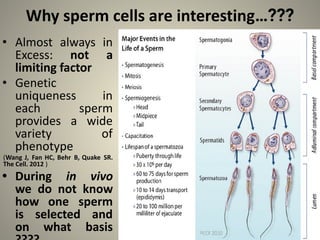
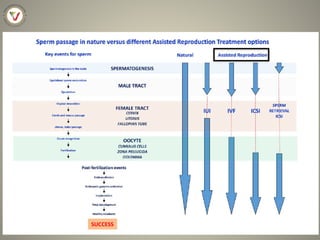
The document discusses various sperm selection methods and their impacts on embryo development and fertility outcomes. It evaluates semen examination, sperm morphology, and advanced selection techniques like IMSI and PICS techniques for improving assisted reproductive technology results. It highlights that proper sperm selection criteria and assessments are vital for enhancing fertilization rates while suggesting that more comprehensive studies are needed to further validate these methods.