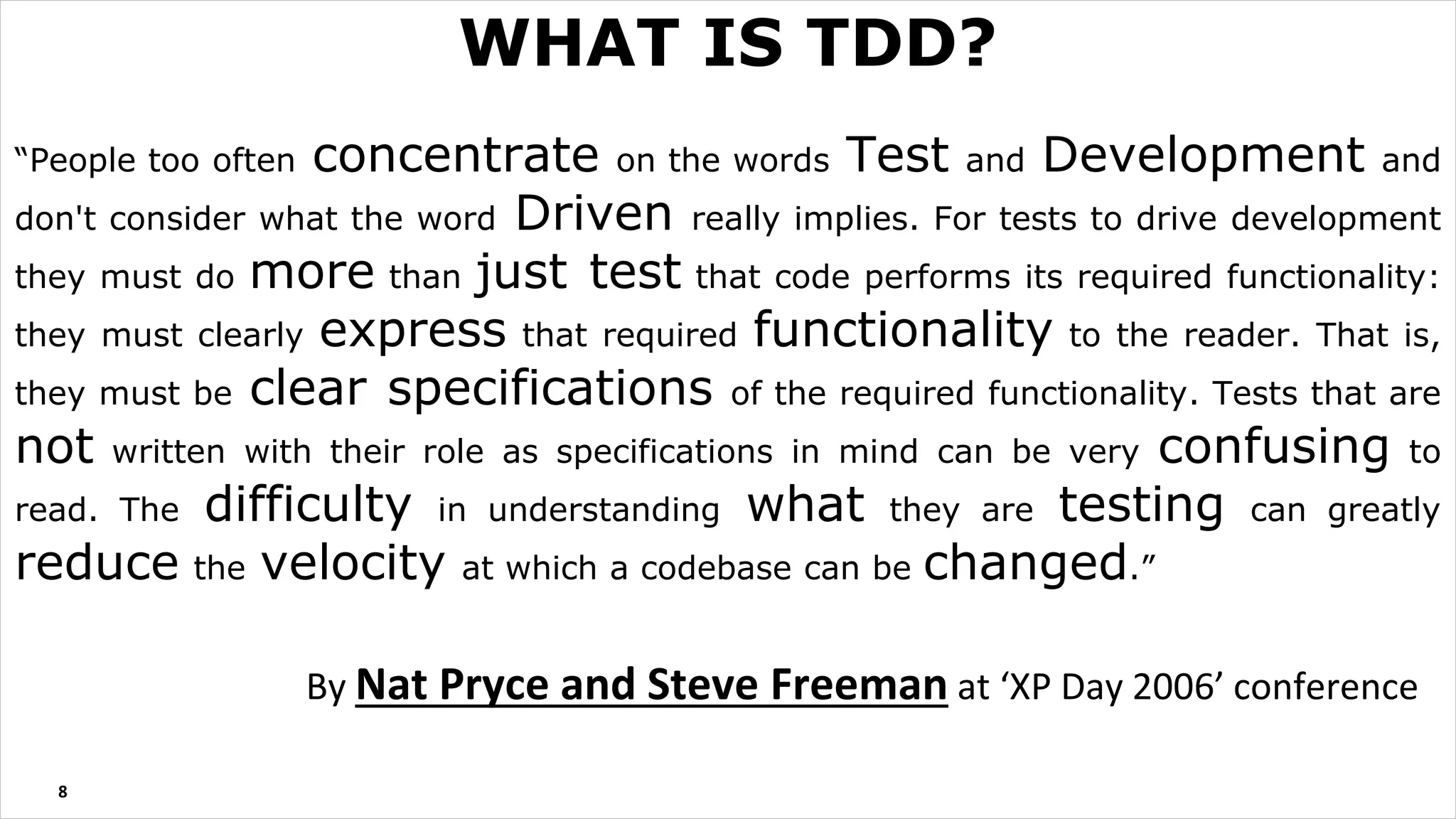
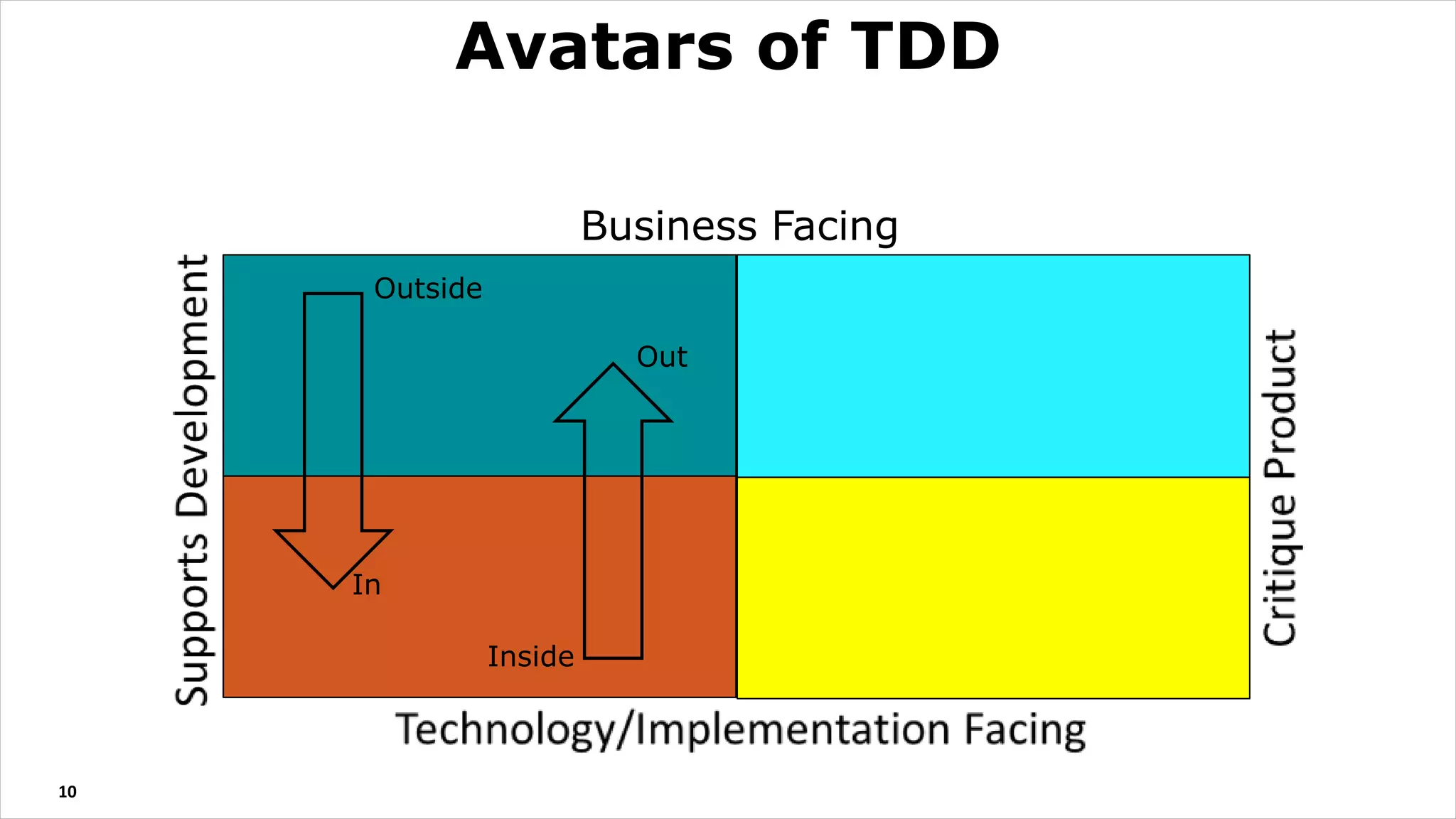
The document discusses test driven development (TDD). It defines TDD and describes the TDD cycle of writing a test, code, and refactoring. It outlines different approaches to TDD like outside-in and inside-out. It discusses the benefits of TDD like aiding design, promoting refactoring, and instilling confidence. It also covers test smells, misconceptions about TDD, and tools used for TDD.






![12
Basket
?
Outside – In TDD (Contd.)
?
TEST
[Calculate total
price]
Mockery
Expectations
Loyalty Point
Calculator
Promotion
Target Object
/ CUT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/anatomyoftdd-161028213431/75/Anatomy-of-Test-Driven-Development-12-2048.jpg)
![13
Inside – Out TDD
Basket
Loyalty
Point
Calculator
Promotions
TEST
[Calculate total
price]
Target Object
/ CUT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/anatomyoftdd-161028213431/75/Anatomy-of-Test-Driven-Development-13-2048.jpg)