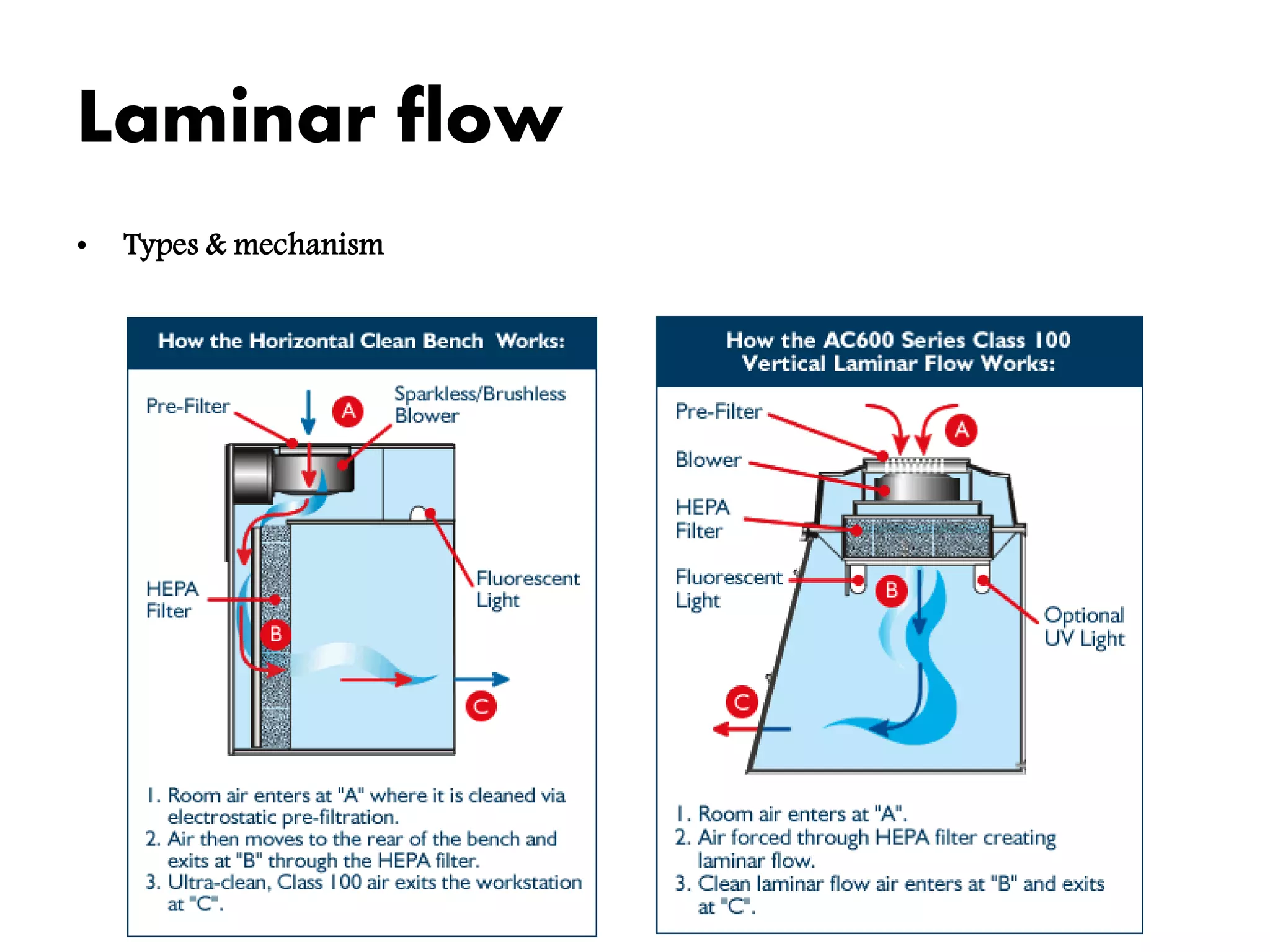
The document outlines the essential components and considerations for setting up a micro-sized IVF laboratory, including various functional zones such as patient procedural areas, laboratory zones, and staff support areas. It emphasizes the importance of maintaining optimal environmental conditions for embryo development, including temperature, gas levels, and air quality, as well as establishing standardized operating protocols. The conclusion stresses the need for skilled embryologists and strict quality controls to ensure successful outcomes in assisted reproductive technology.