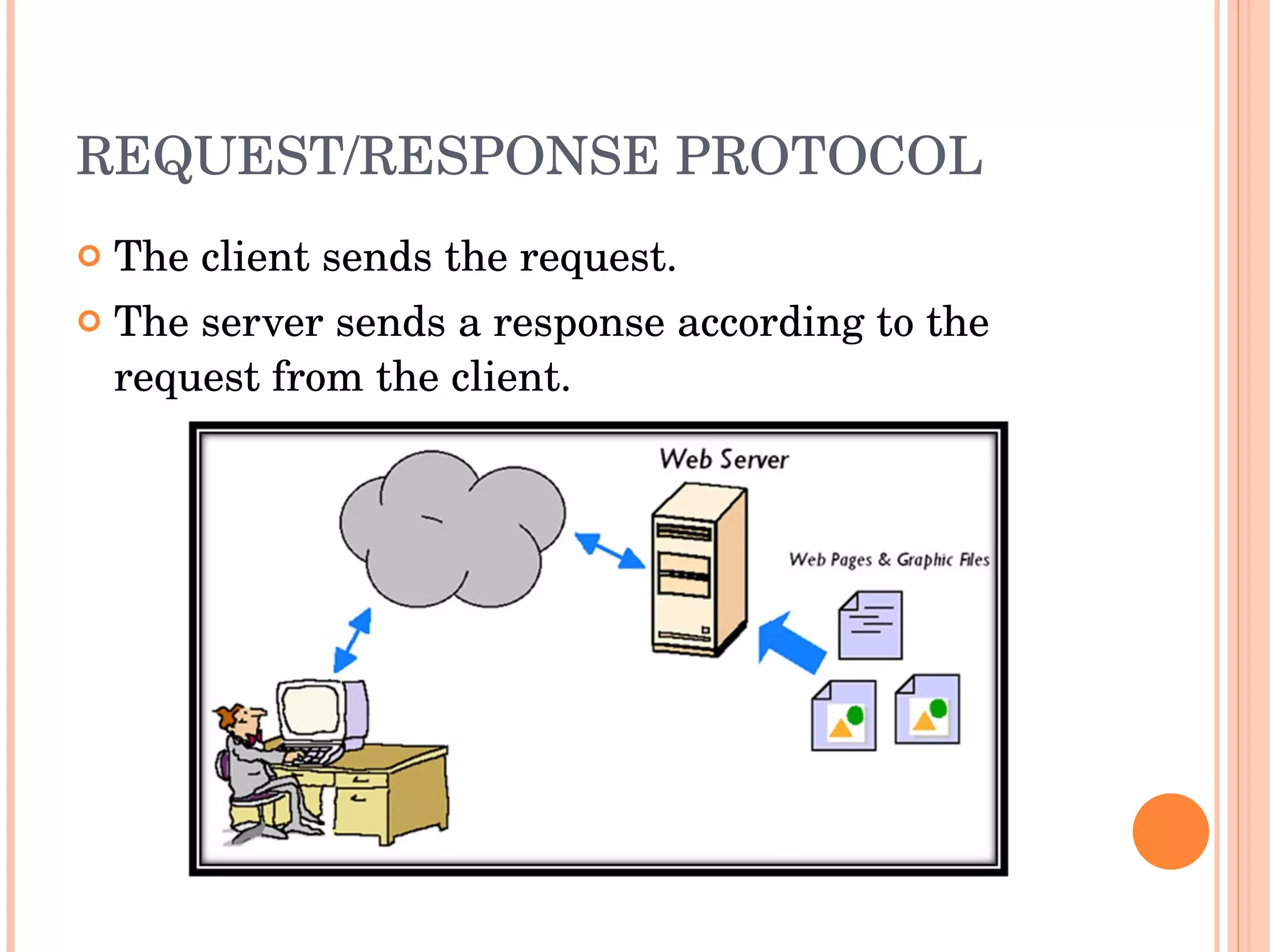
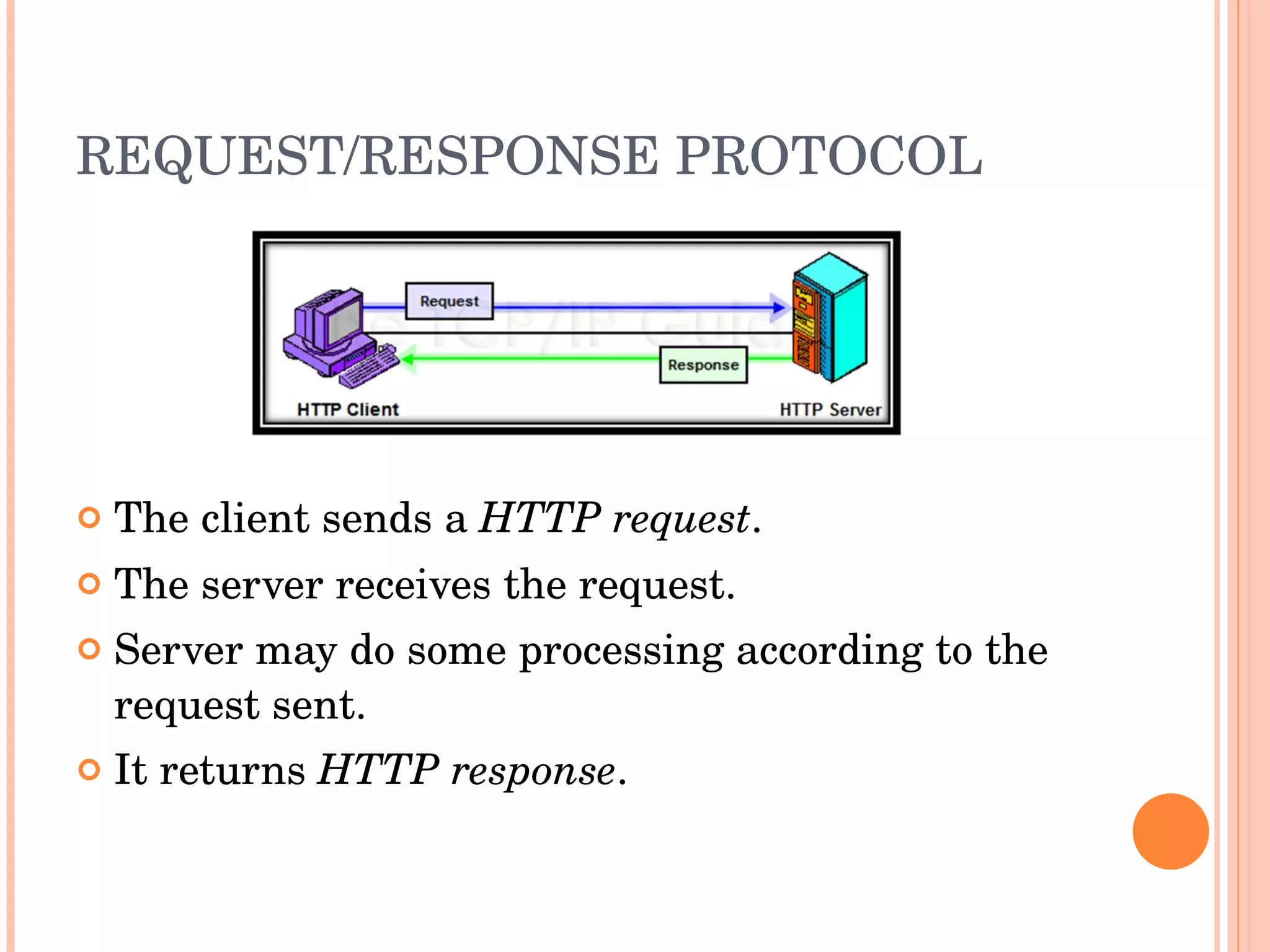
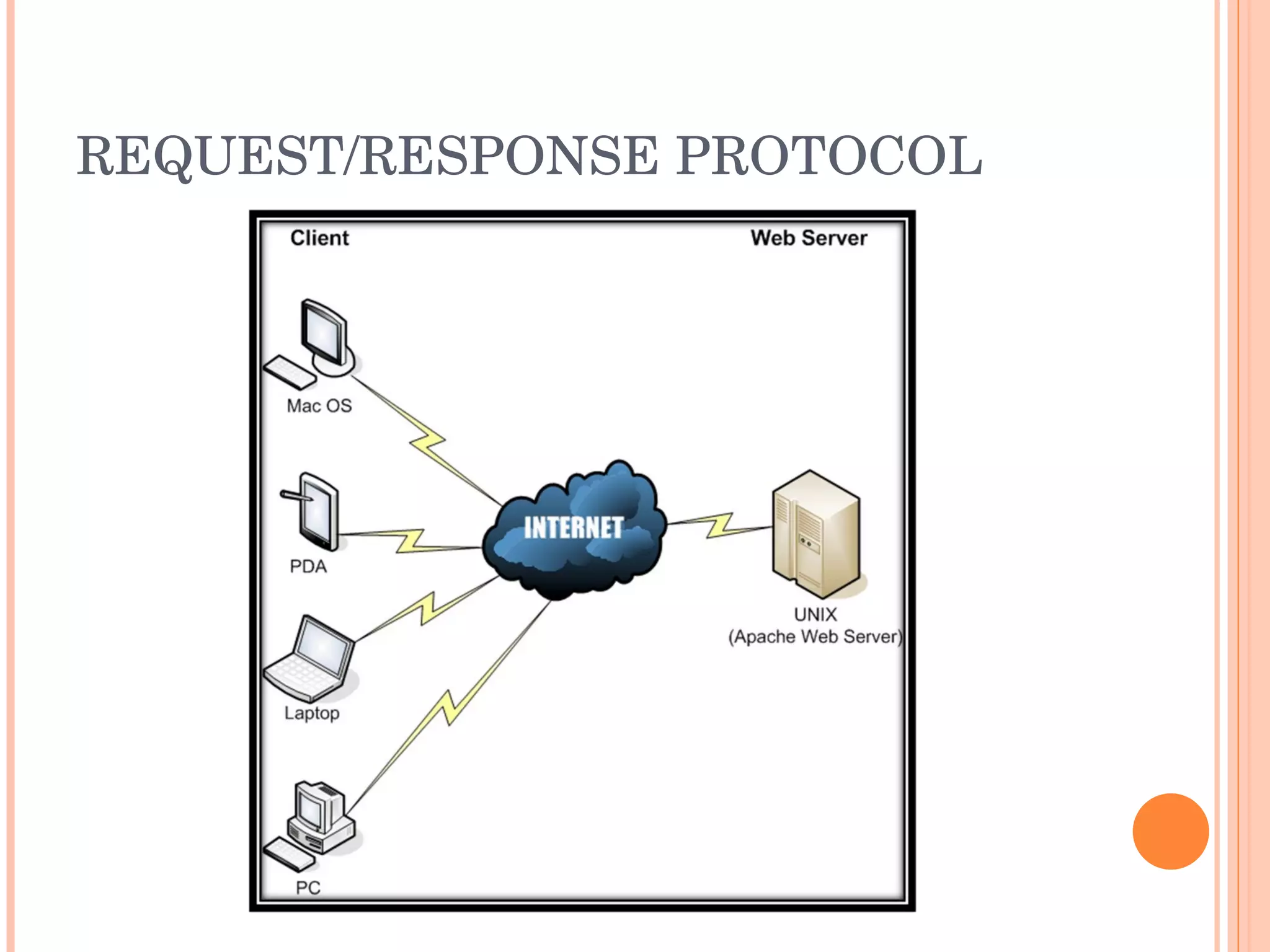
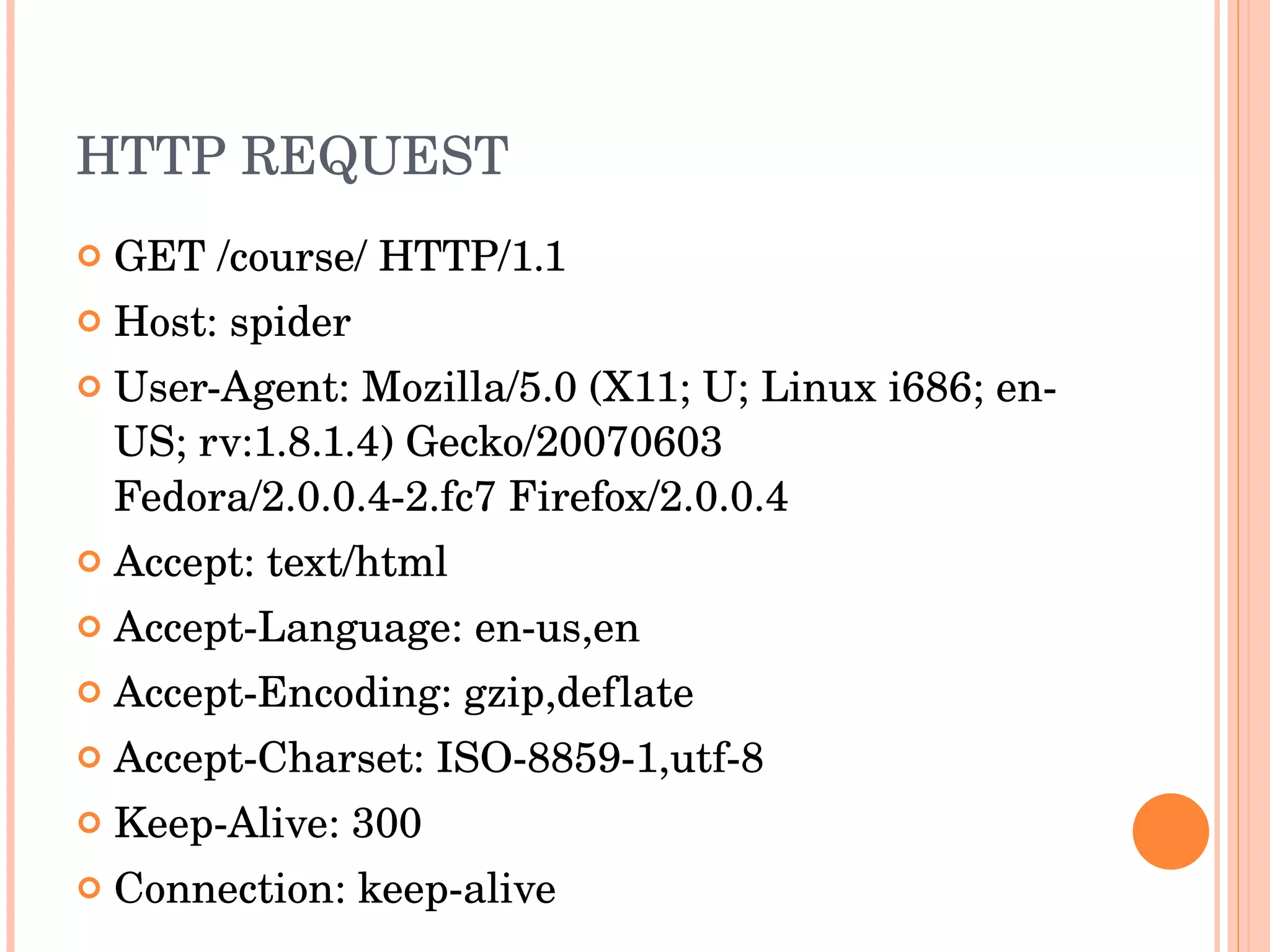
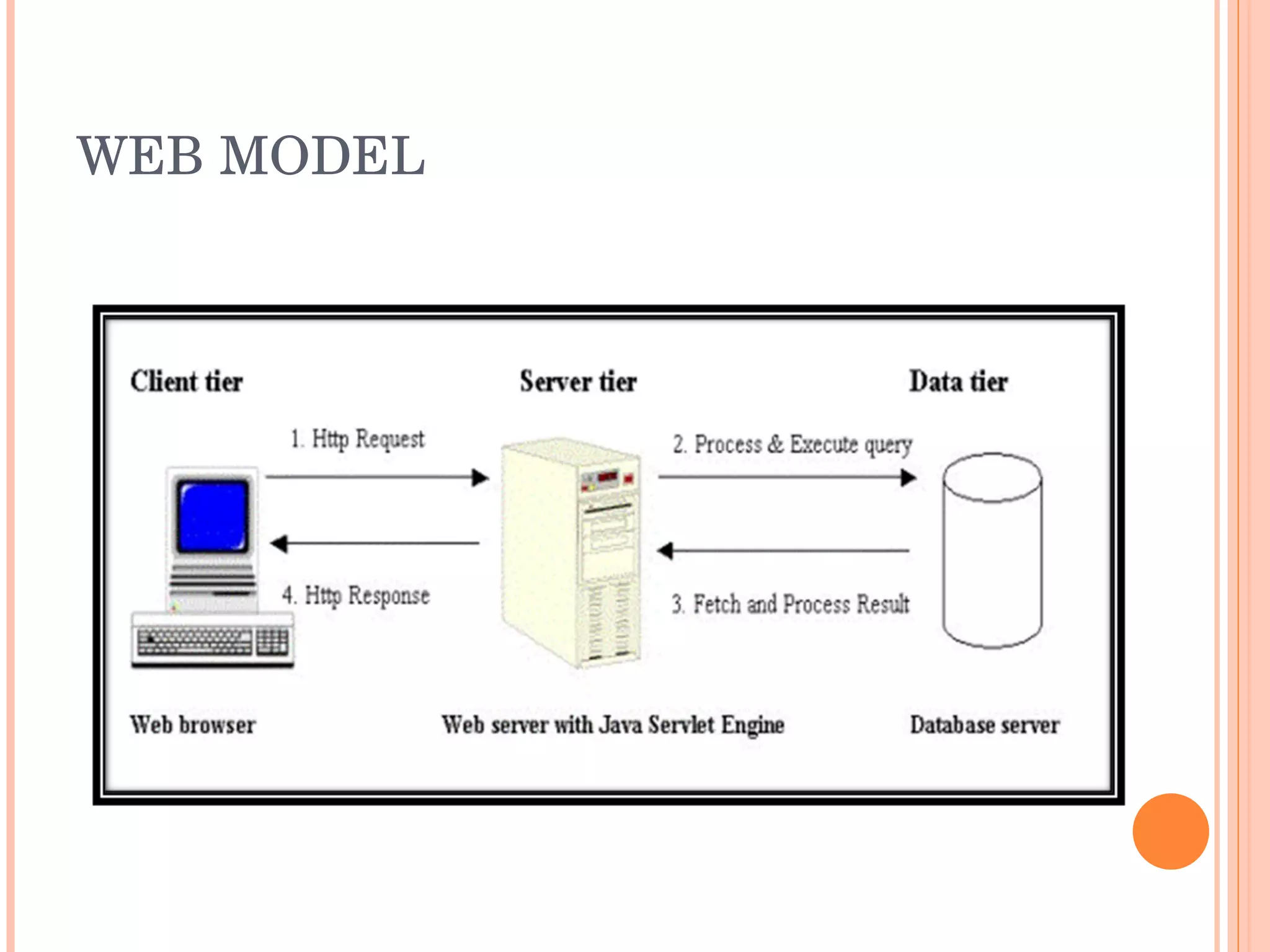
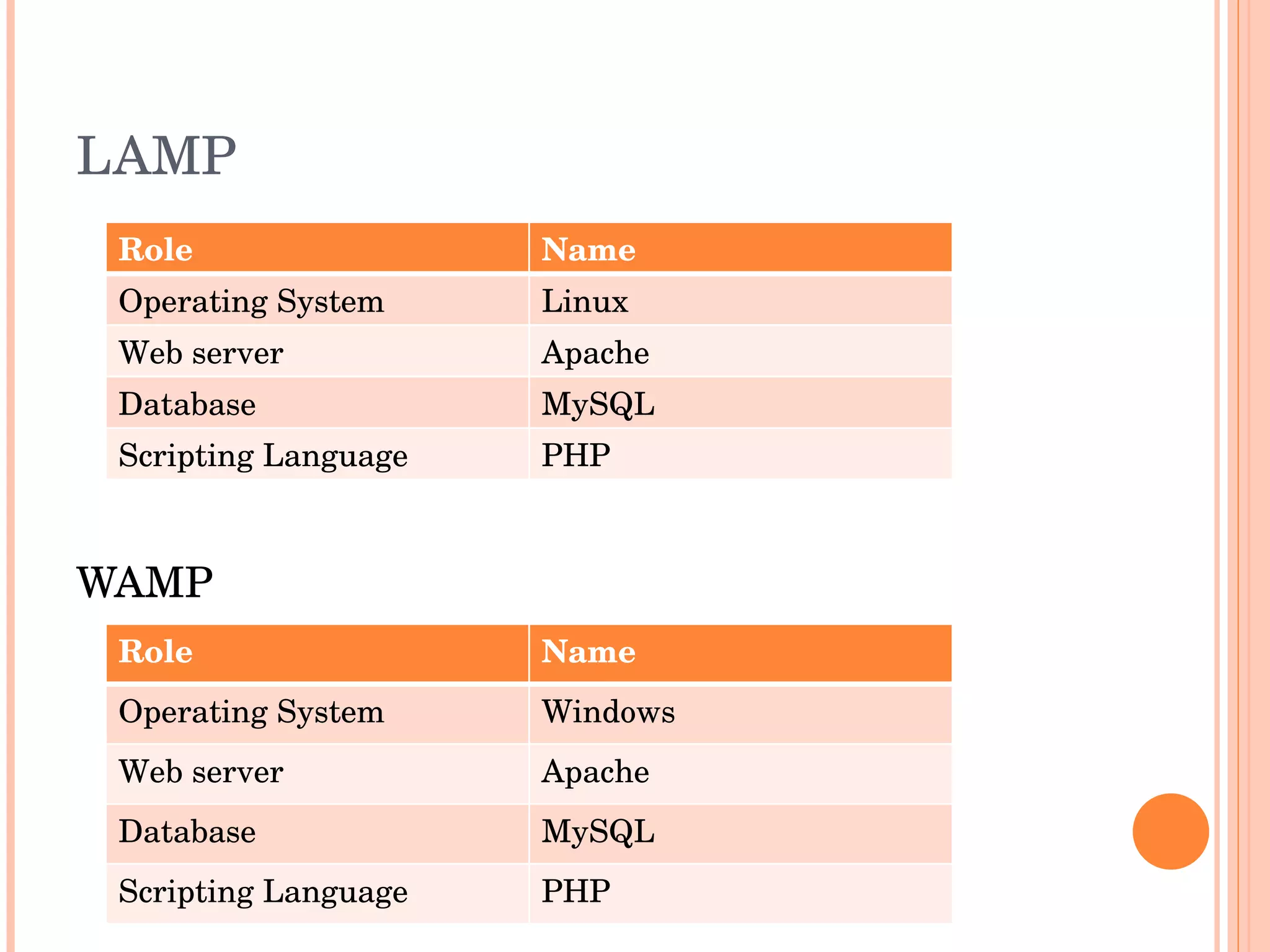
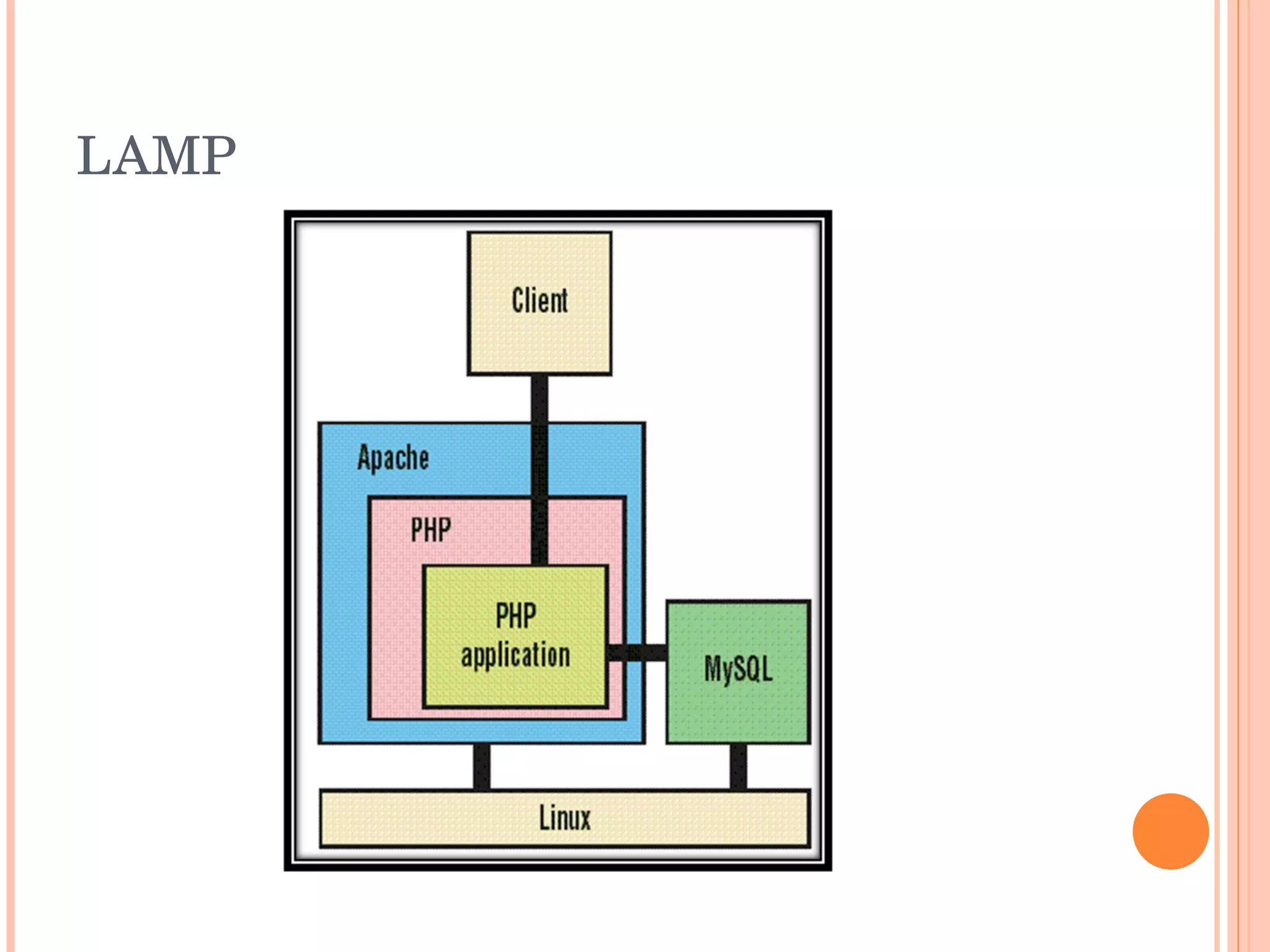
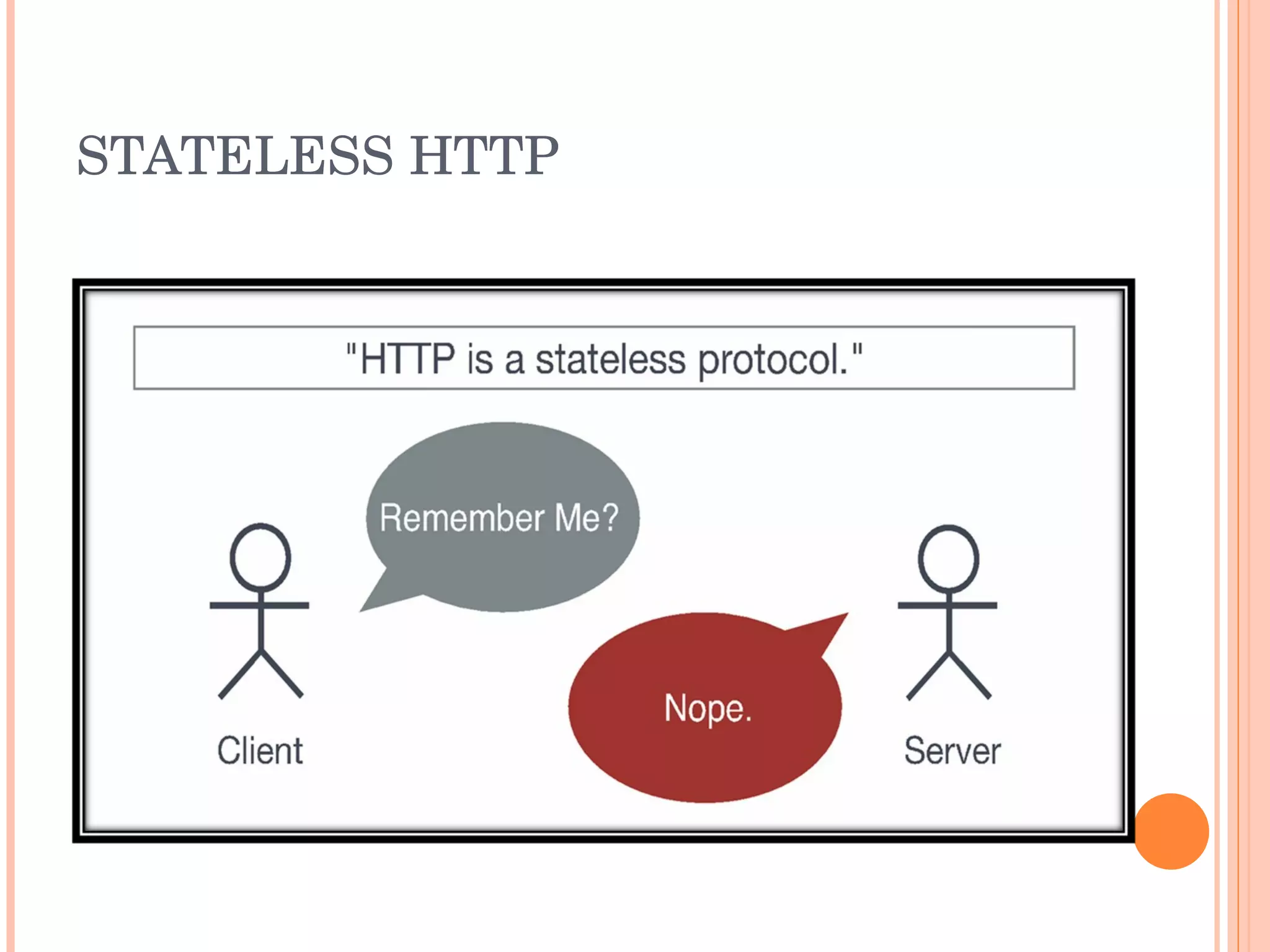
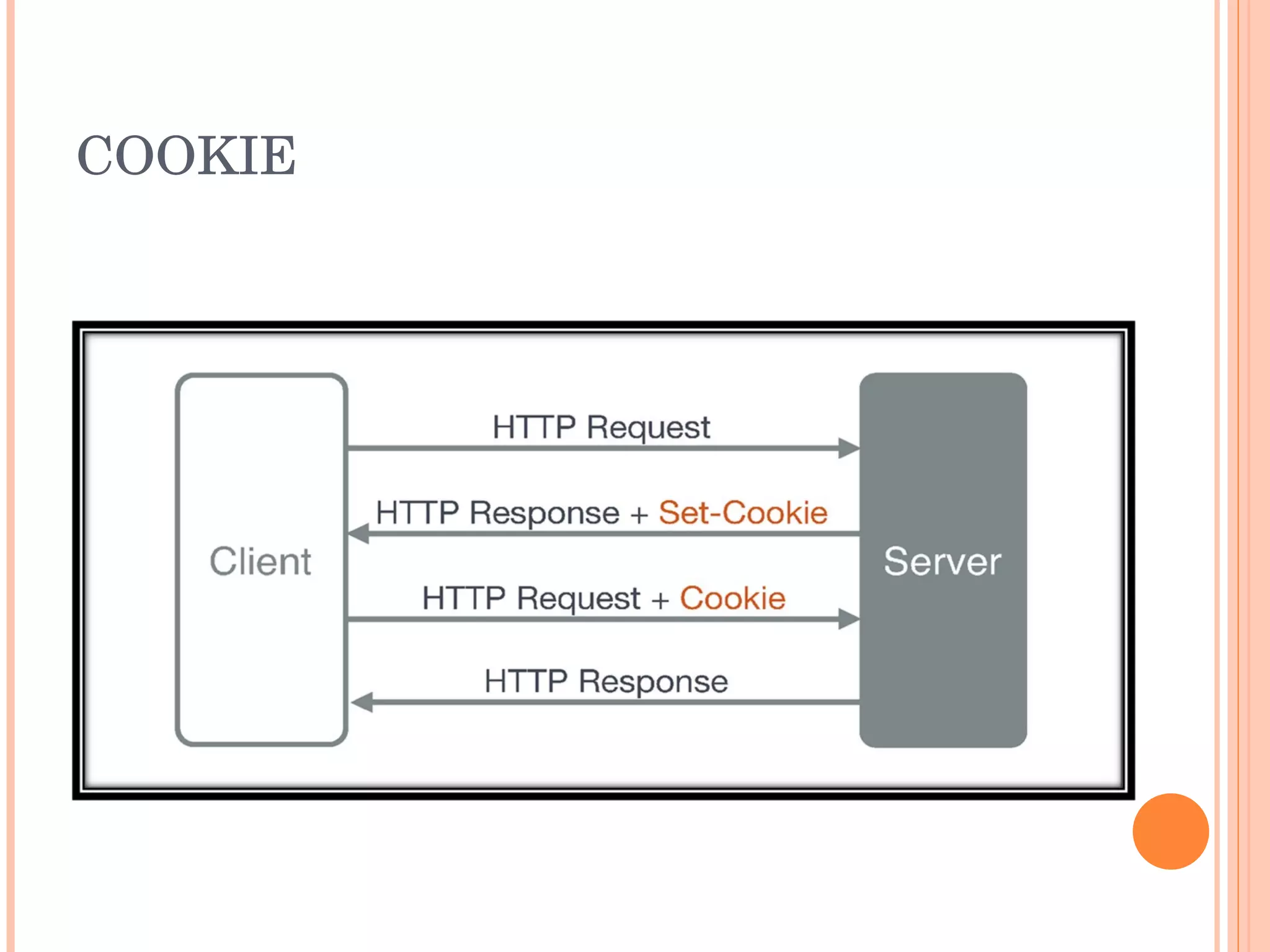
The document provides an introduction to web spider web weaving and discusses key concepts related to HTTP requests and responses between clients and servers. It explains common web technologies like web servers, browsers, spiders, and scripting languages. It also discusses database servers, web models like LAMP and WAMP, HTTP sessions, and introducing a uniform server.