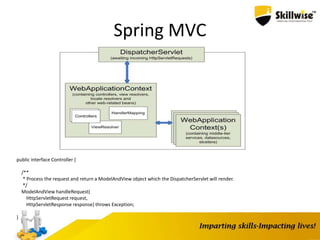
This document provides an overview of the Spring framework and its various modules. It discusses Spring concepts like dependency injection and inversion of control. It also covers specific Spring features such as AOP, testing, ORM/Hibernate integration, scheduling, MVC, JMS, email and more. The document includes configuration examples and code snippets for many of these Spring modules.