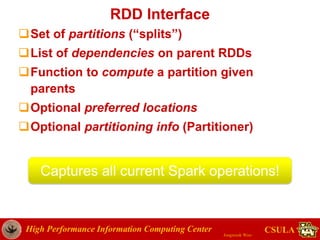
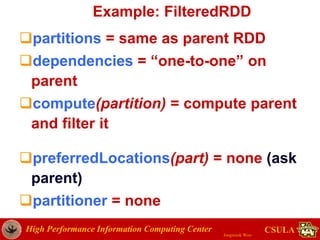
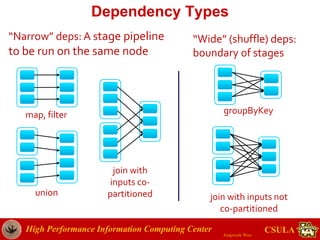
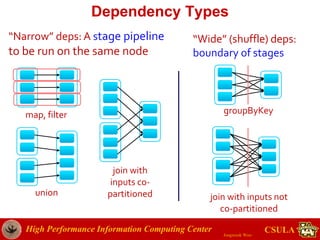
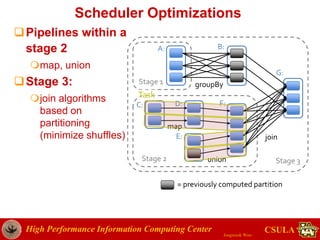
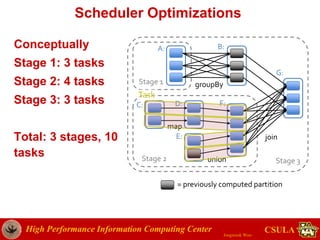
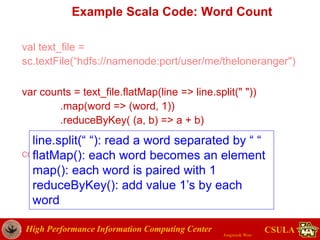
- The document discusses a presentation given by Jongwook Woo on introducing Spark and its uses for big data analysis. It includes information on Woo's background and experience with big data, an overview of Spark and its components like RDDs and task scheduling, and examples of using Spark for different types of data analysis and use cases.




































![High Performance Information Computing Center
Jongwook Woo
CSULA
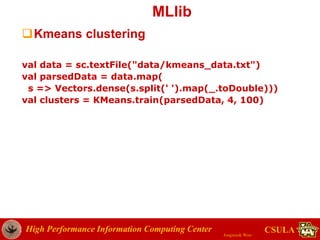
WordCount.java (Driver)
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;
public class WordCount {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
if (args.length != 2) {
System.out.println("usage: [input] [output]");
System.exit(-1);
}
Job job = Job.getInstance(new Configuration());
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
job.setMapperClass(WordMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(SumReducer.class);
job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
job.setJarByClass(WordCount.class);
job.submit(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sparktutorial2015-150625011040-lva1-app6892/85/Spark-tutorial-KCC-2015-52-320.jpg)










![High Performance Information Computing Center
Jongwook Woo
CSULA
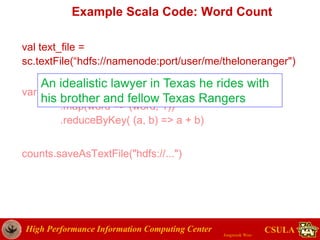
Example Code: Market Basket
Analysis
// ngrams to pair items
def ngram(s: String, inSep: String, outSep: String, n:Int): Set[String] = {
s.toLowerCase.split(inSep).sliding(n).map(_.sorted.mkString(outSep)).toSet
}
val fPath = "jwoo/files3.2G.dat"
val lines = sc.textFile(fPath) // lines: Array[String]
val ngramNo = 2
val result = lines.flatMap(line => ngram(line, " ", "+", ngramNo)).map(word => (word,
1)).reduceByKey((a, b) => a+b)
val sortedResult = result.map(pair => pair.swap).sortByKey(false)
//save result to HDFS
sortedResult.saveAsTextFile("jwoo/result3.2")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sparktutorial2015-150625011040-lva1-app6892/85/Spark-tutorial-KCC-2015-65-320.jpg)
![High Performance Information Computing Center
Jongwook Woo
CSULA
Example Code: Market Basket
Analysis
// ngrams to pair items
def ngram(s: String, inSep: String, outSep: String, n:Int):
Set[String] = {
s.toLowerCase.split(inSep).sliding(n).map(_.sorted.
mkString(outSep)).toSet
}toLowerCase(): convert to lower letters
split(inSep): split by the separator inSep
sliding(n): select n words as a group
_.sorted: sort the elements in the group
mkString(outSep): the elements are appended
with outSep
toSet: make the group as a set with unique elmts](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sparktutorial2015-150625011040-lva1-app6892/85/Spark-tutorial-KCC-2015-66-320.jpg)
![High Performance Information Computing Center
Jongwook Woo
CSULA
Example Code: Market Basket
Analysis
val fPath = "jwoo/files3.2G.dat"
val lines = sc.textFile(fPath) // lines: Array[String]
val ngramNo = 2
val result = lines.flatMap(line => ngram(line, " ", "+",
ngramNo)).map(word => (word, 1)).reduceByKey((a, b) =>
a+b)
val sortedResult = result.map(pair =>
pair.swap).sortByKey(false)
//save result to HDFS
sortedResult.saveAsTextFile(“jwoo/result32G”)
Extract and count bigram](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sparktutorial2015-150625011040-lva1-app6892/85/Spark-tutorial-KCC-2015-67-320.jpg)
![High Performance Information Computing Center
Jongwook Woo
CSULA
Example Code: Market Basket
Analysis
val fPath = "jwoo/files3.2G.dat"
val lines = sc.textFile(fPath) // lines: Array[String]
val ngramNo = 2
val result = lines.flatMap(line => ngram(line, " ", "+",
ngramNo)).map(word => (word, 1)).reduceByKey((a, b) =>
a+b)
val sortedResult = result.map(pair =>
pair.swap).sortByKey(false)
//save result to HDFS
sortedResult.saveAsTextFile(“jwoo/result32G”)
Sort the bigram in descending
order of the value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sparktutorial2015-150625011040-lva1-app6892/85/Spark-tutorial-KCC-2015-68-320.jpg)












