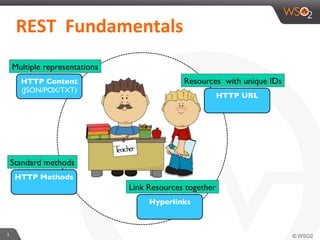
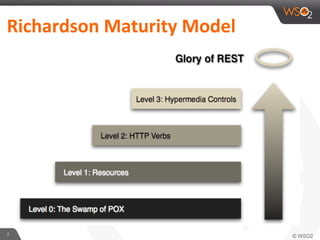
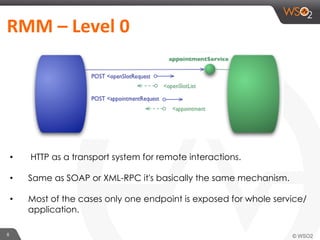
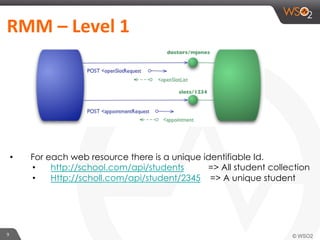
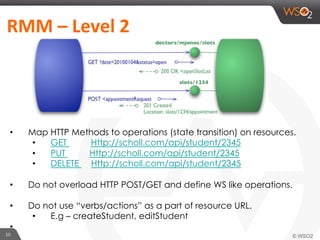
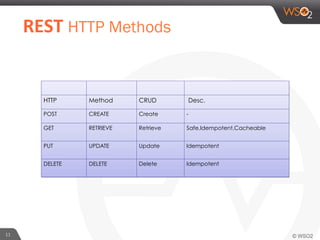
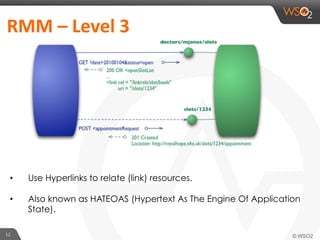
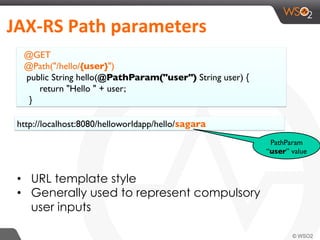
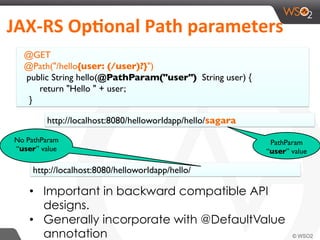
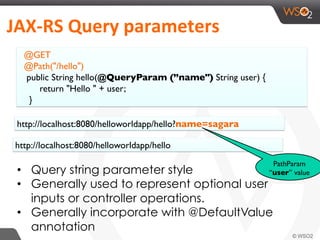
This document provides an overview of REST and JAX-RS. It defines REST as an architectural style using HTTP for data communication. Key REST fundamentals are discussed such as resources with unique IDs, standard HTTP methods, and hyperlinks to relate resources. The Richardson Maturity Model for REST APIs is introduced with levels ranging from using HTTP as a simple transport to fully leveraging hypermedia. JAX-RS is defined as a Java annotation-based framework for developing RESTful web services, with annotations explained for defining resources, request parameters, responses, and error handling. The document also covers REST concepts like pagination, authentication, and linking resources.