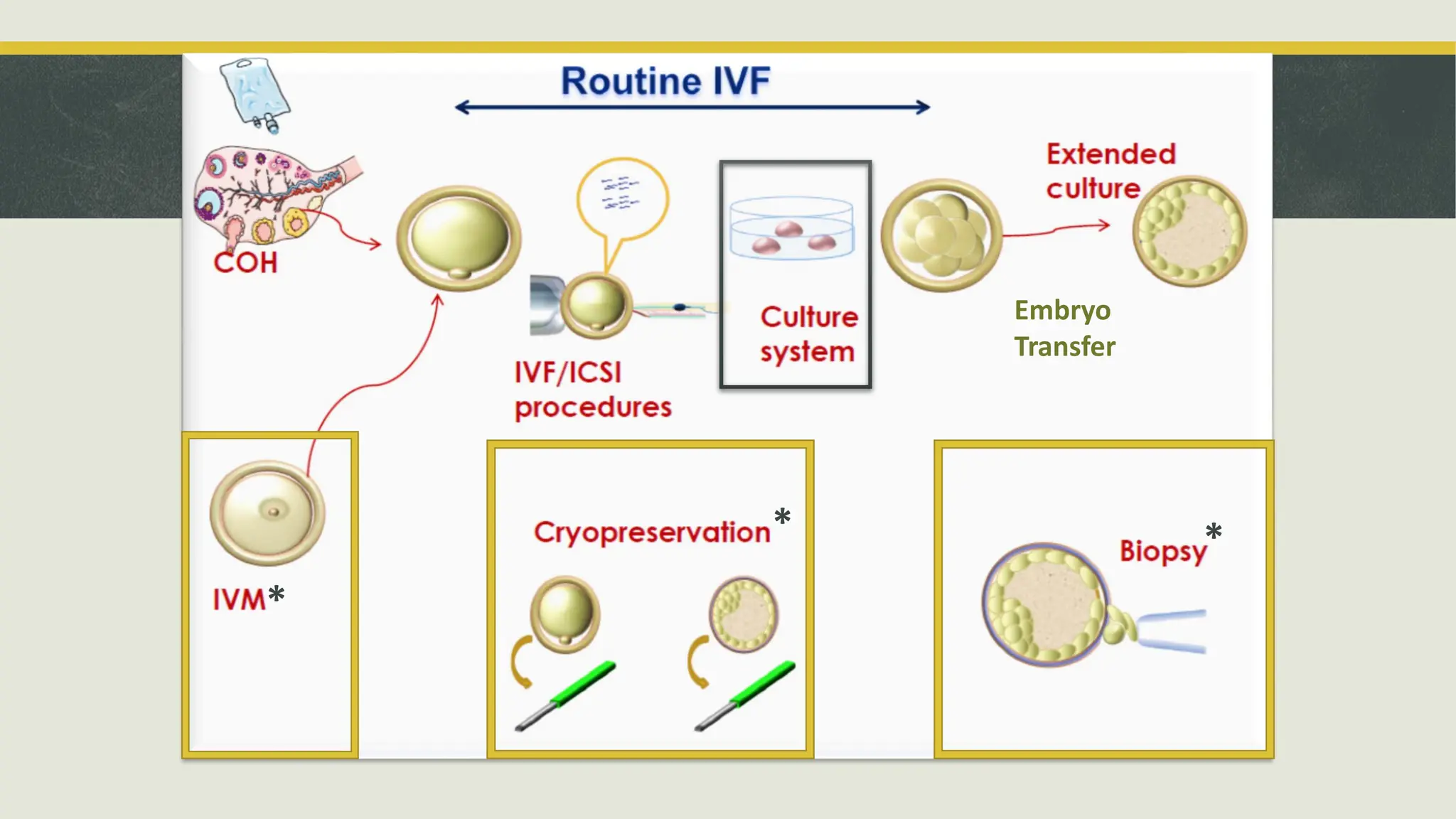
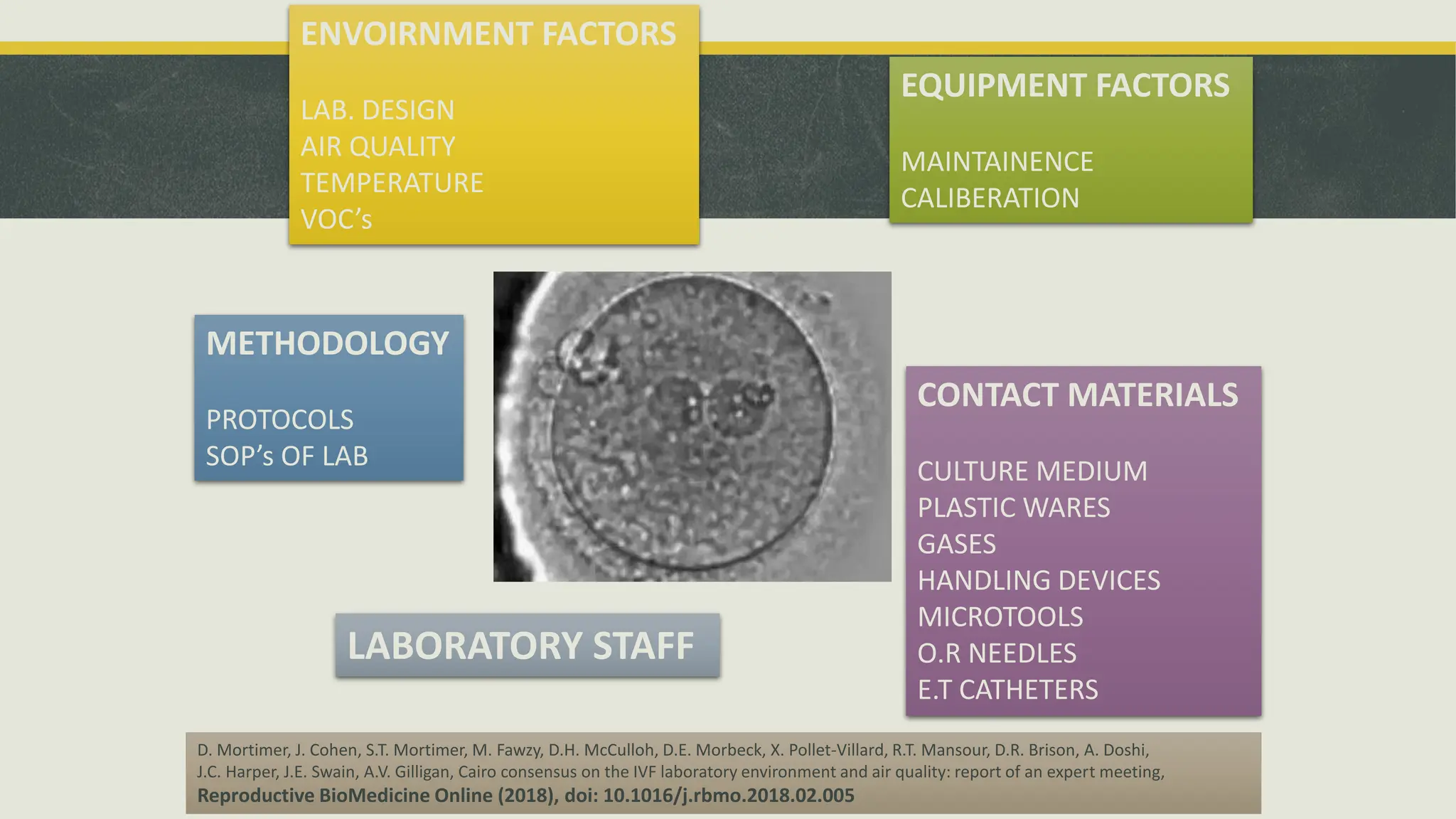
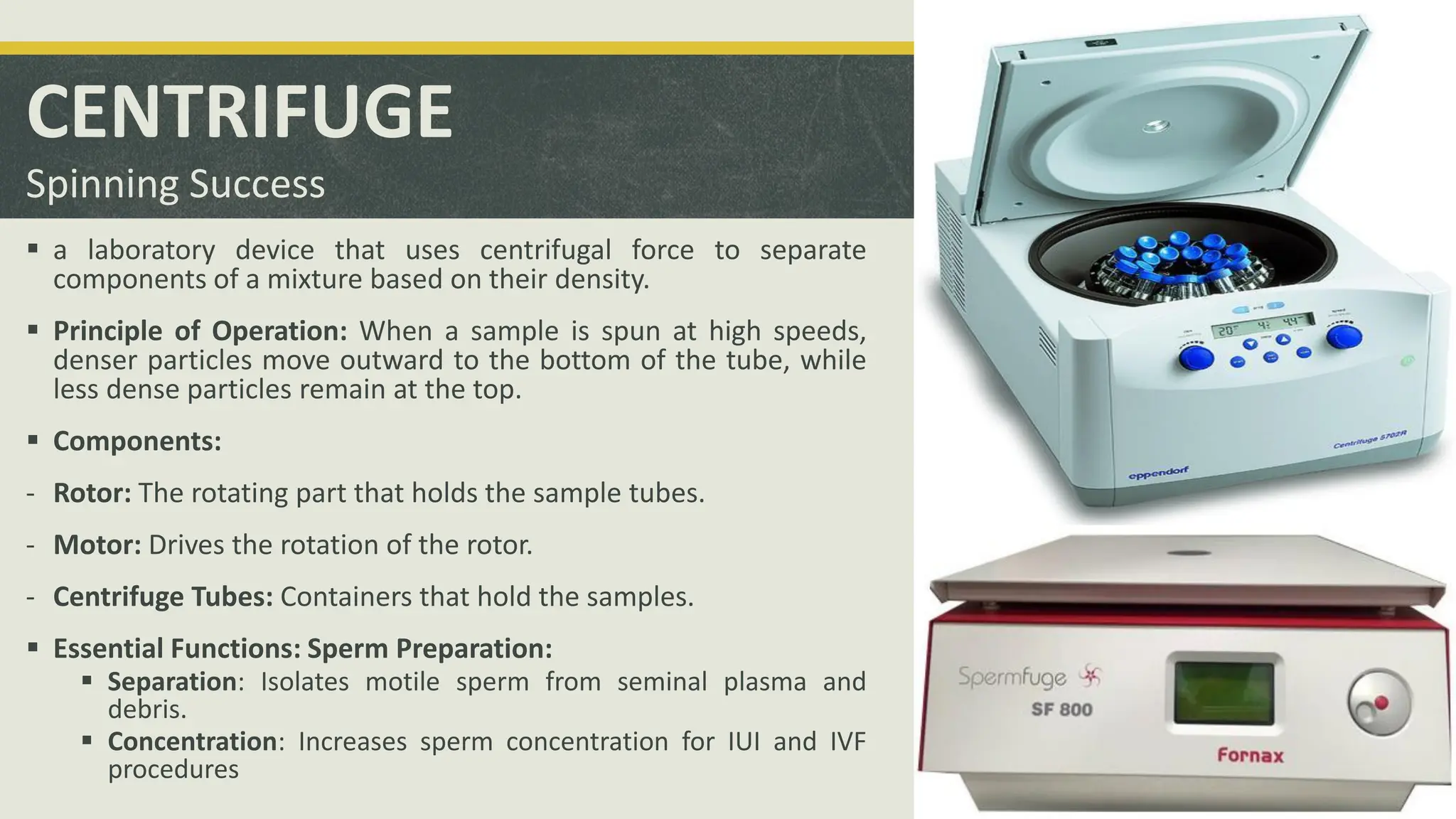
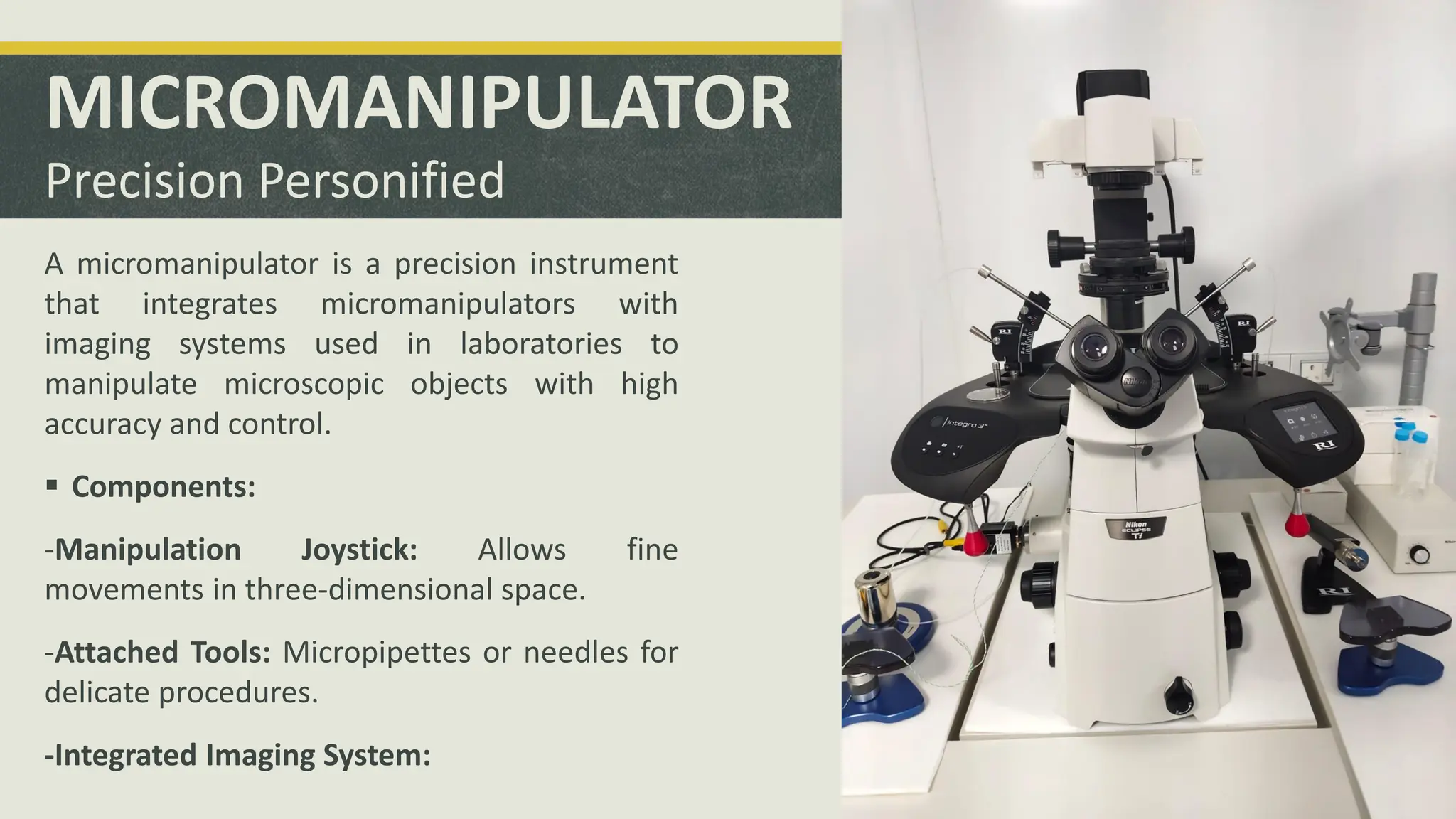
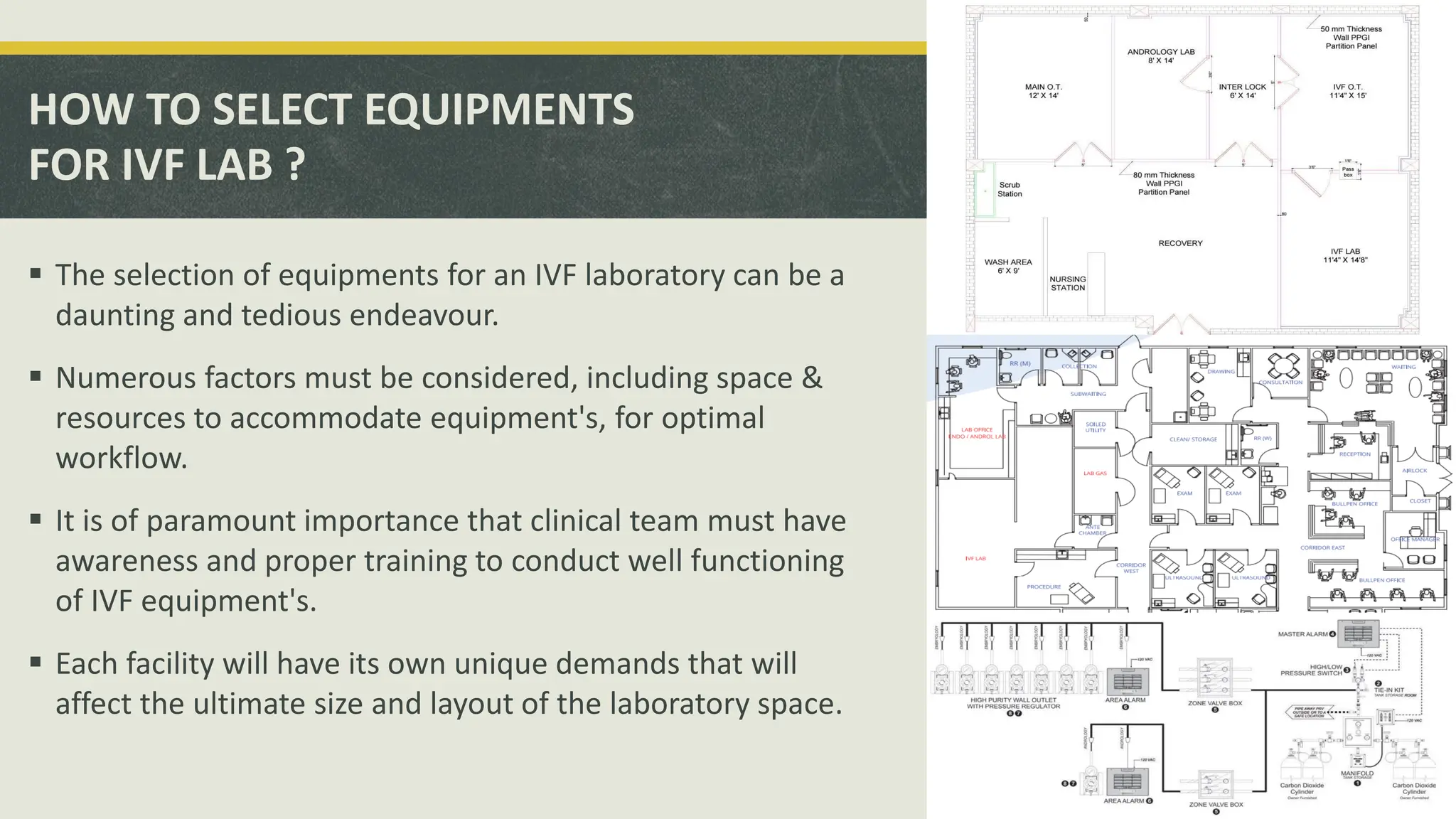
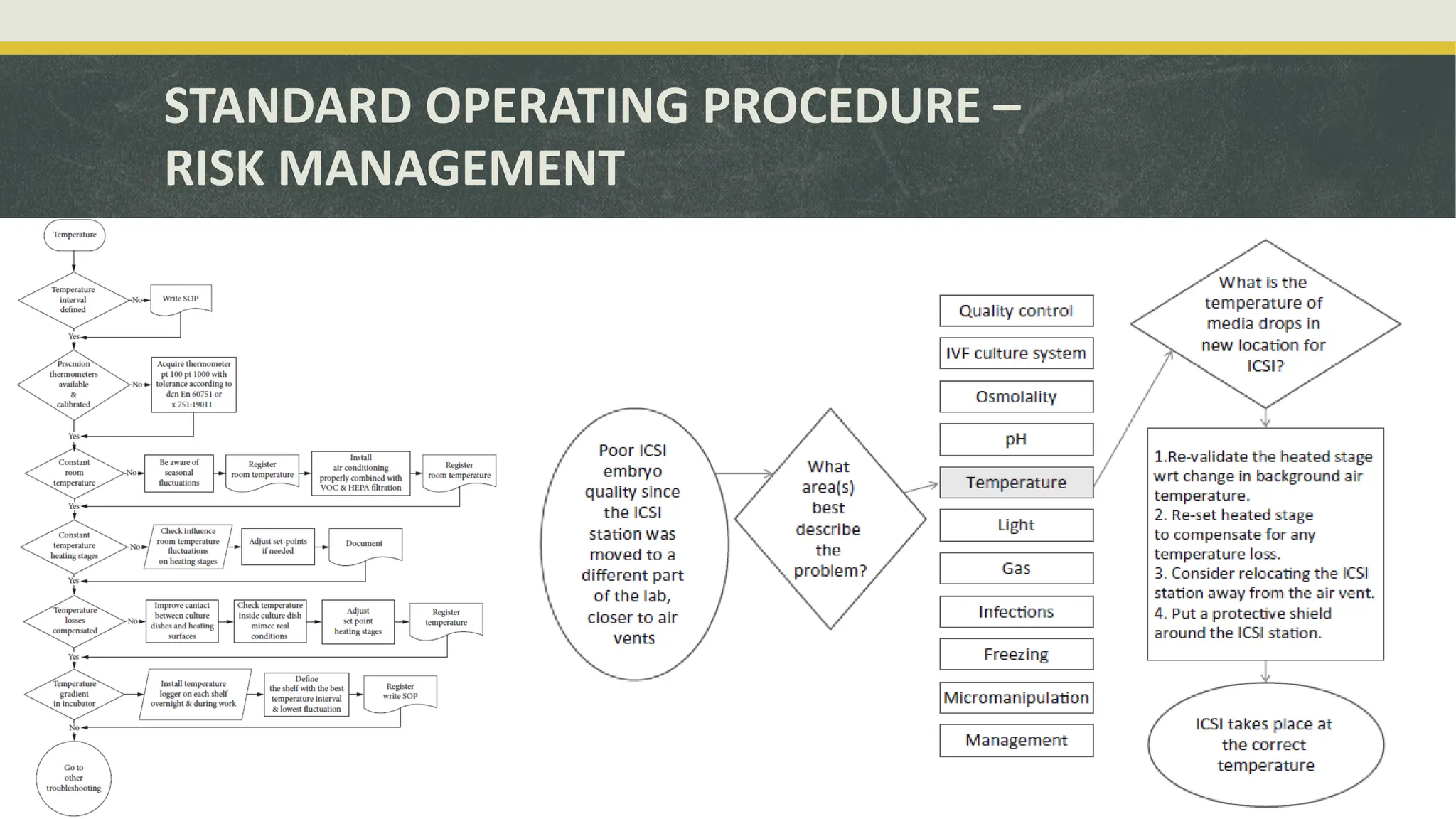
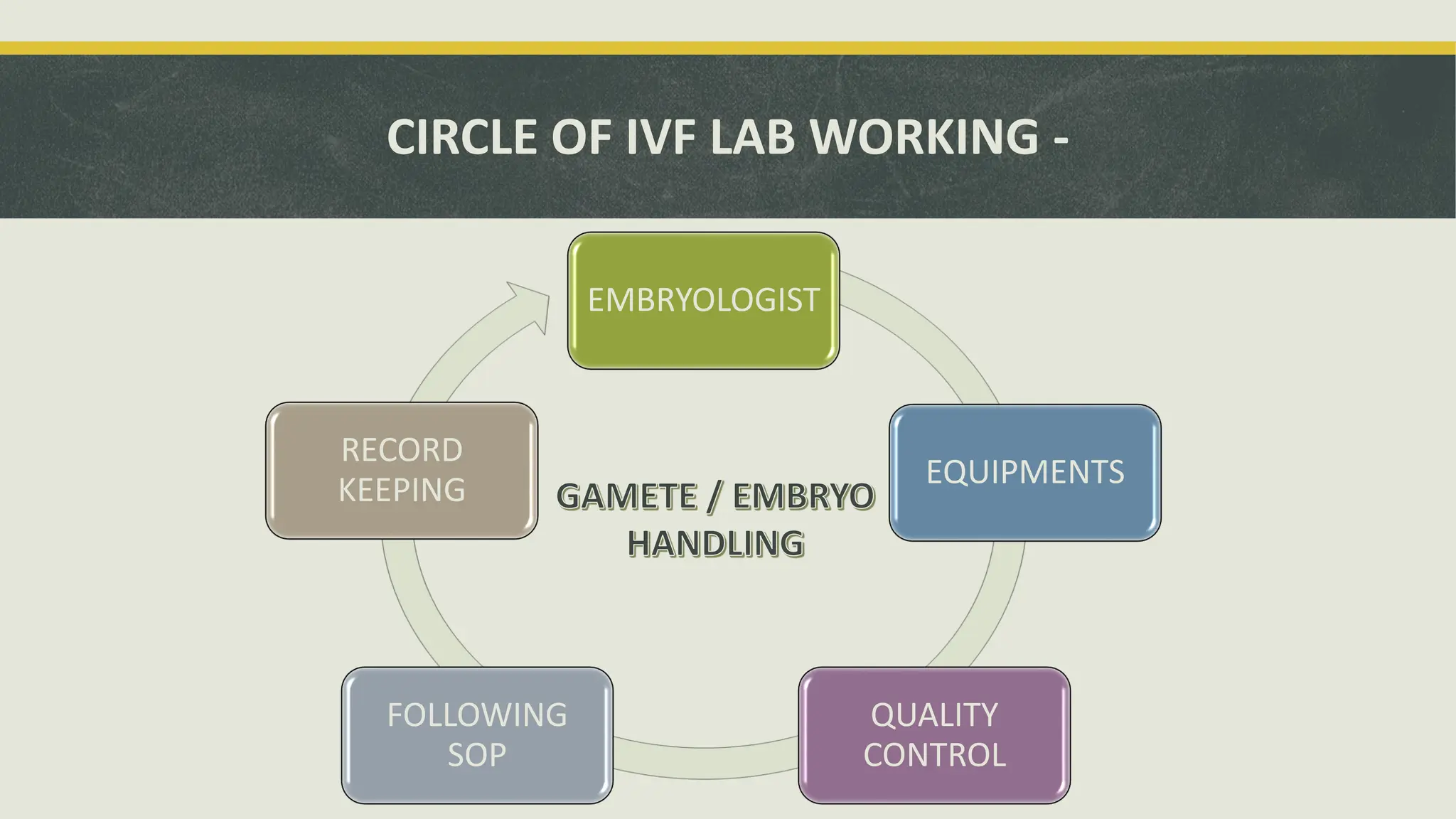
The document outlines the essential equipment and instruments required in an IVF laboratory, emphasizing their role in achieving high take-home baby rates. It details the importance of proper selection, validation, and good laboratory practices for maintaining an optimal environment for embryo culture. Key equipment includes incubators, centrifuges, and microscopes, each serving crucial functions in the assisted reproductive technology process.