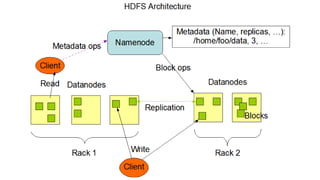
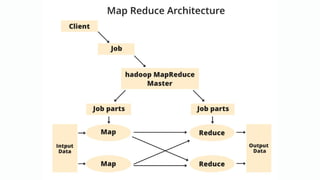
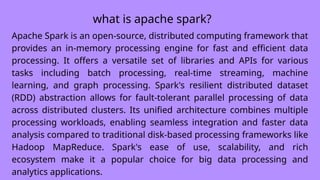
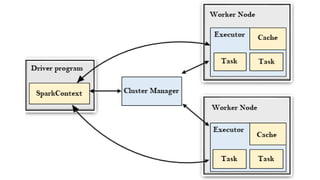
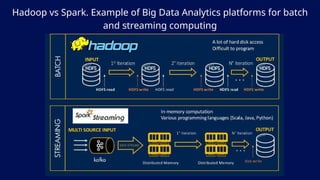
Big data processing refers to the methods and technologies used to handle large volumes of data that traditional data processing applications can't manage efficiently. This data typically comes from various sources such as social media, sensors, machines, transactions, and more.