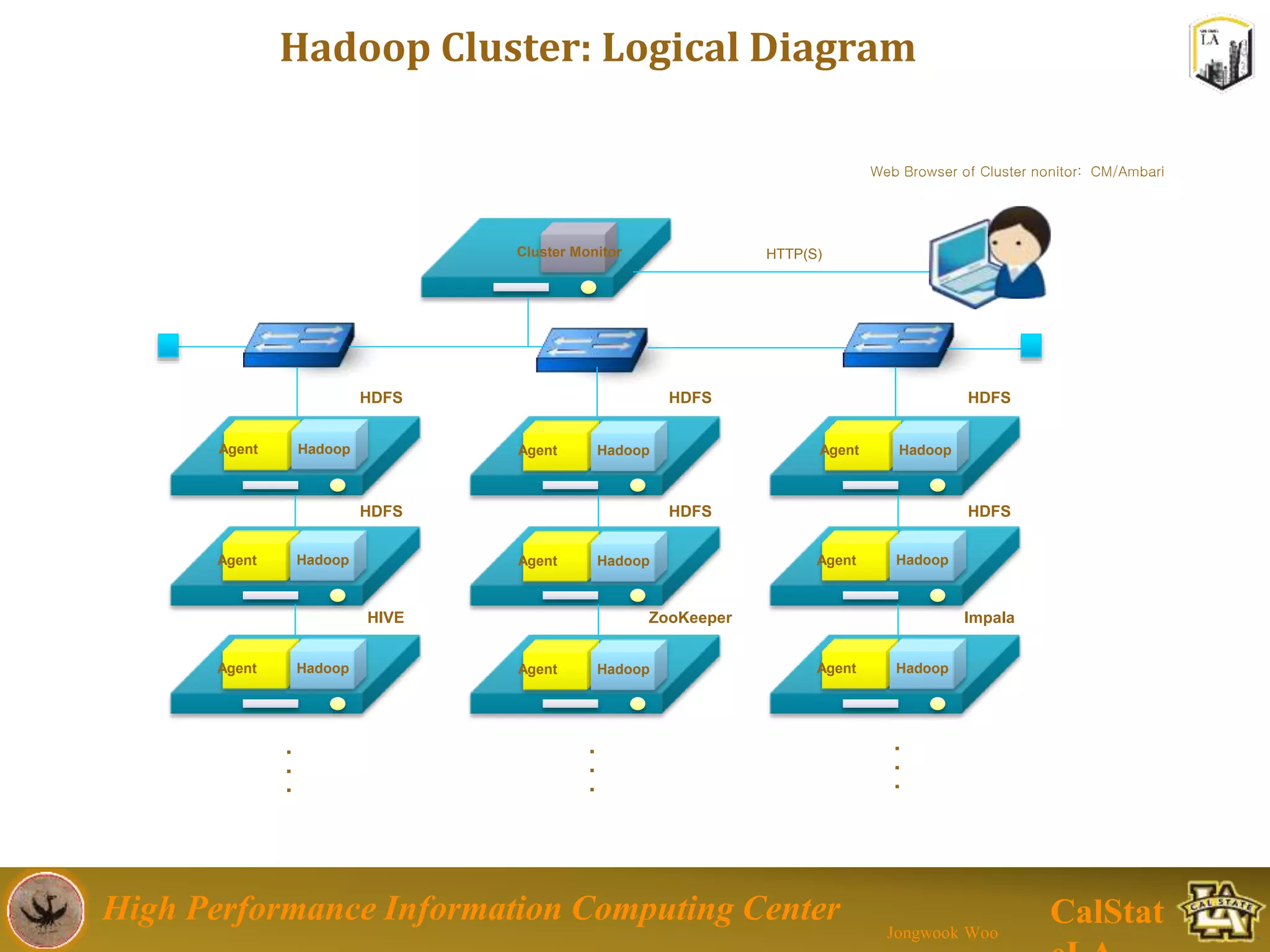
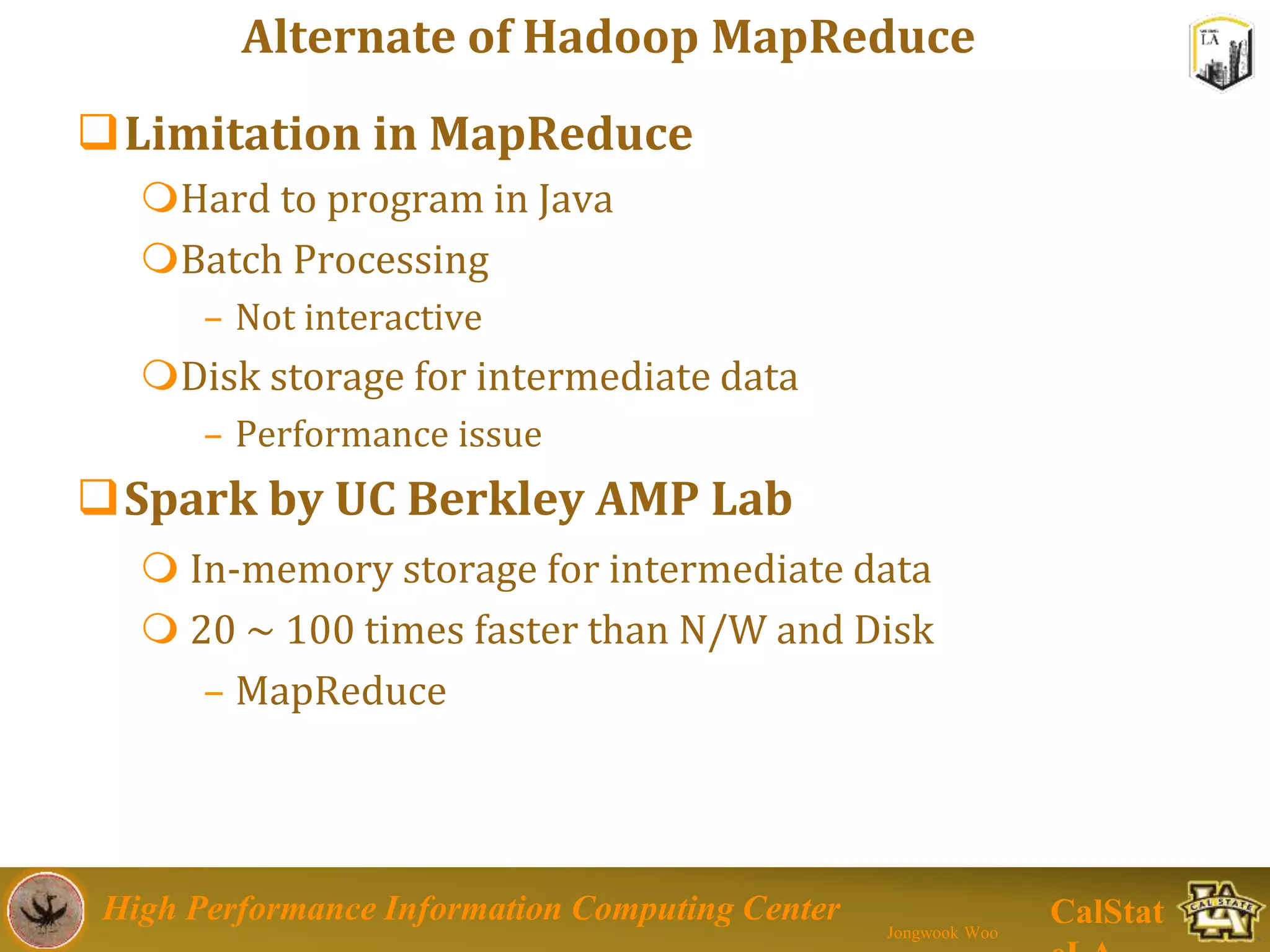
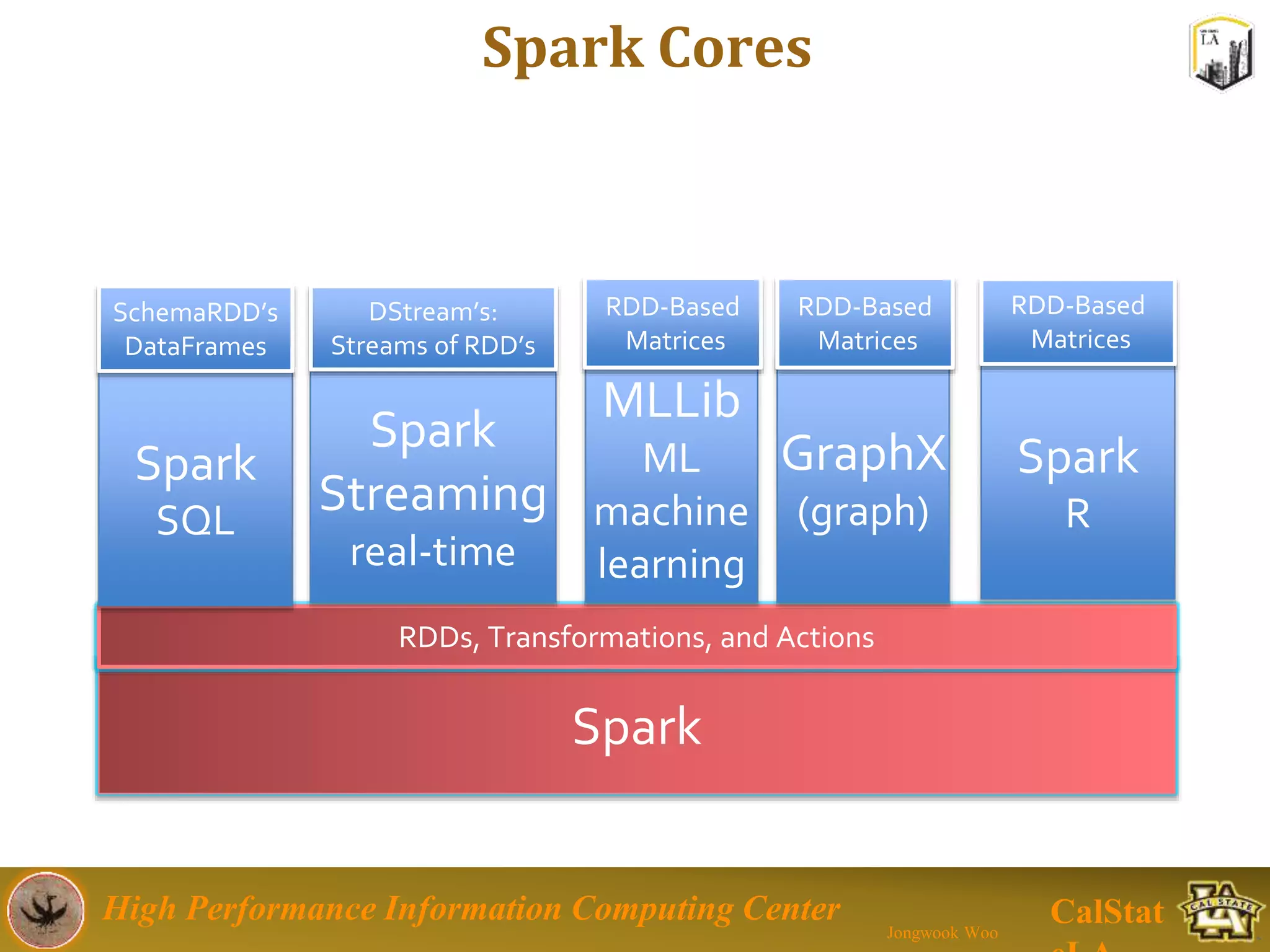
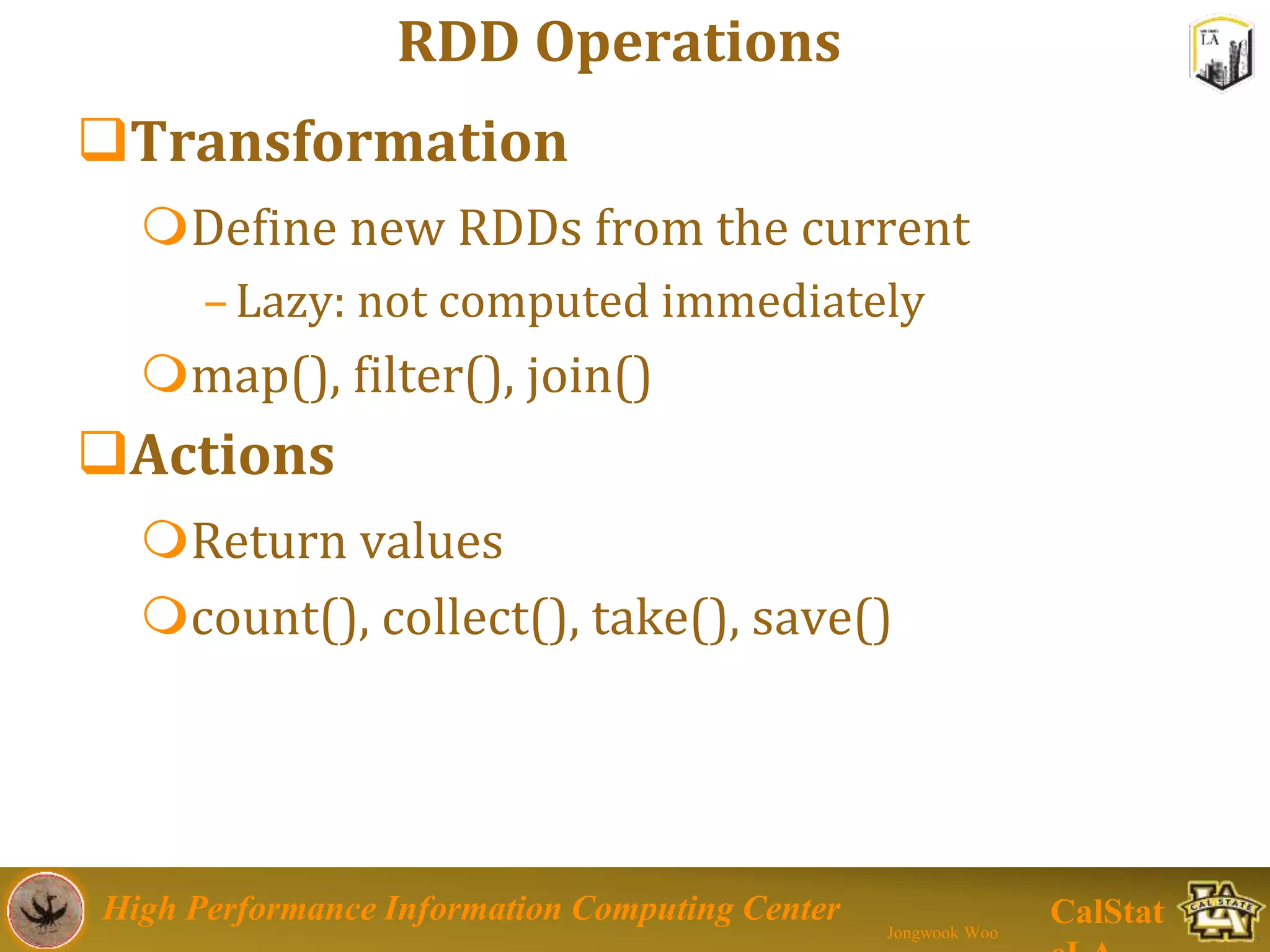
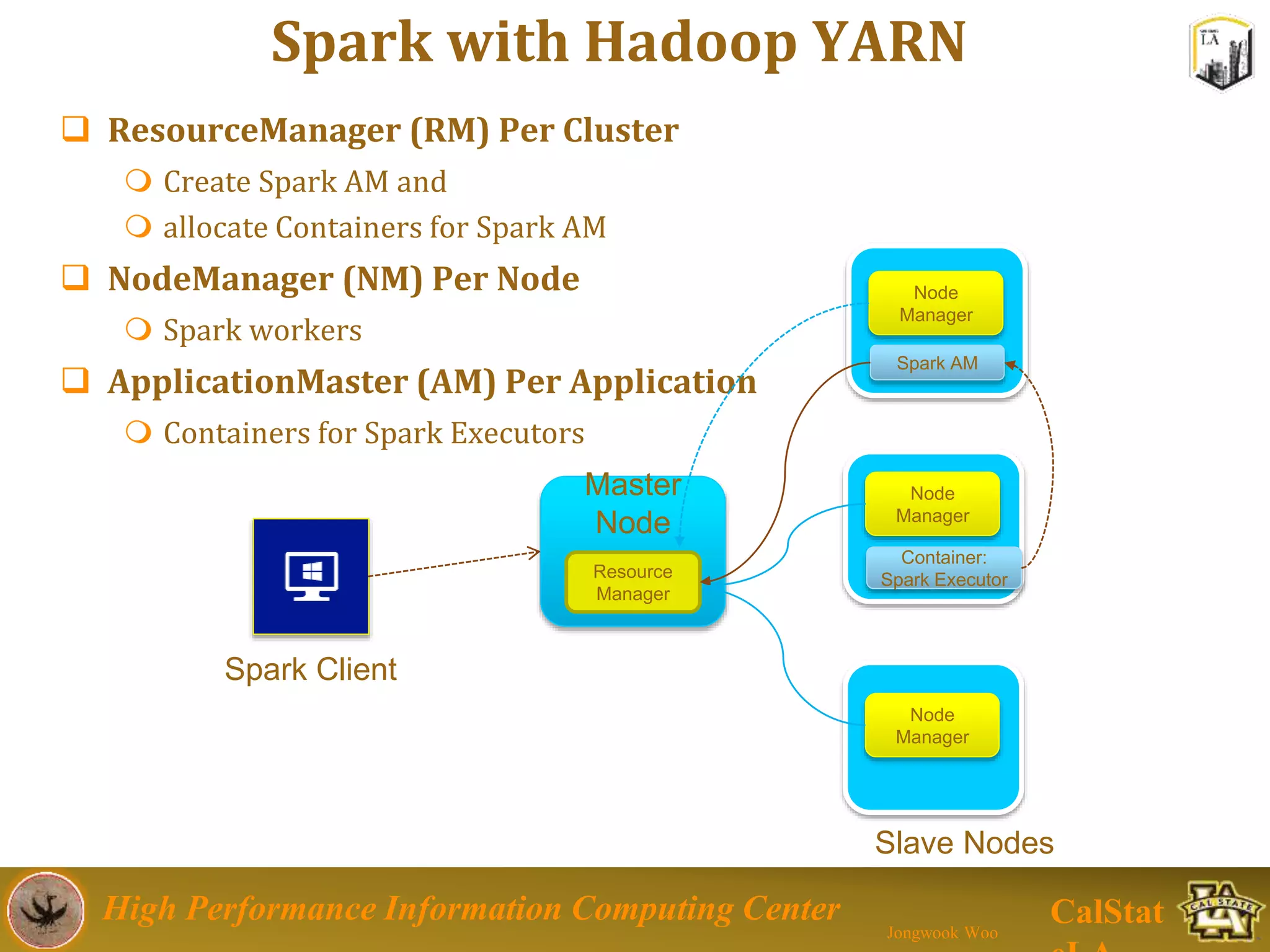
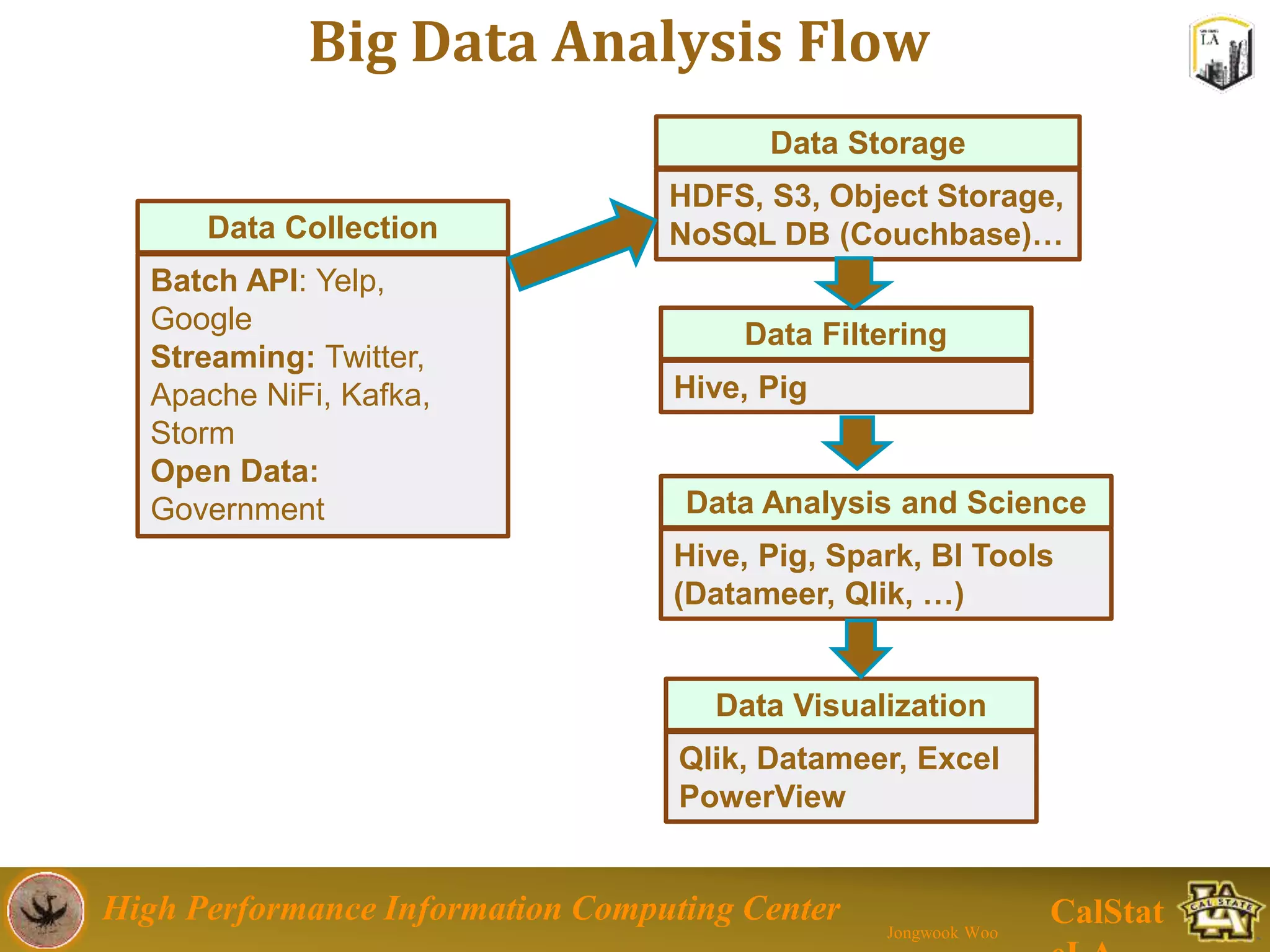
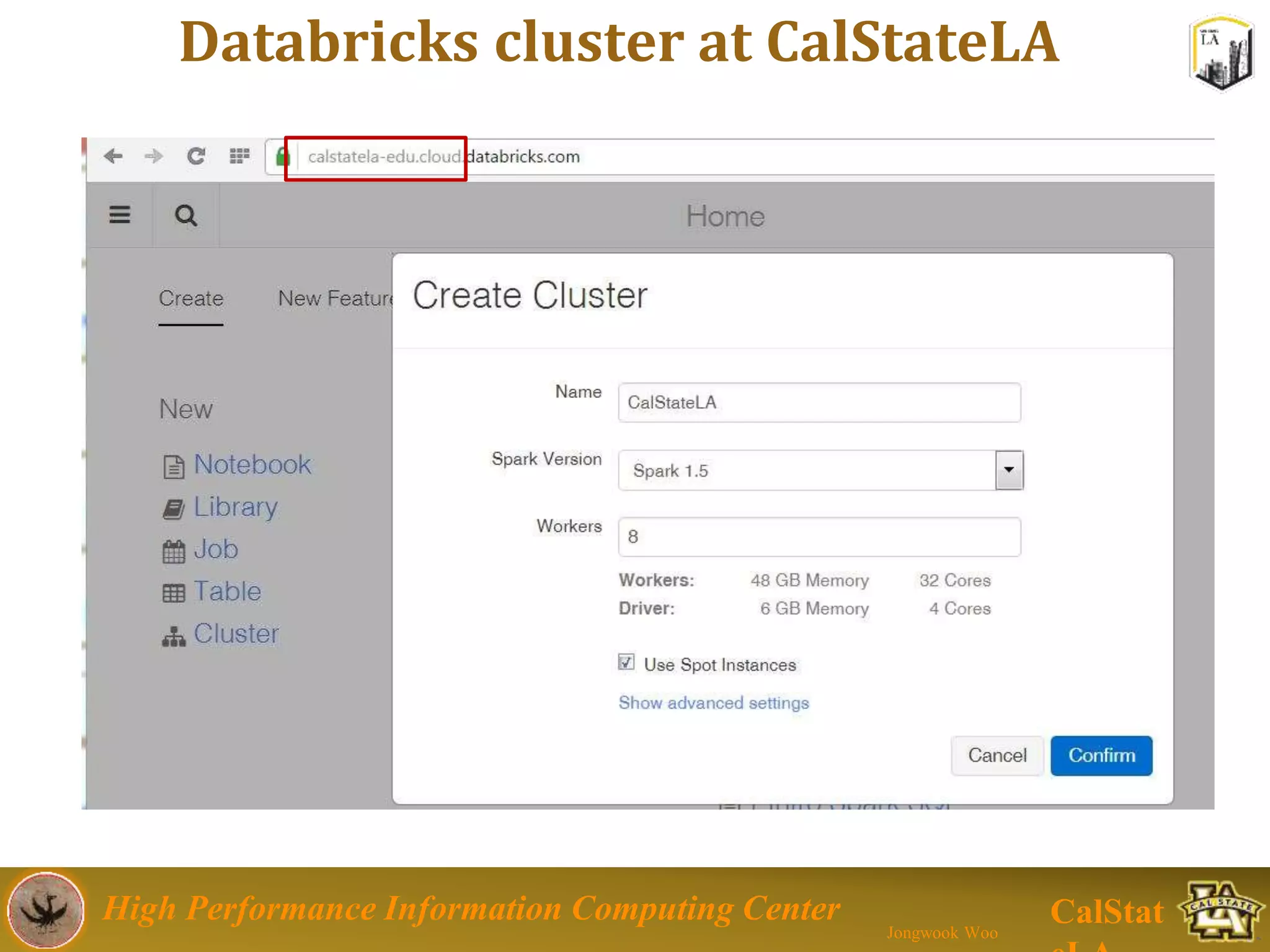
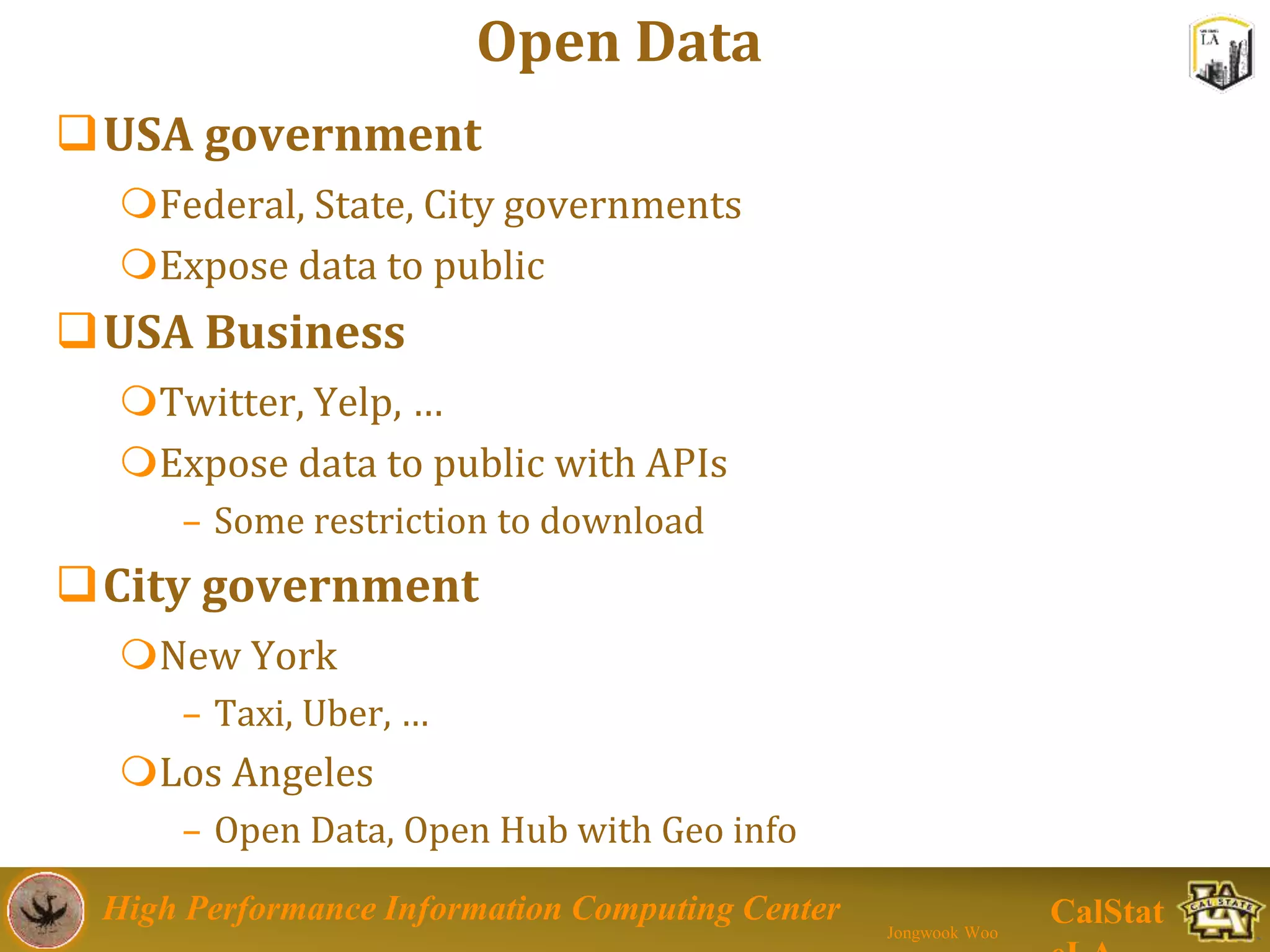
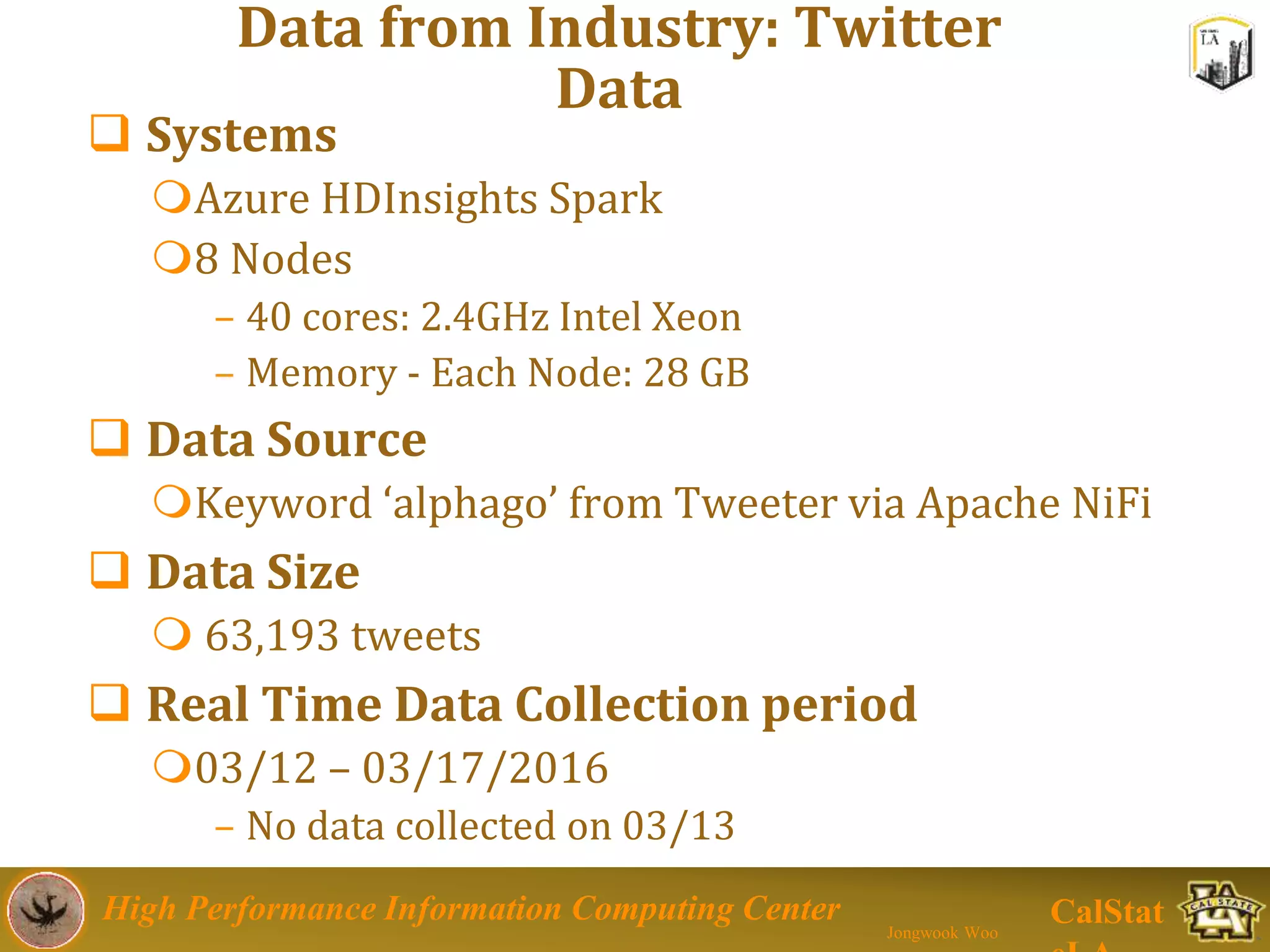
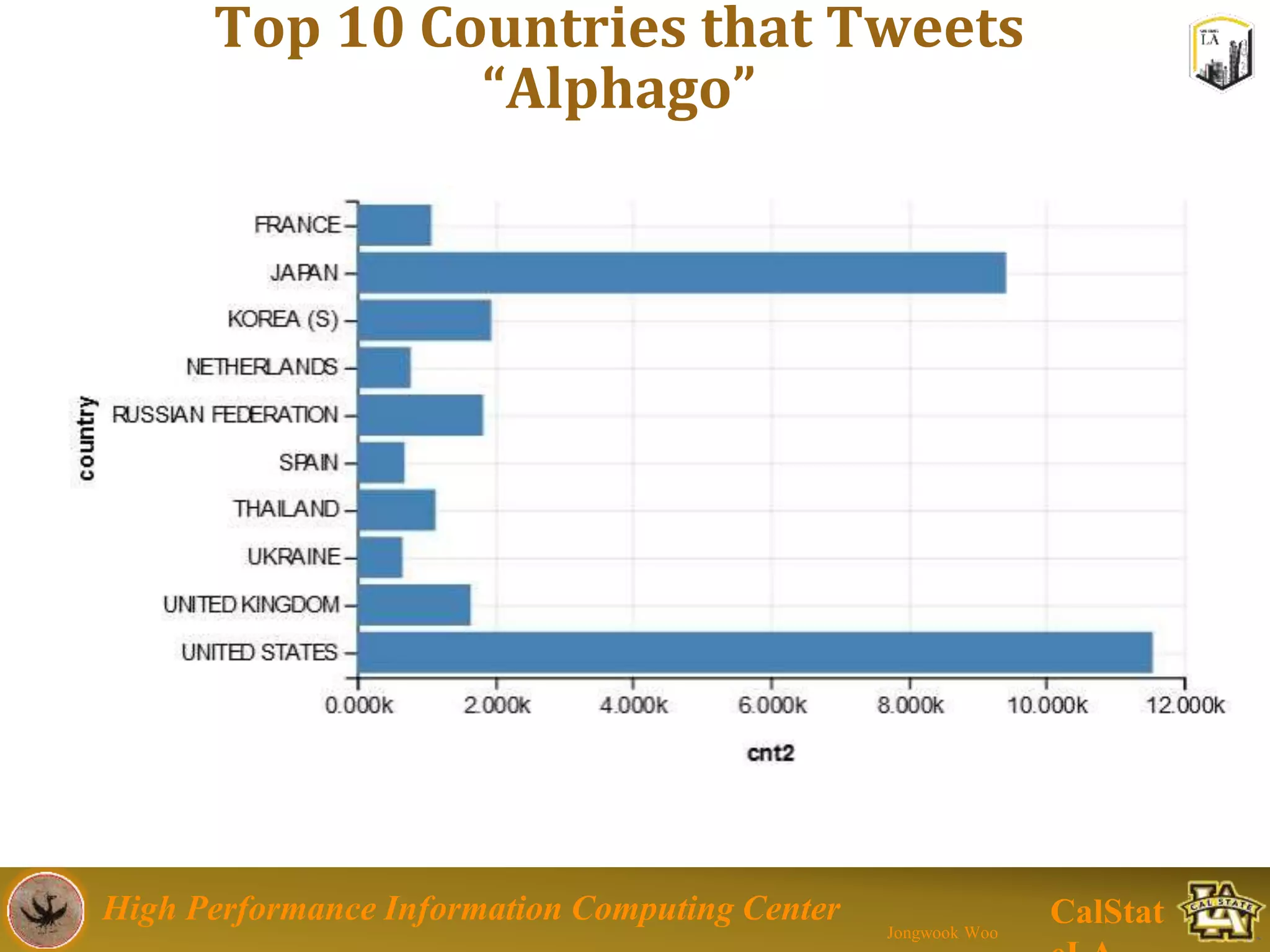
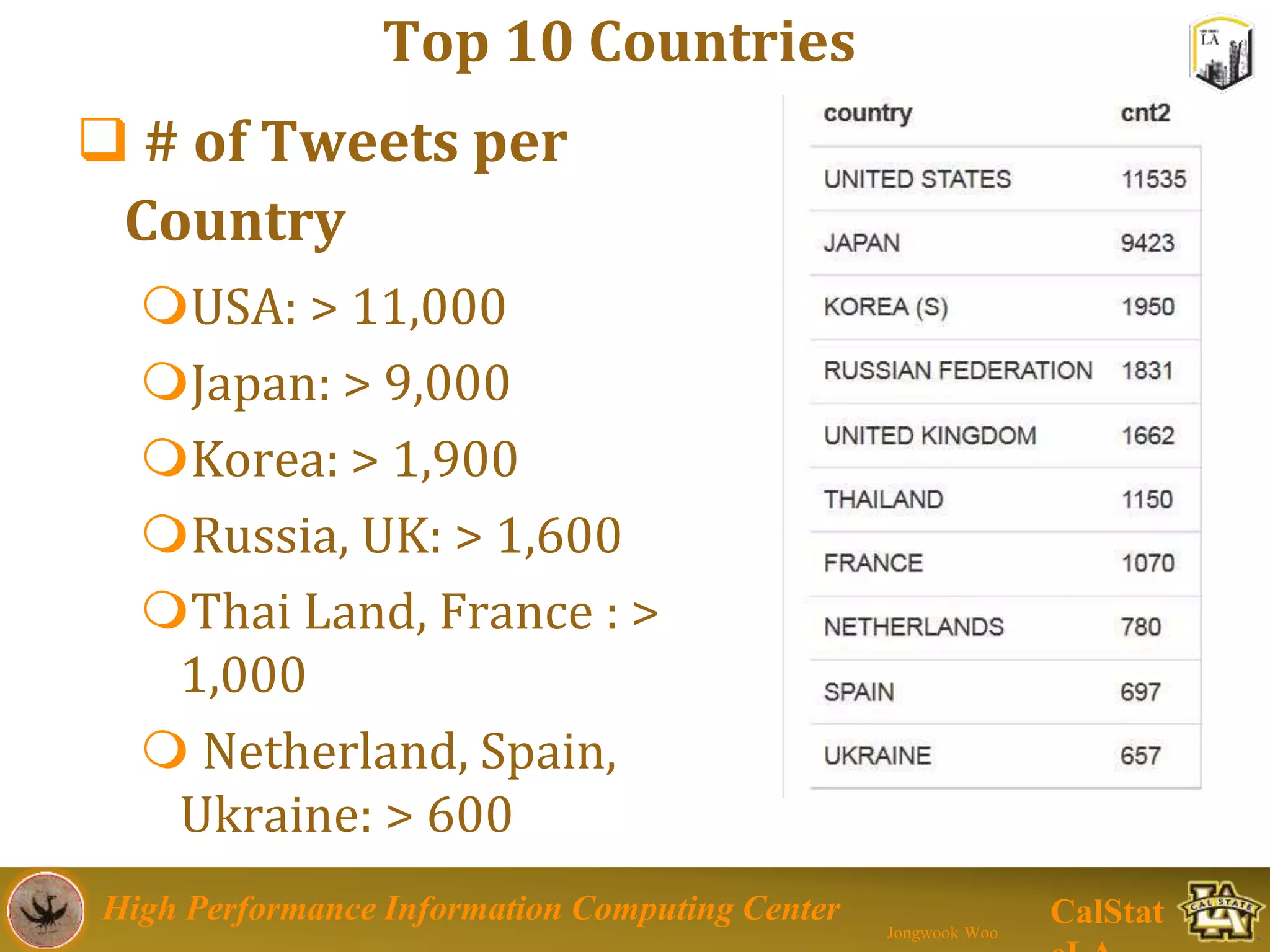
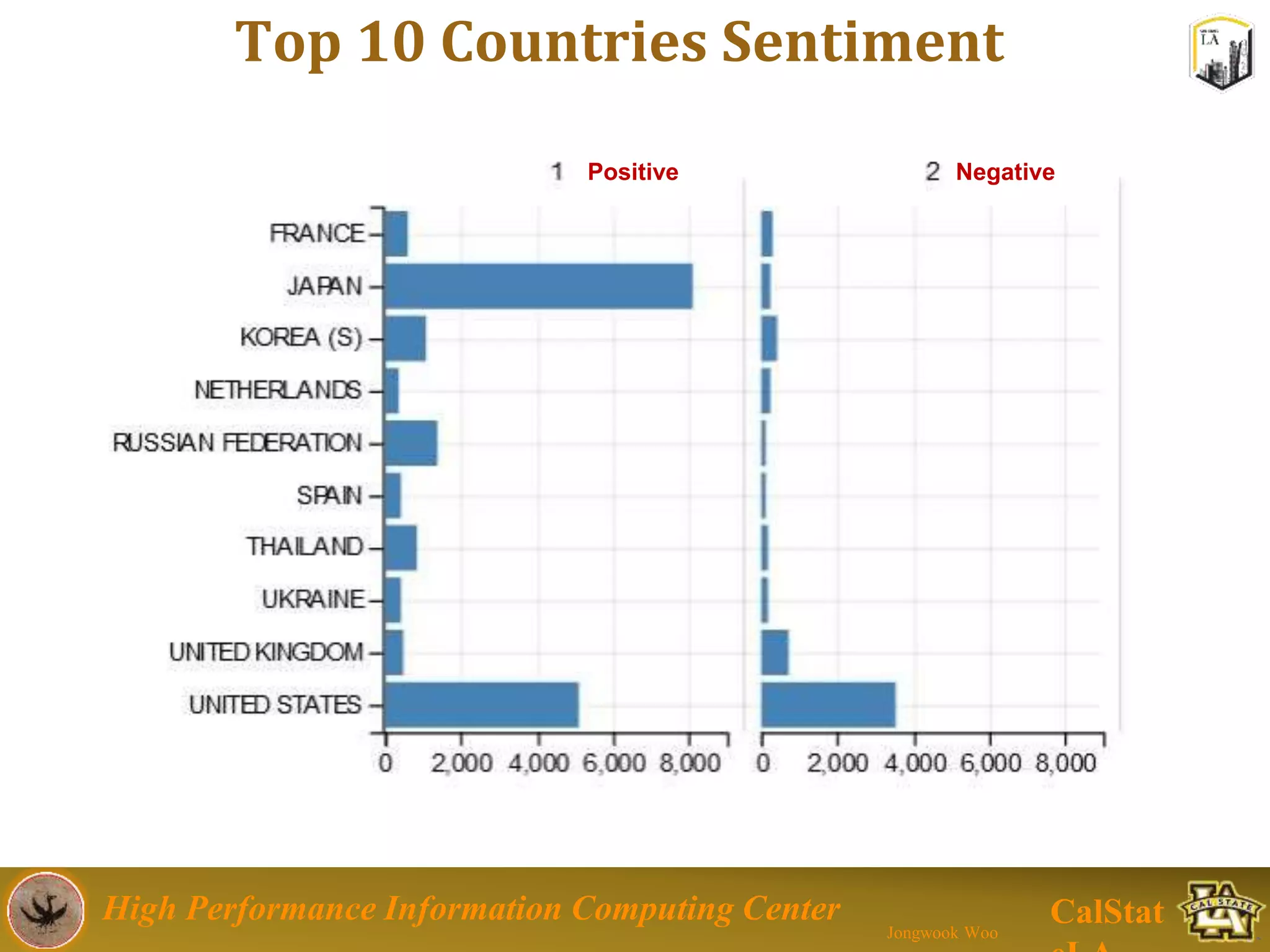
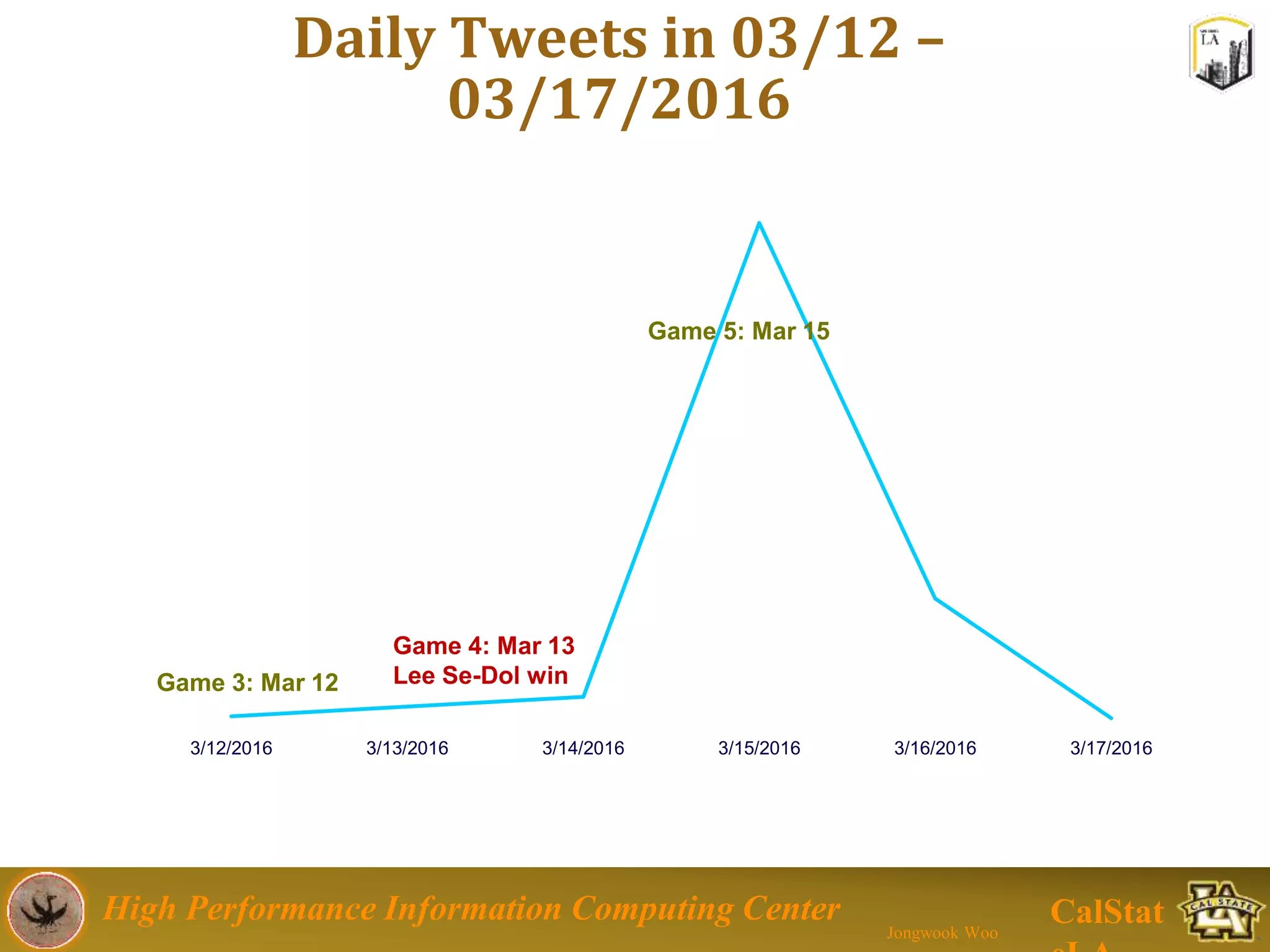
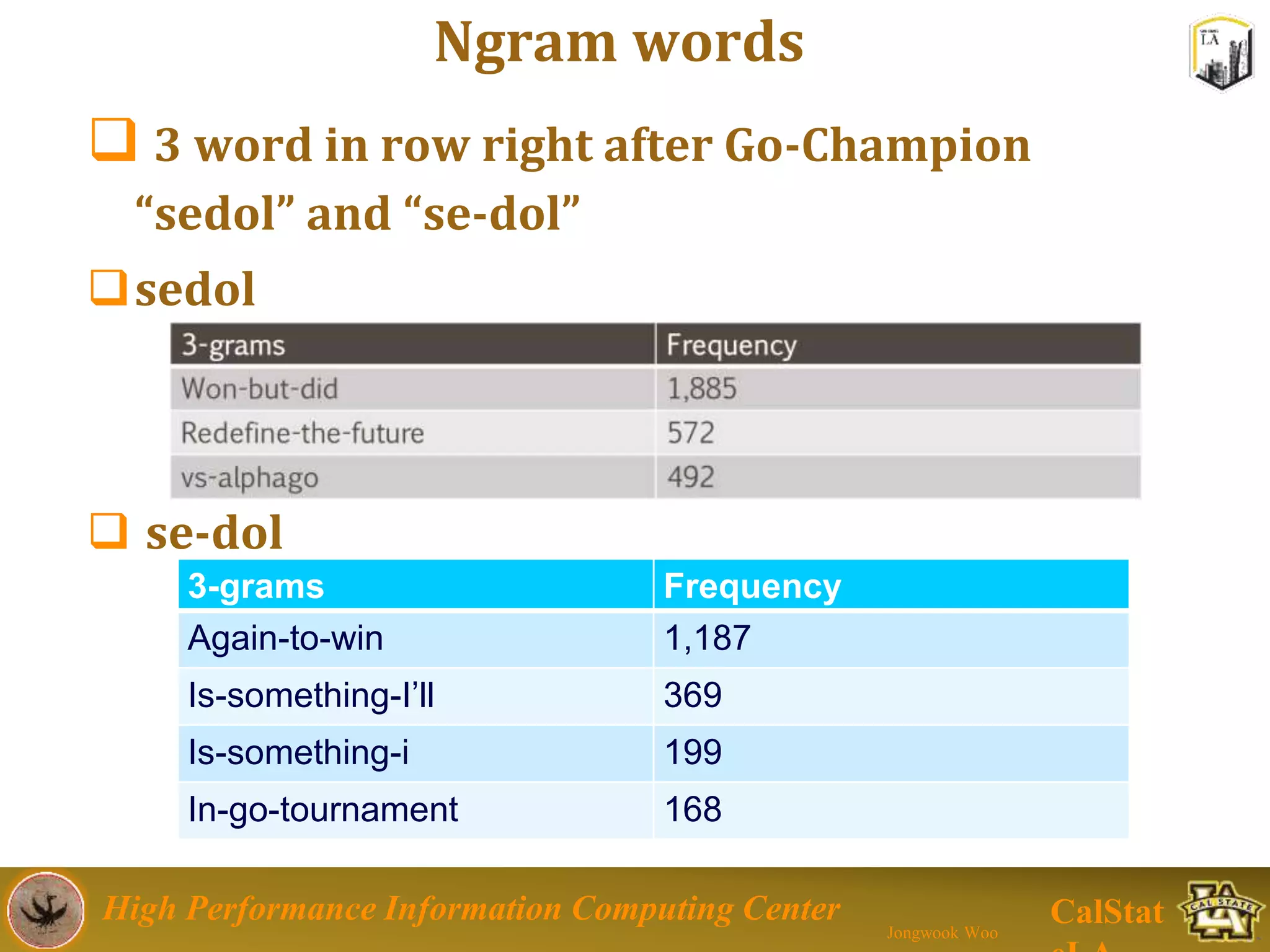
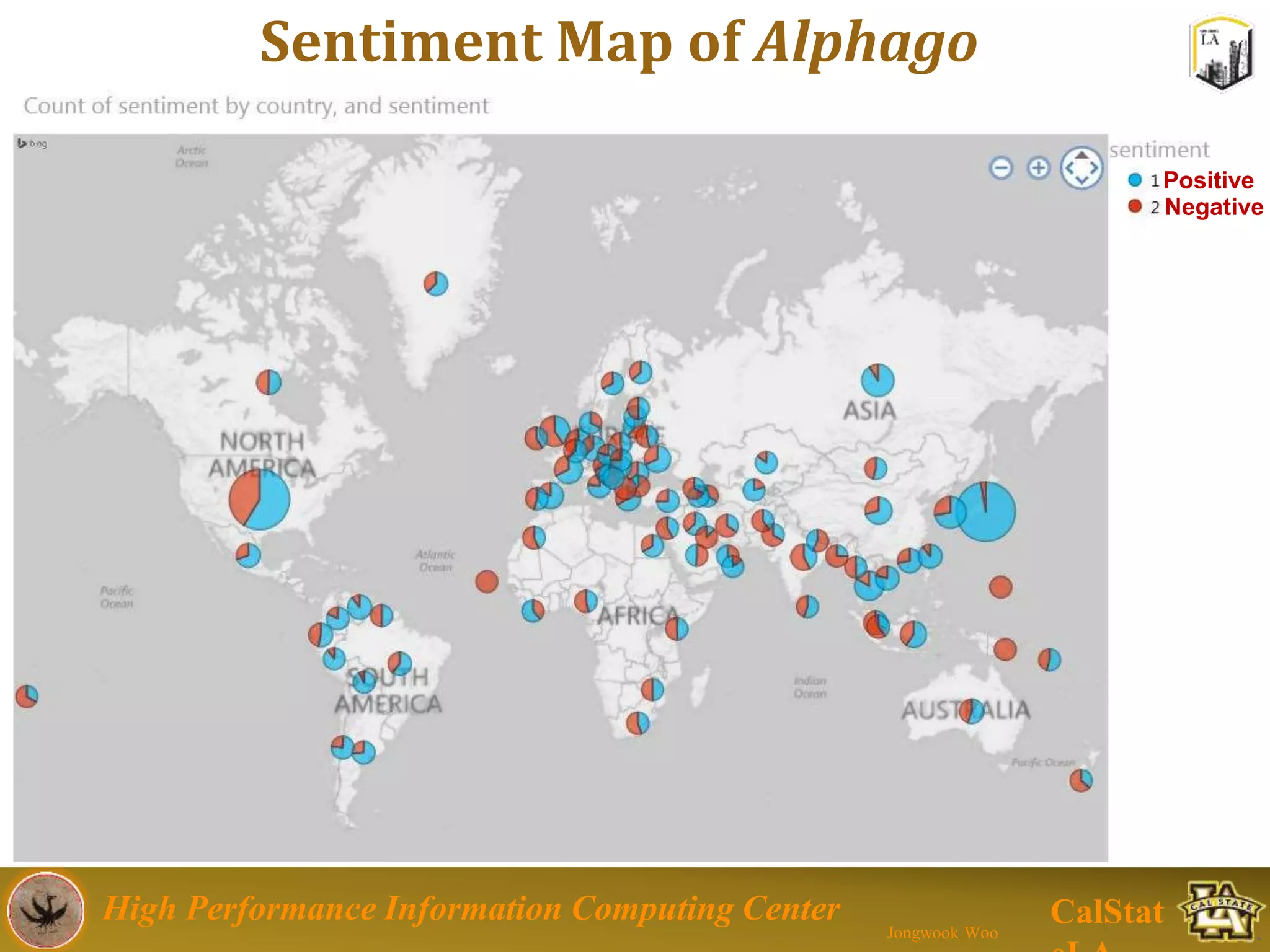
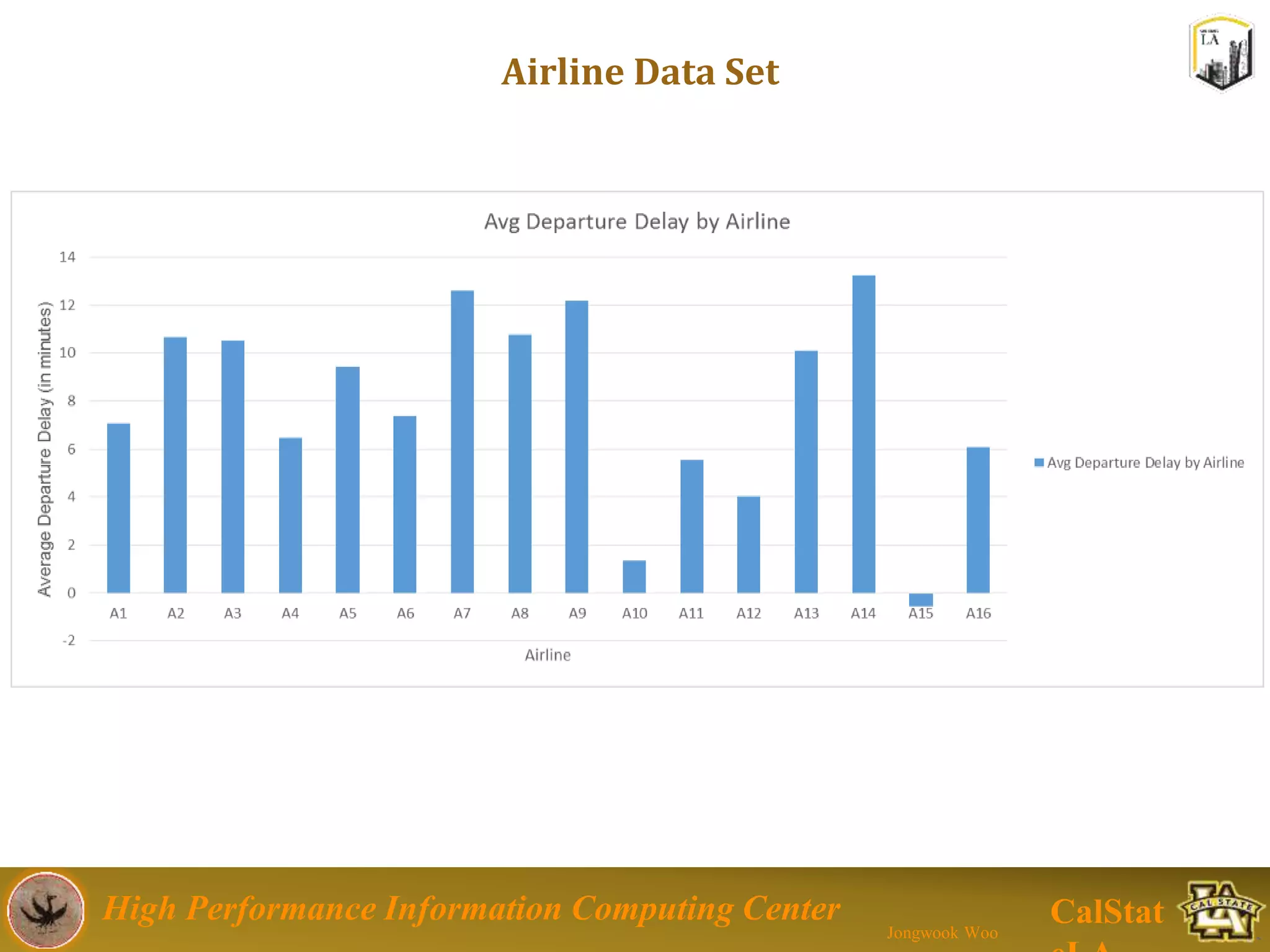
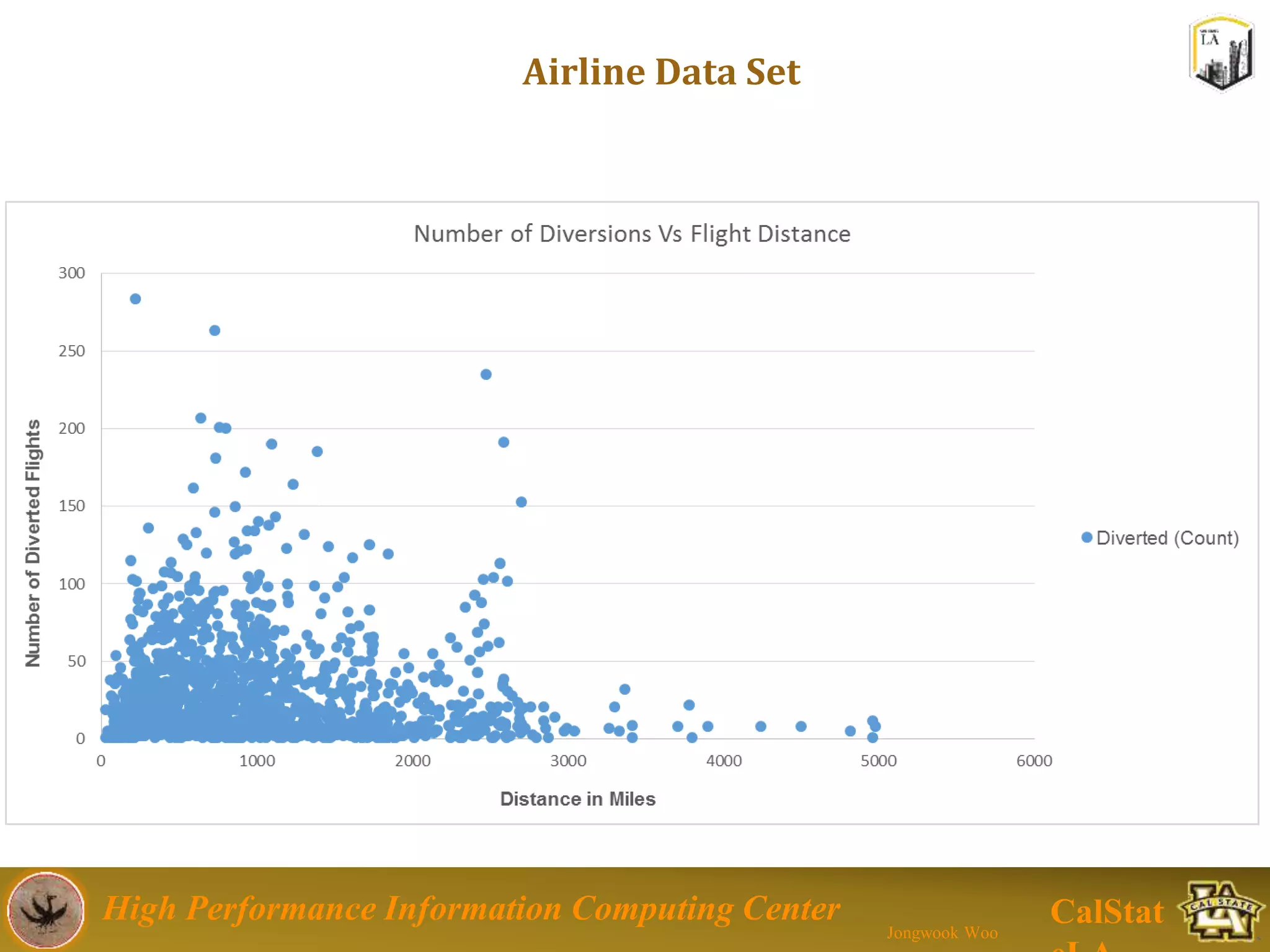
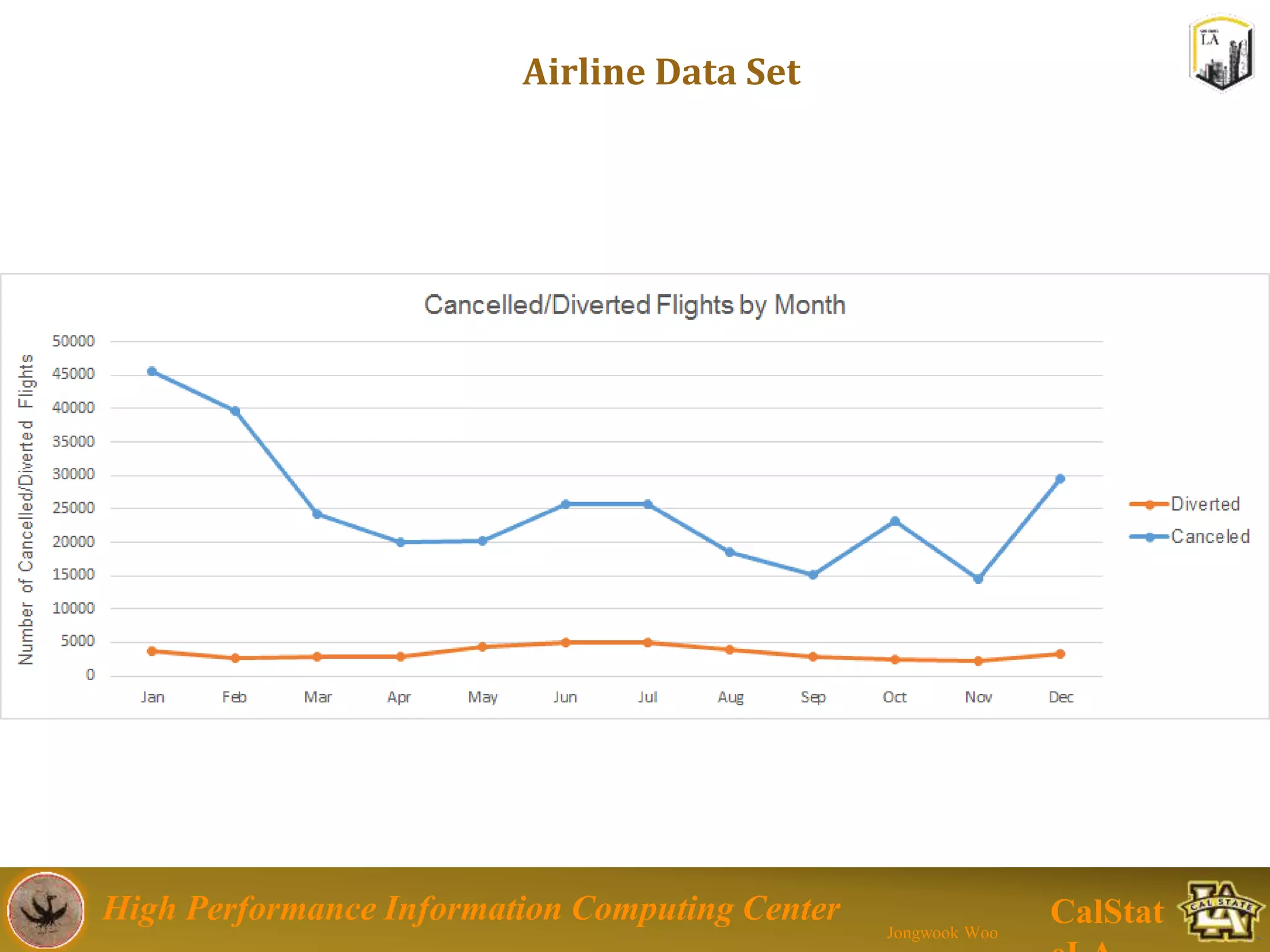
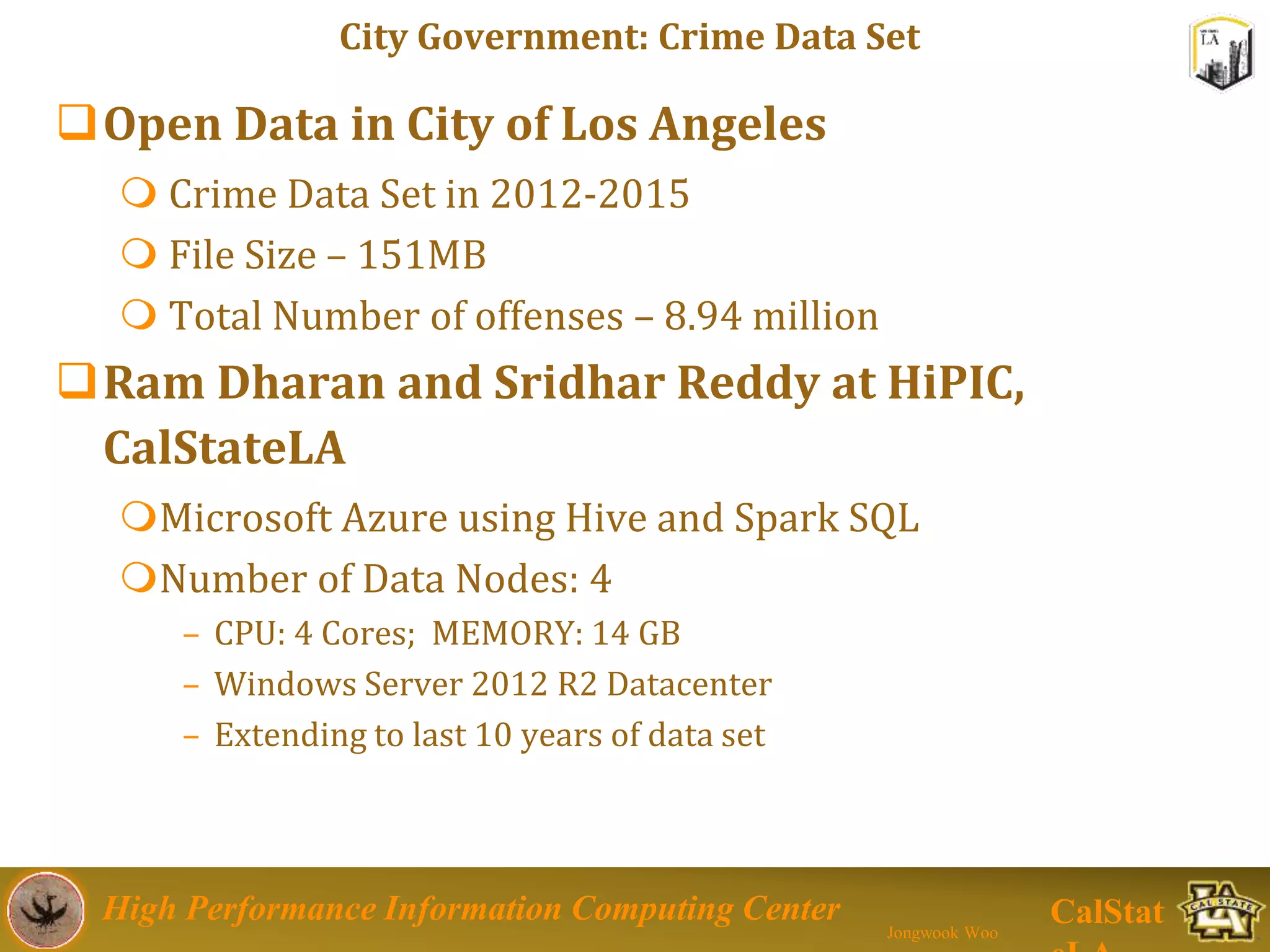
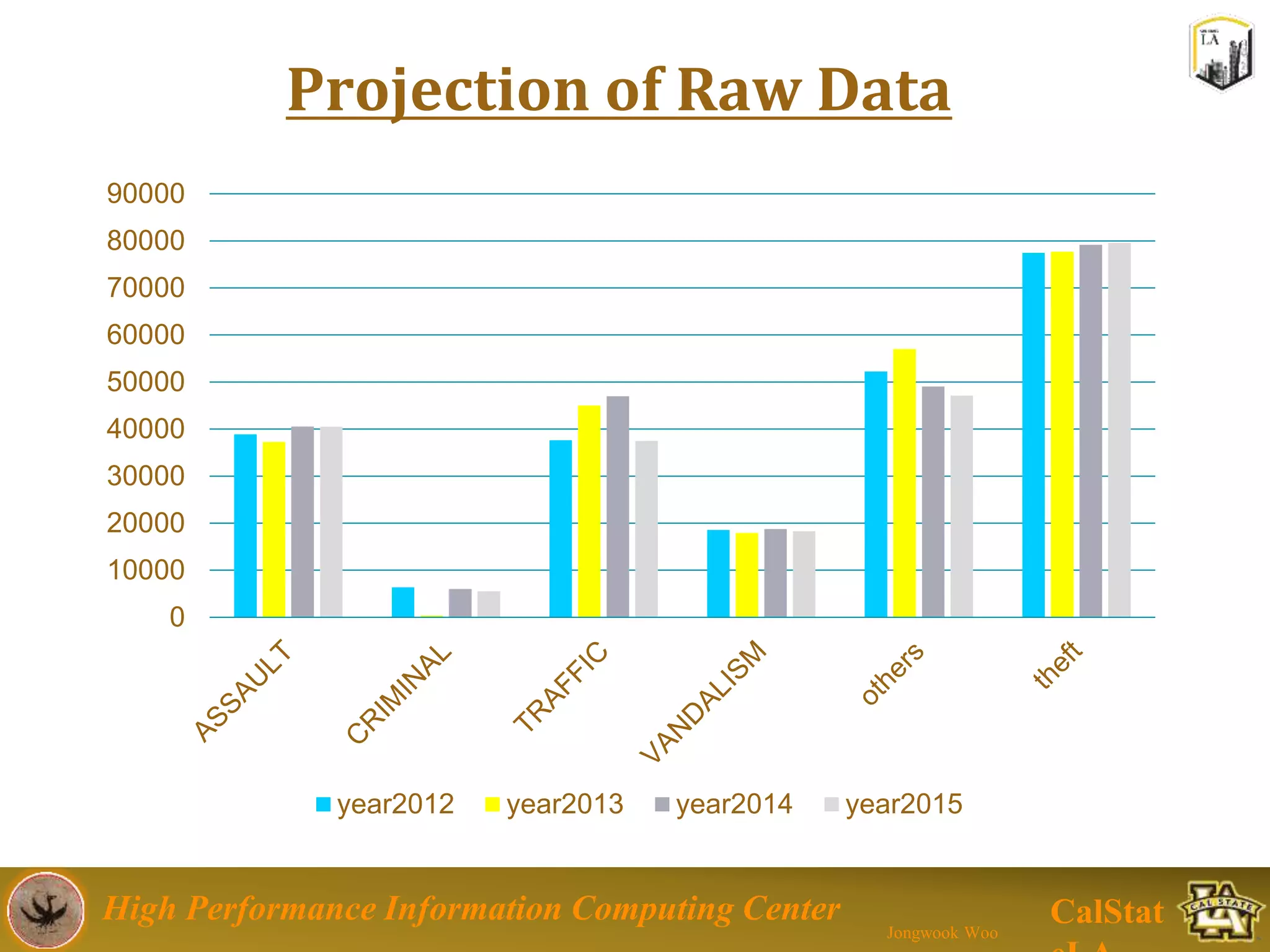
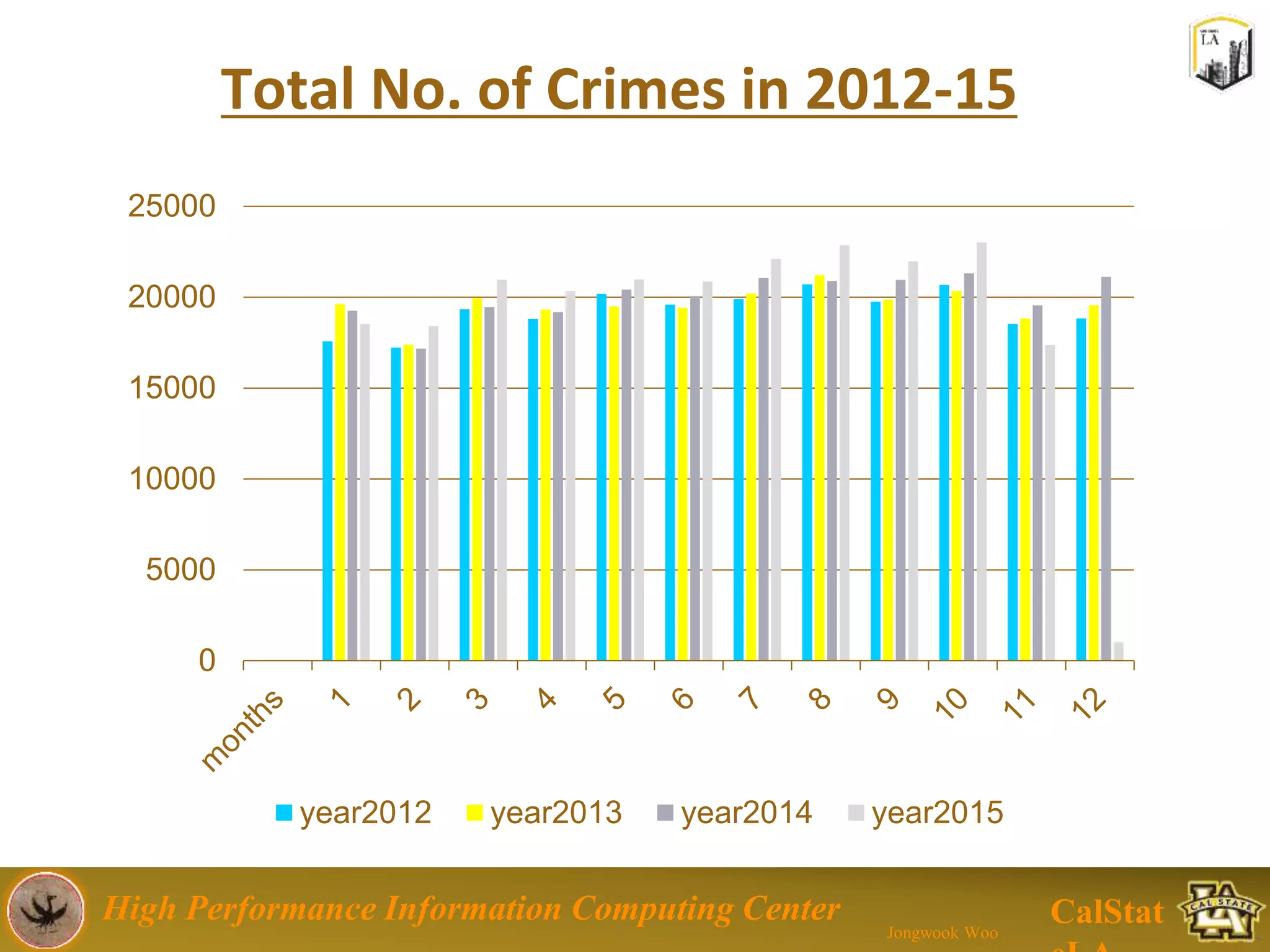
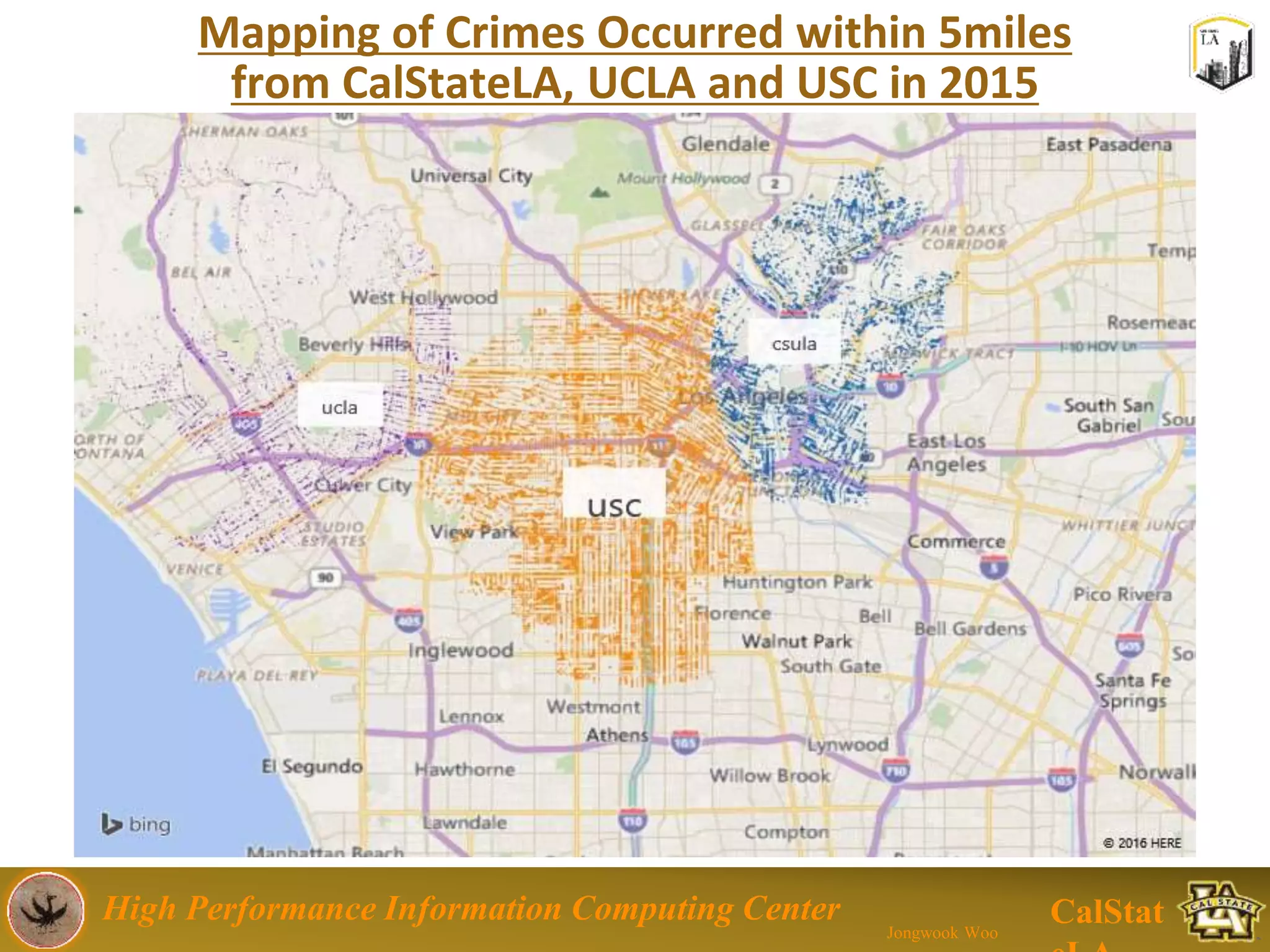
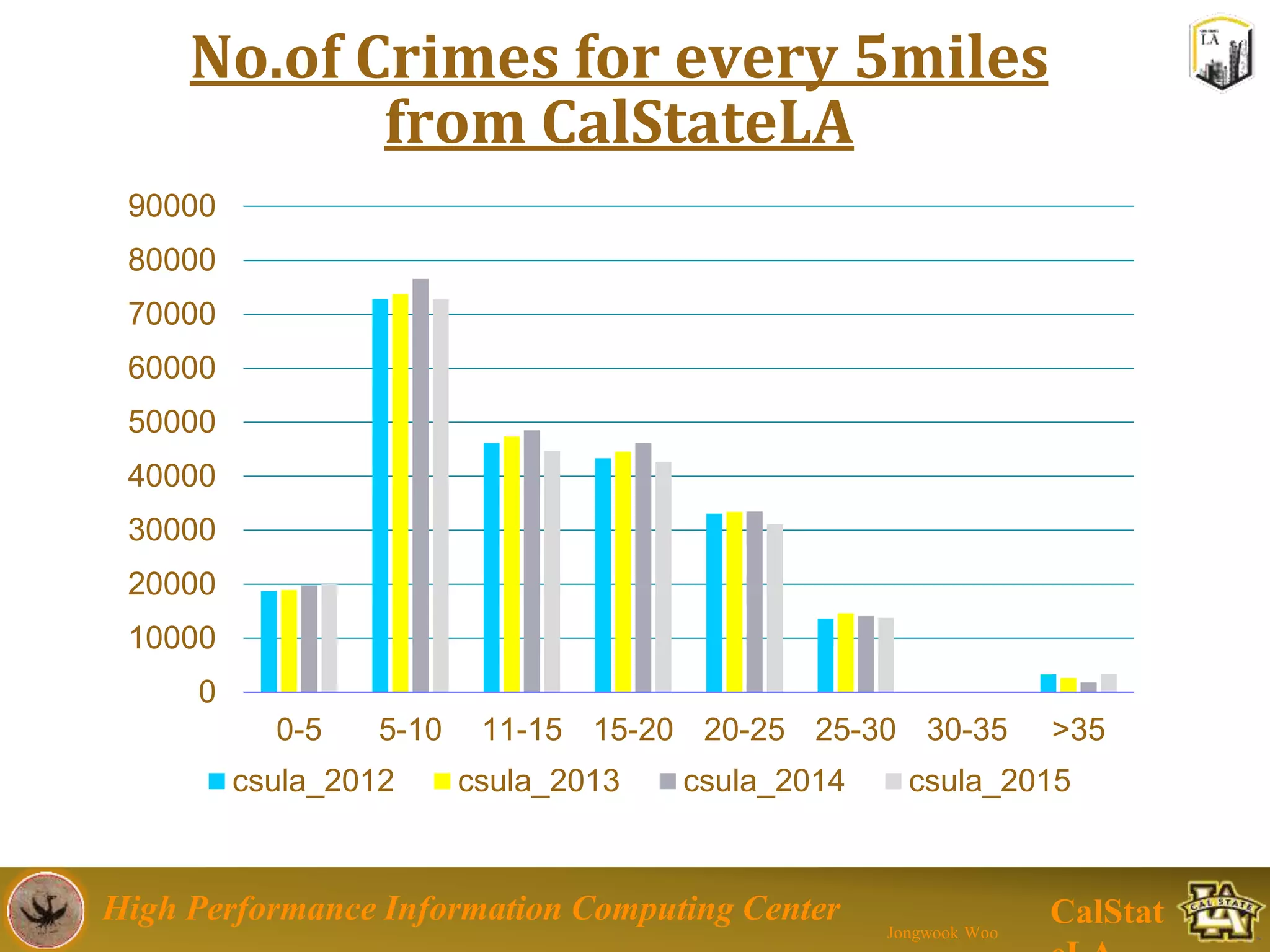
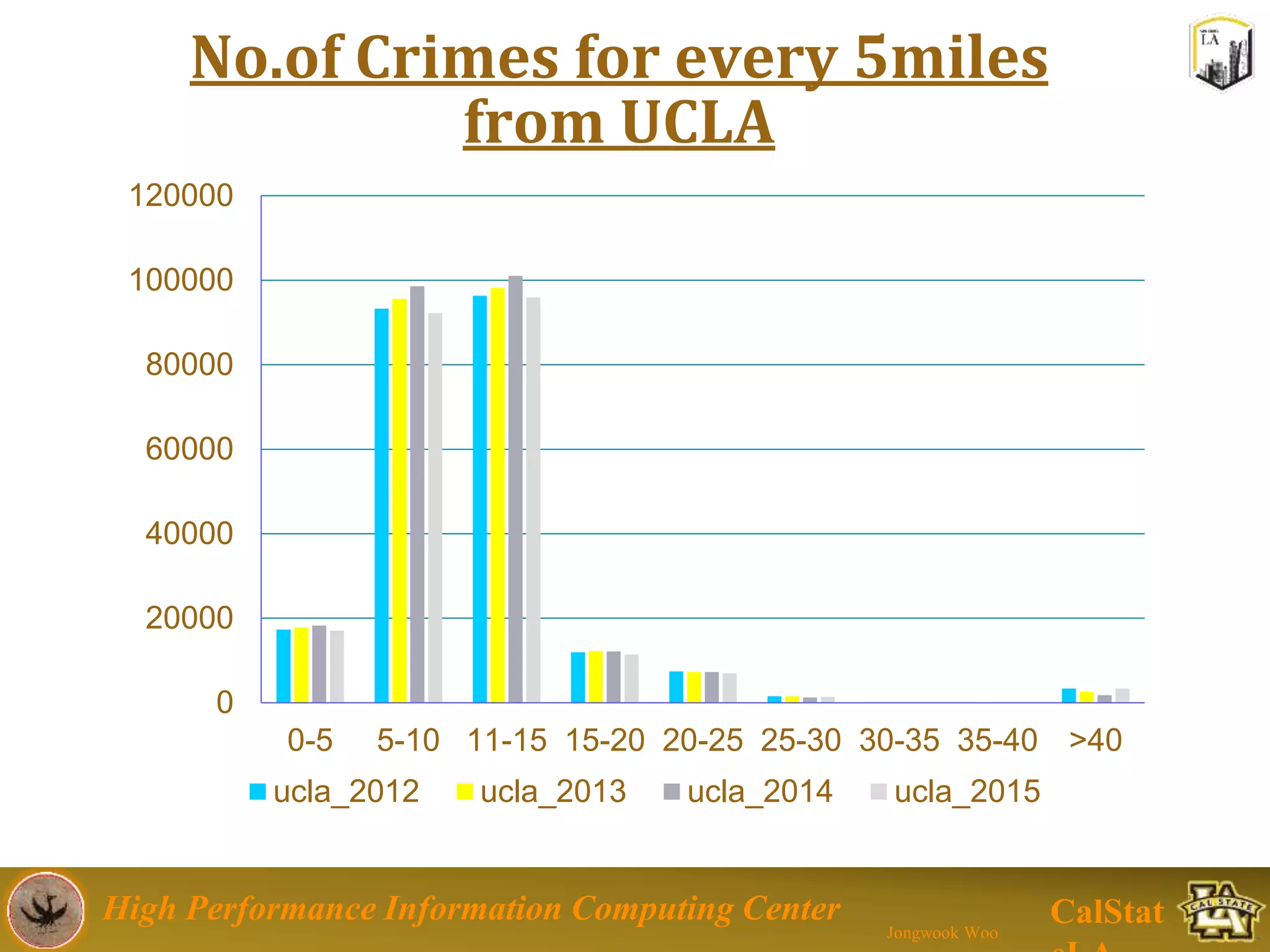
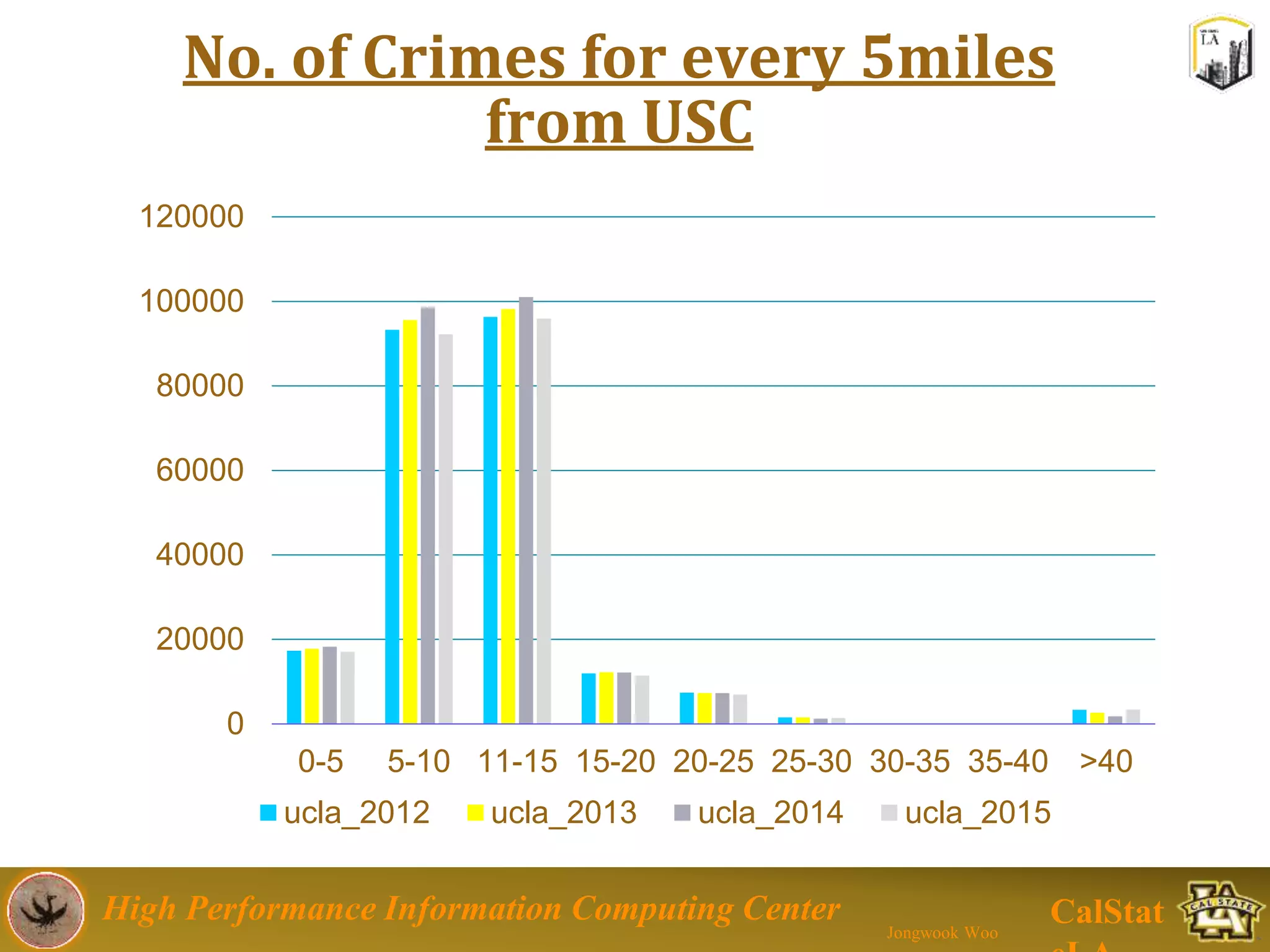
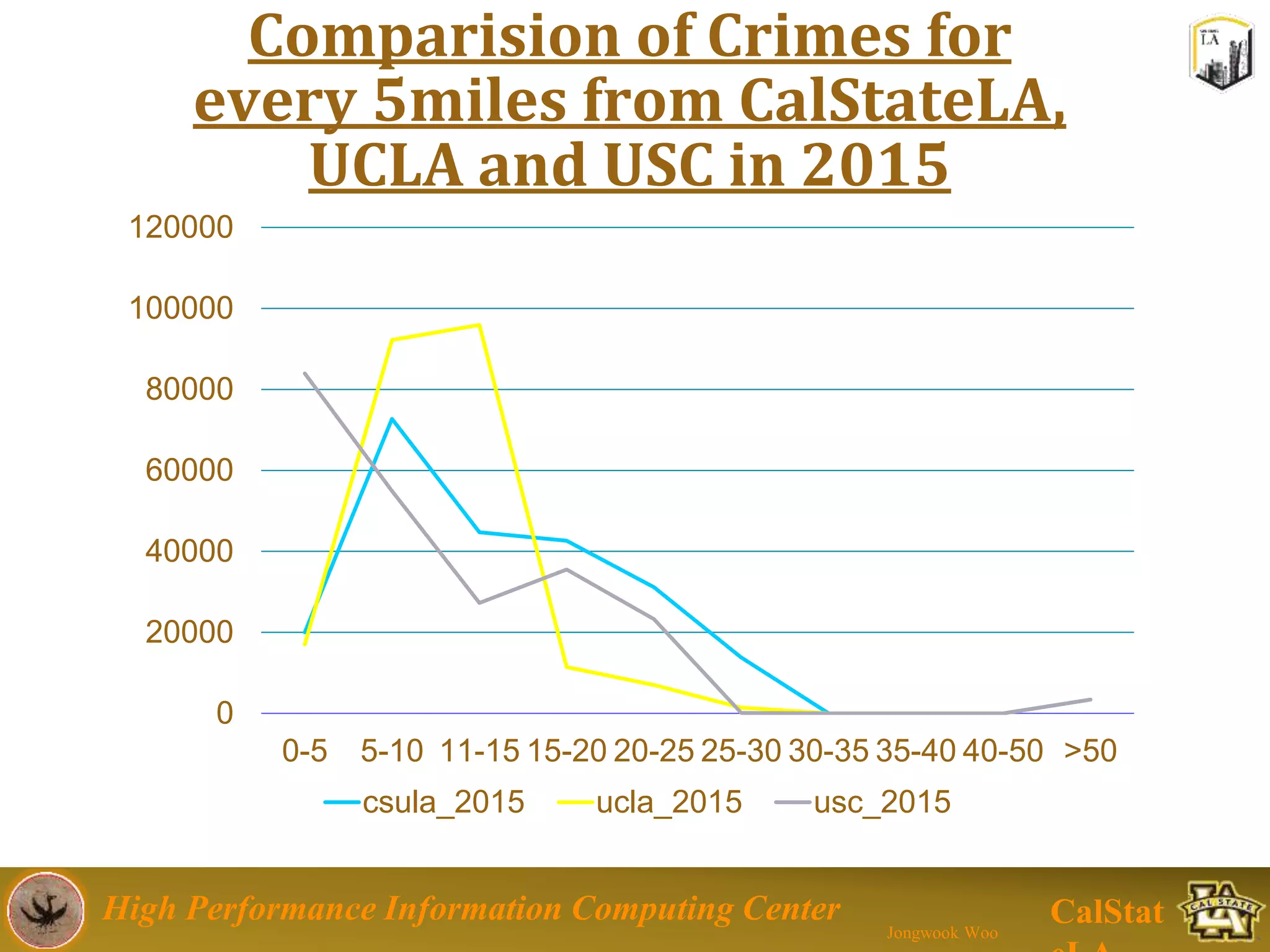
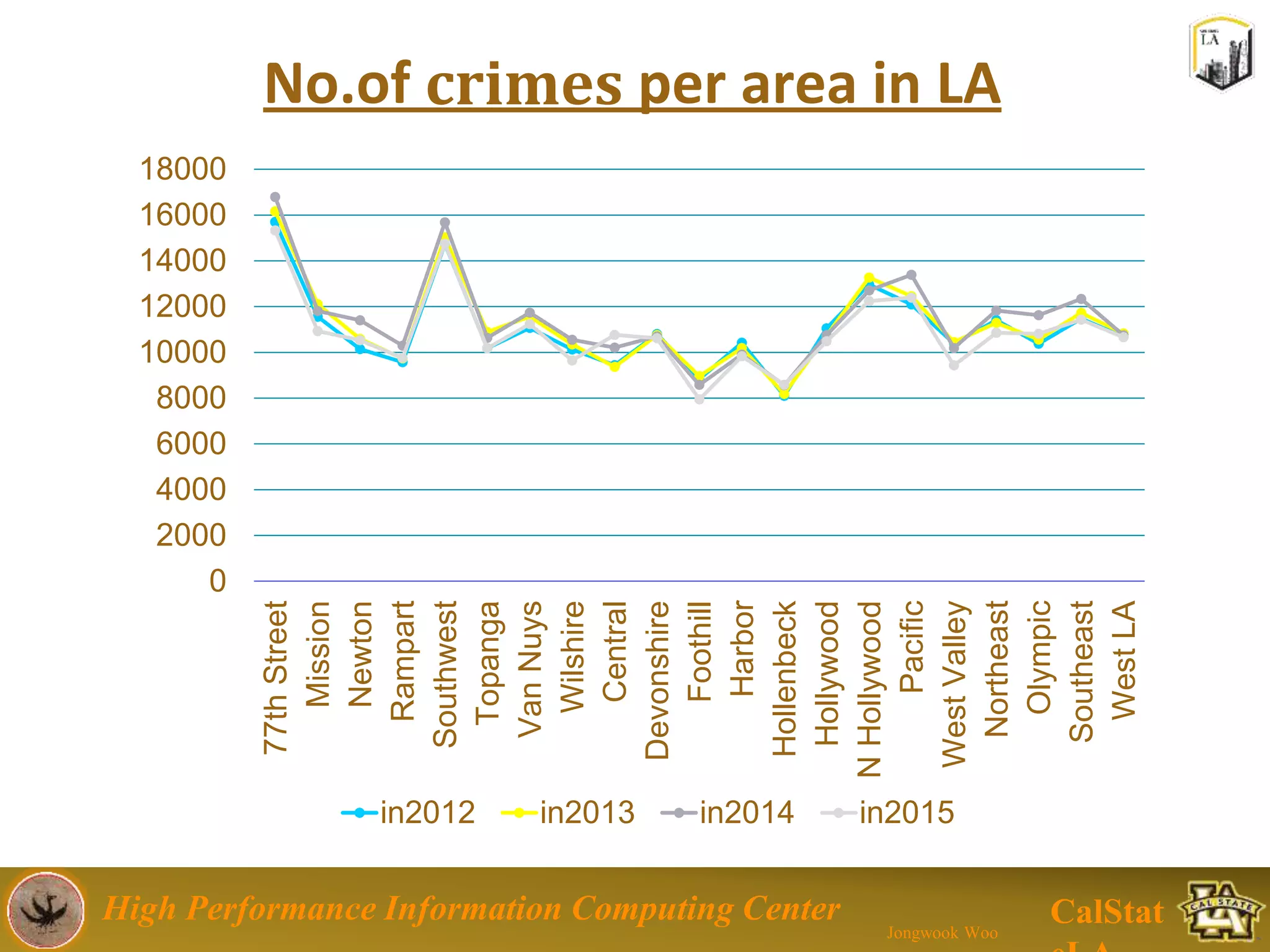
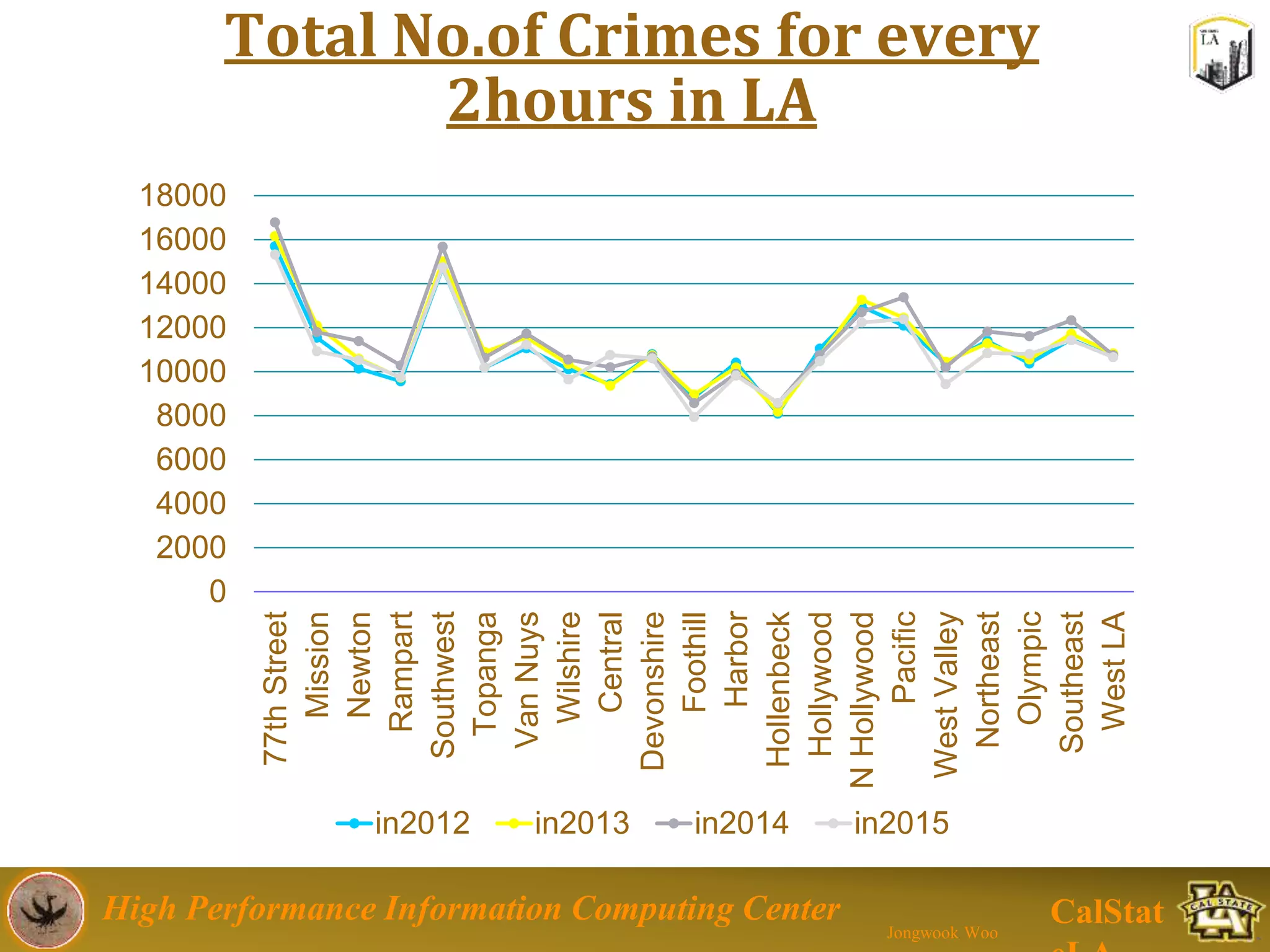
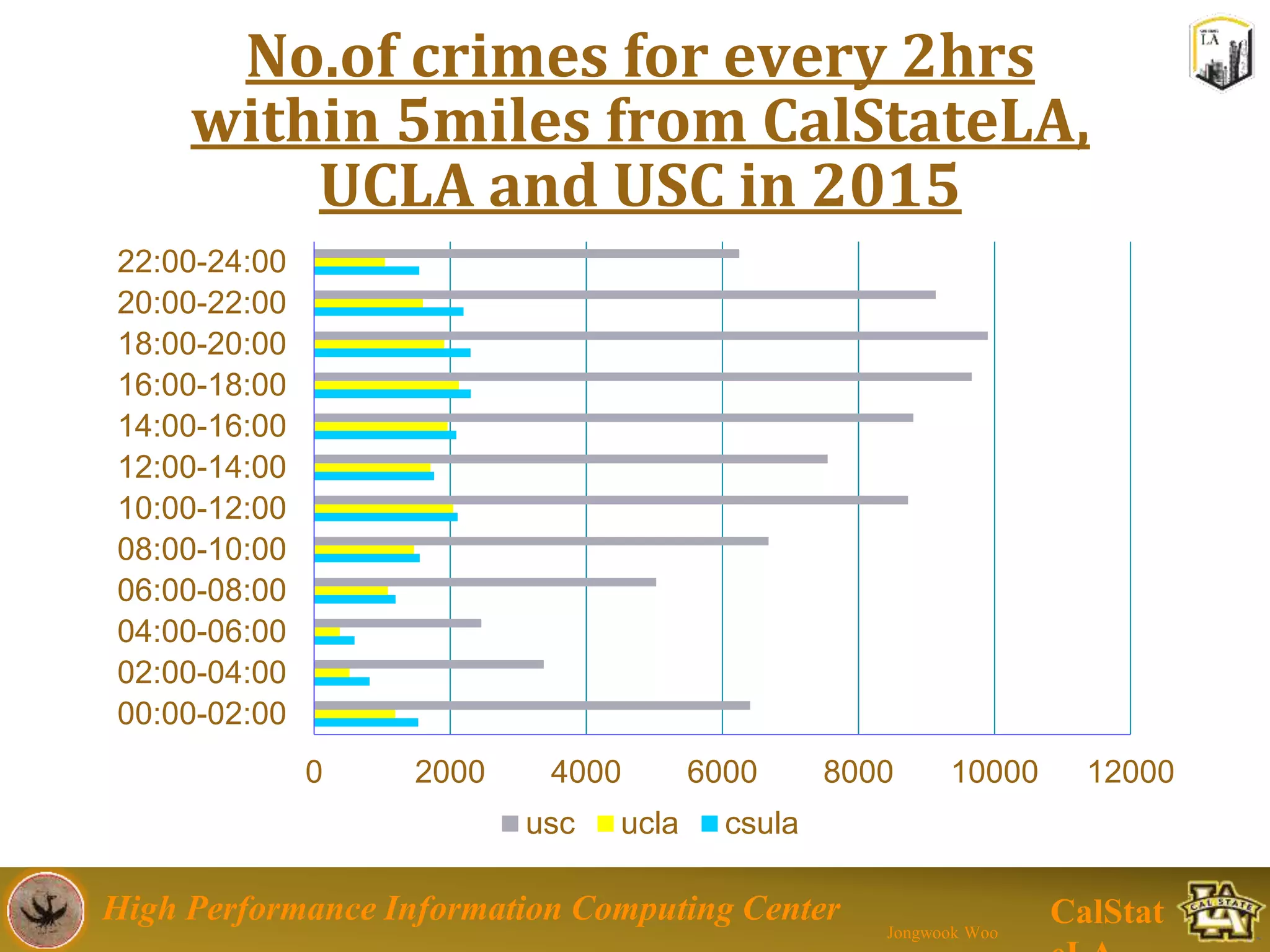
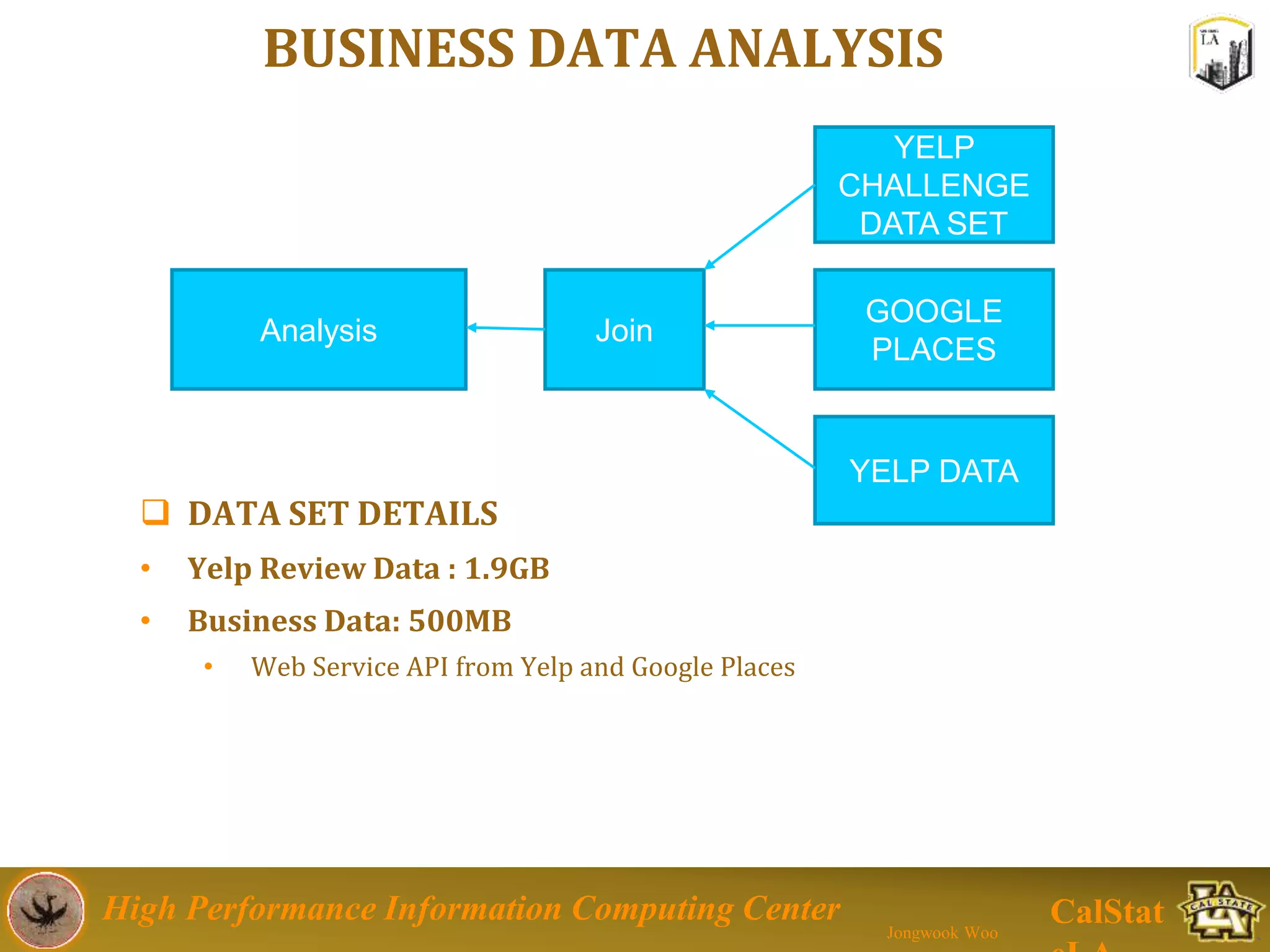
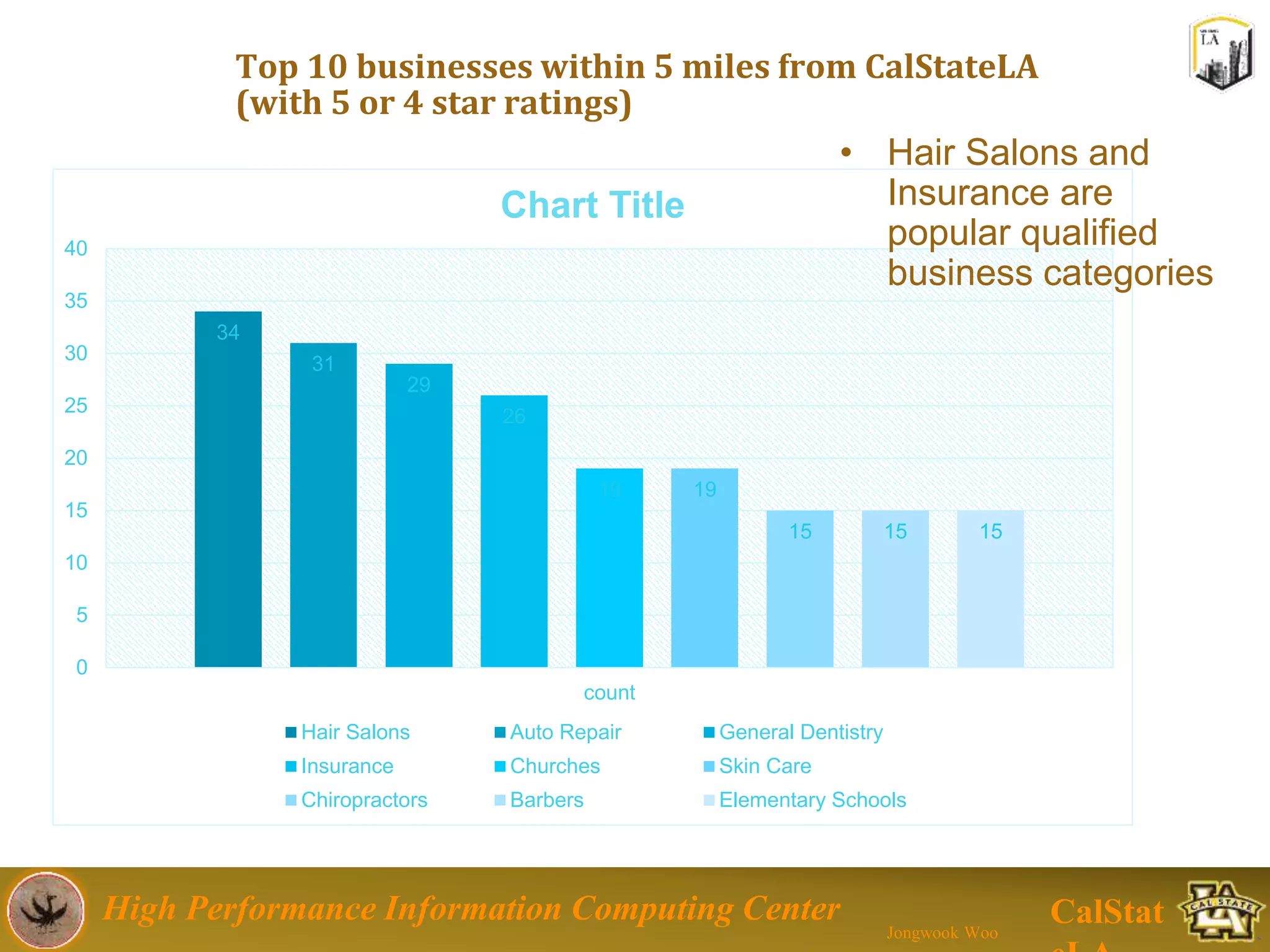
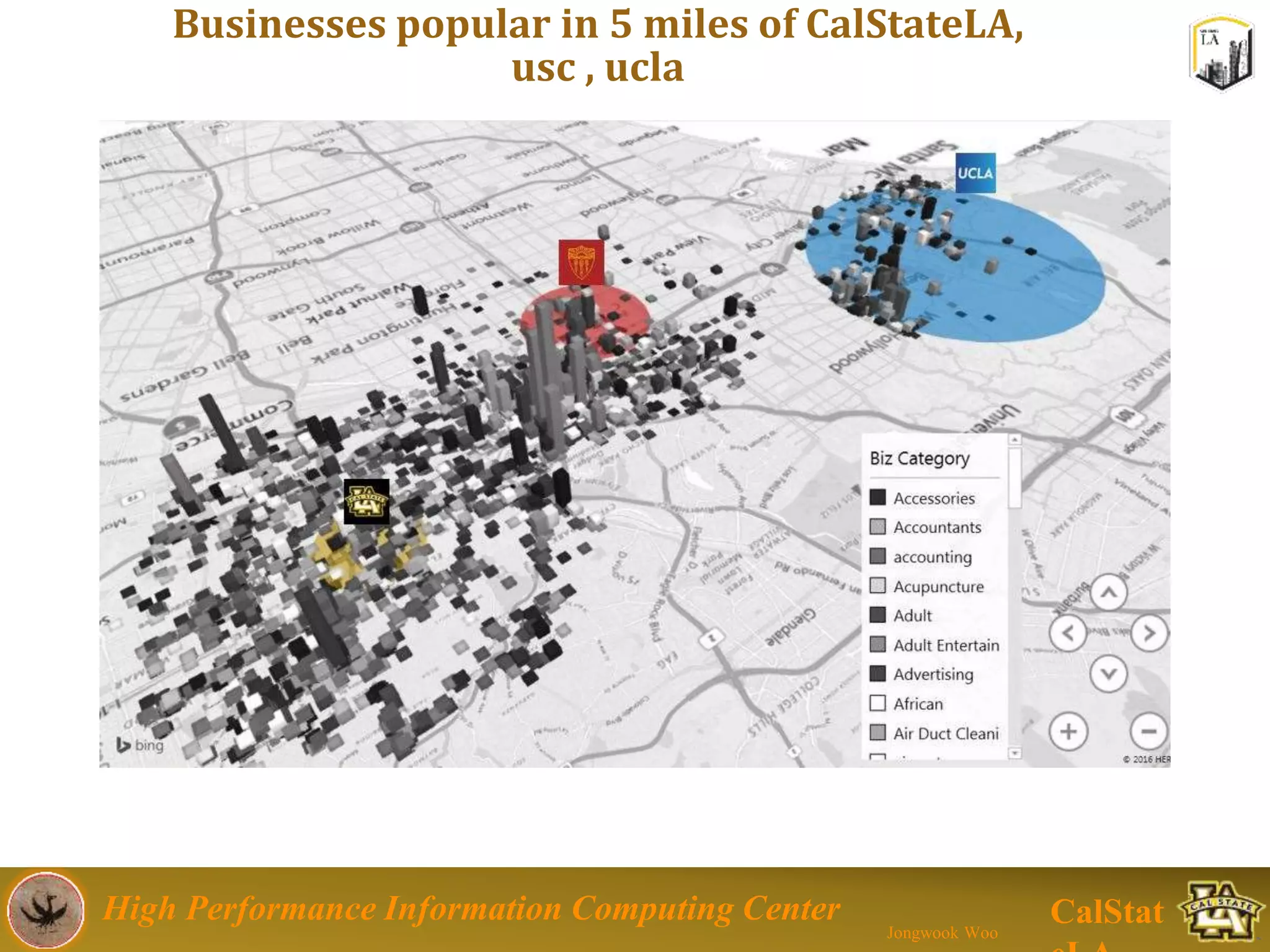
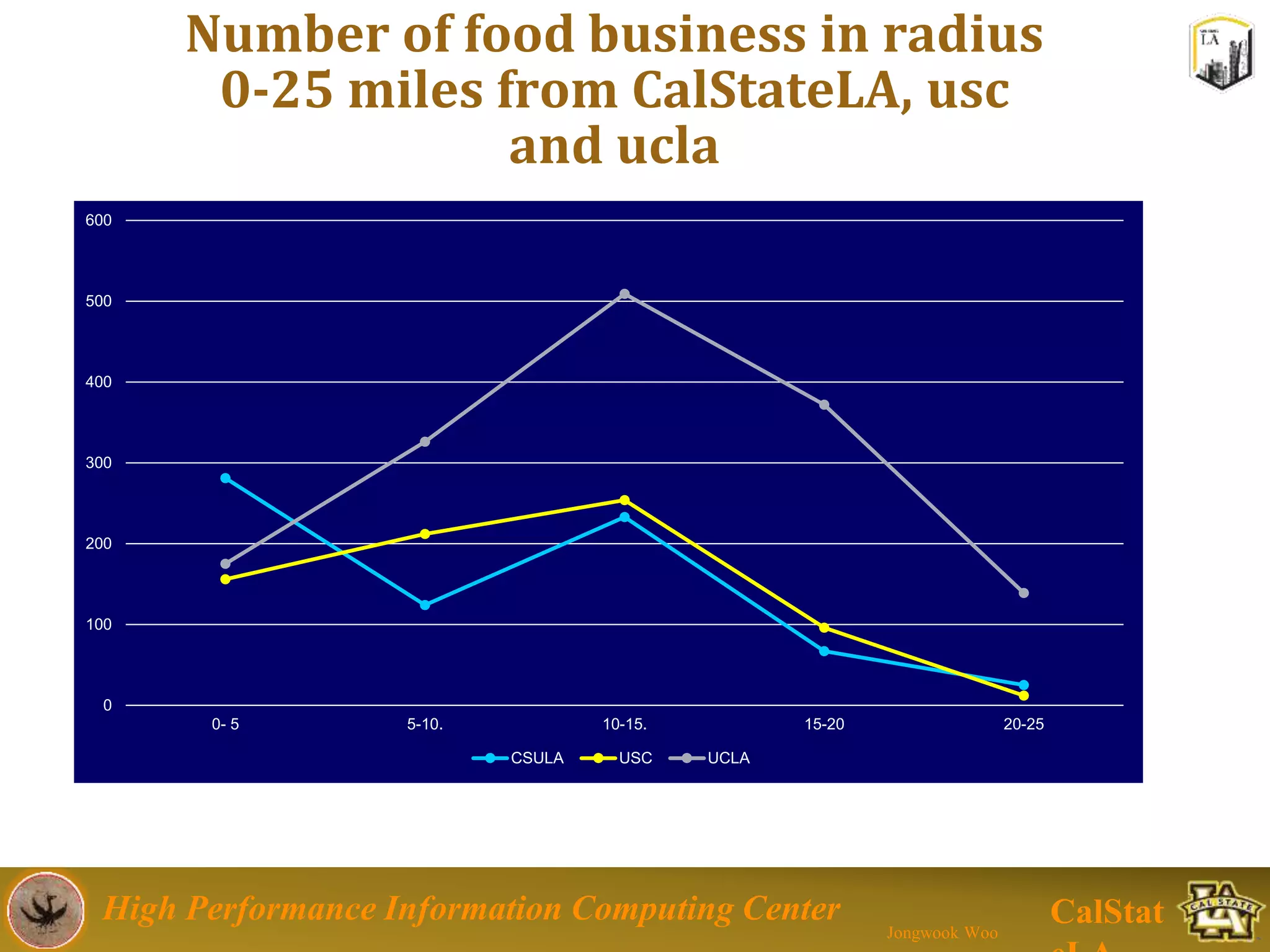
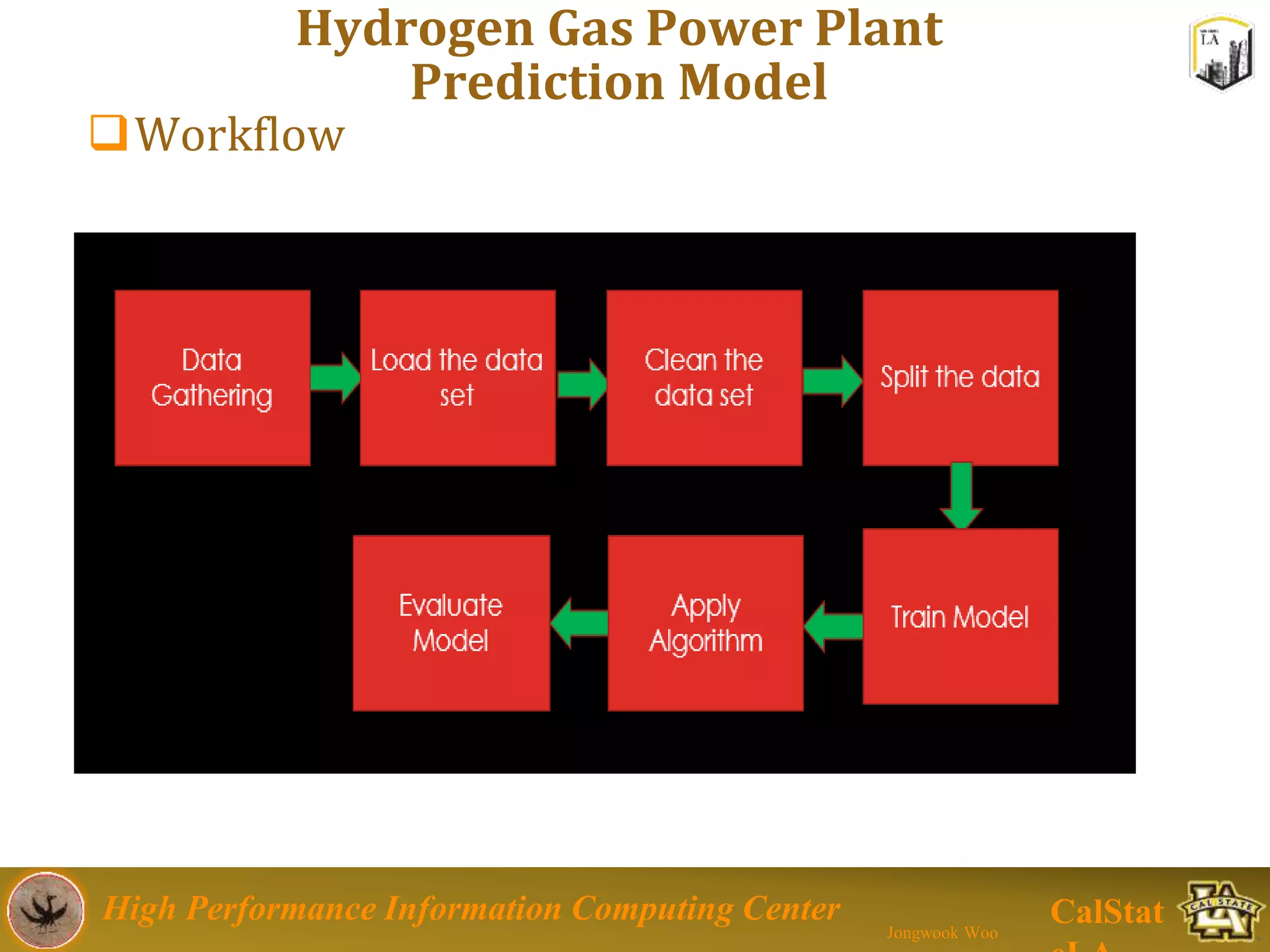
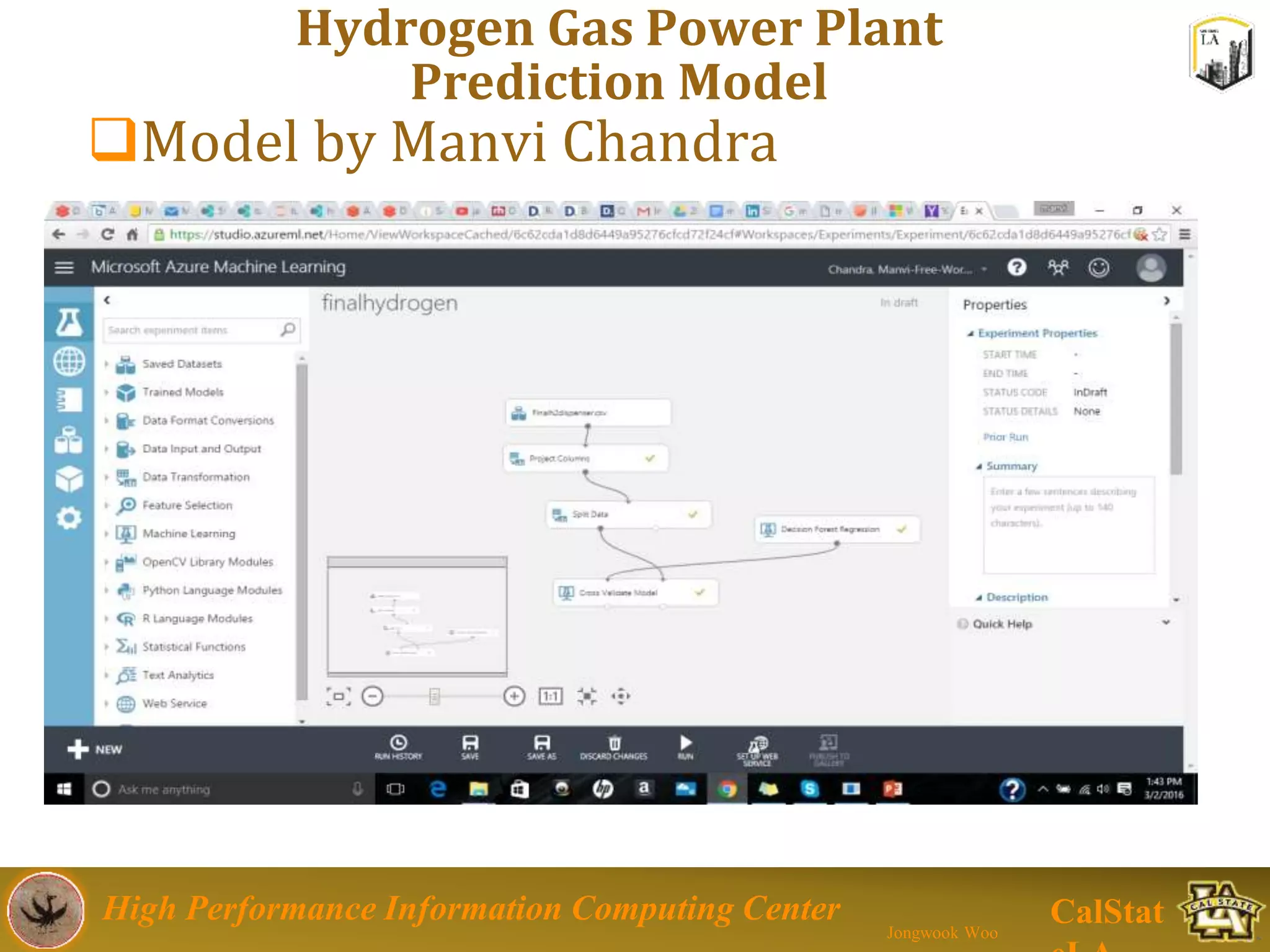
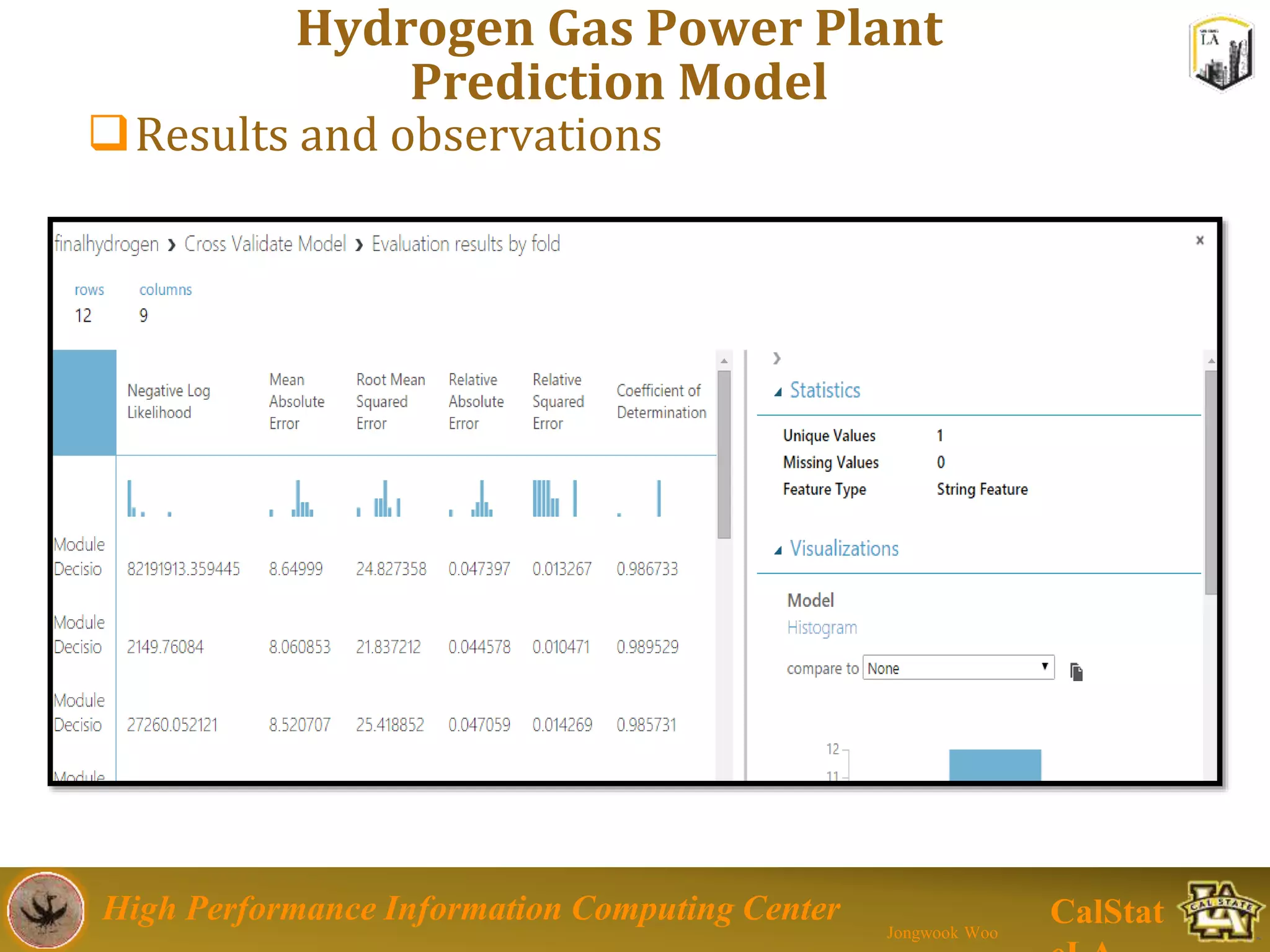
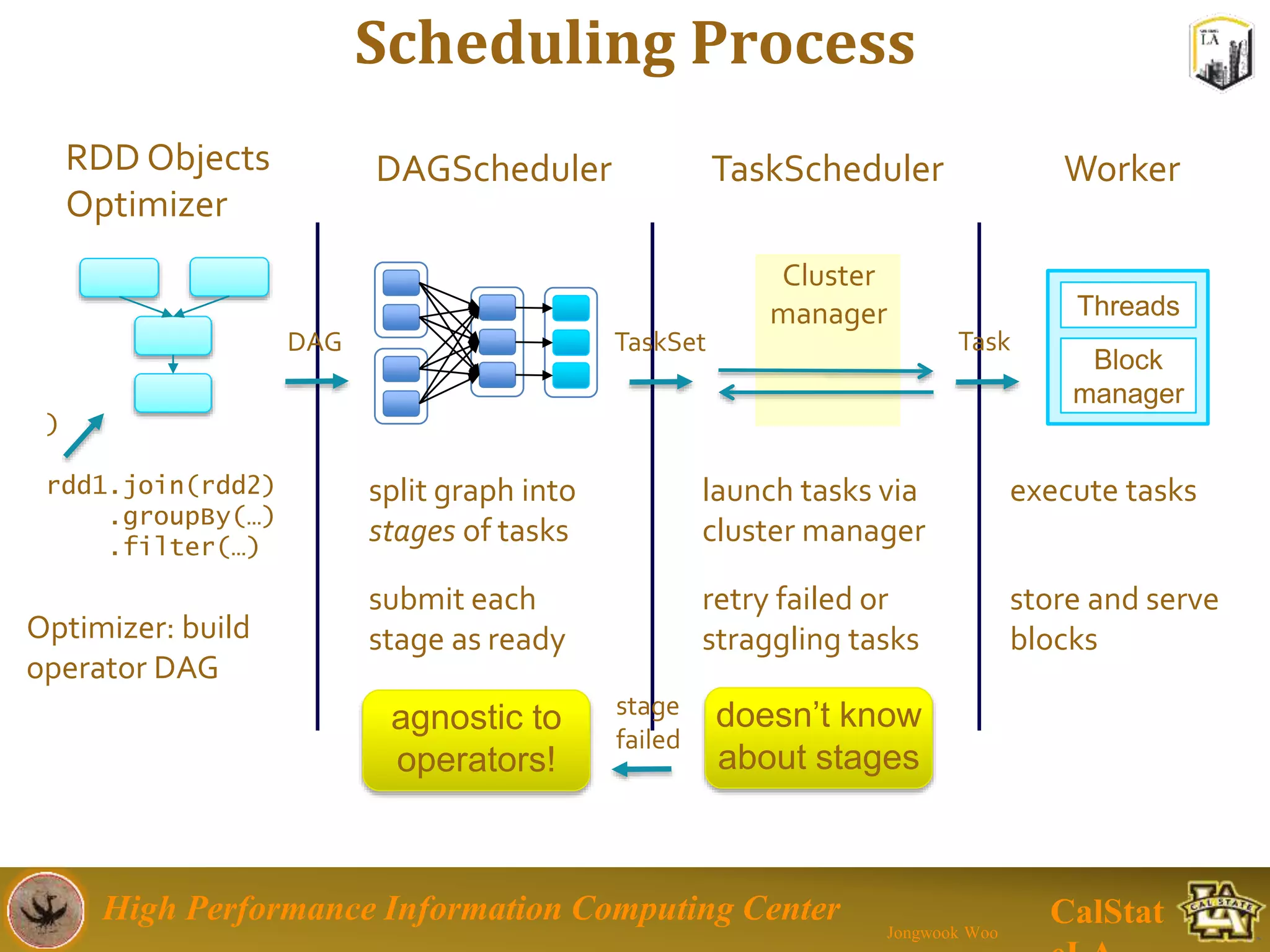
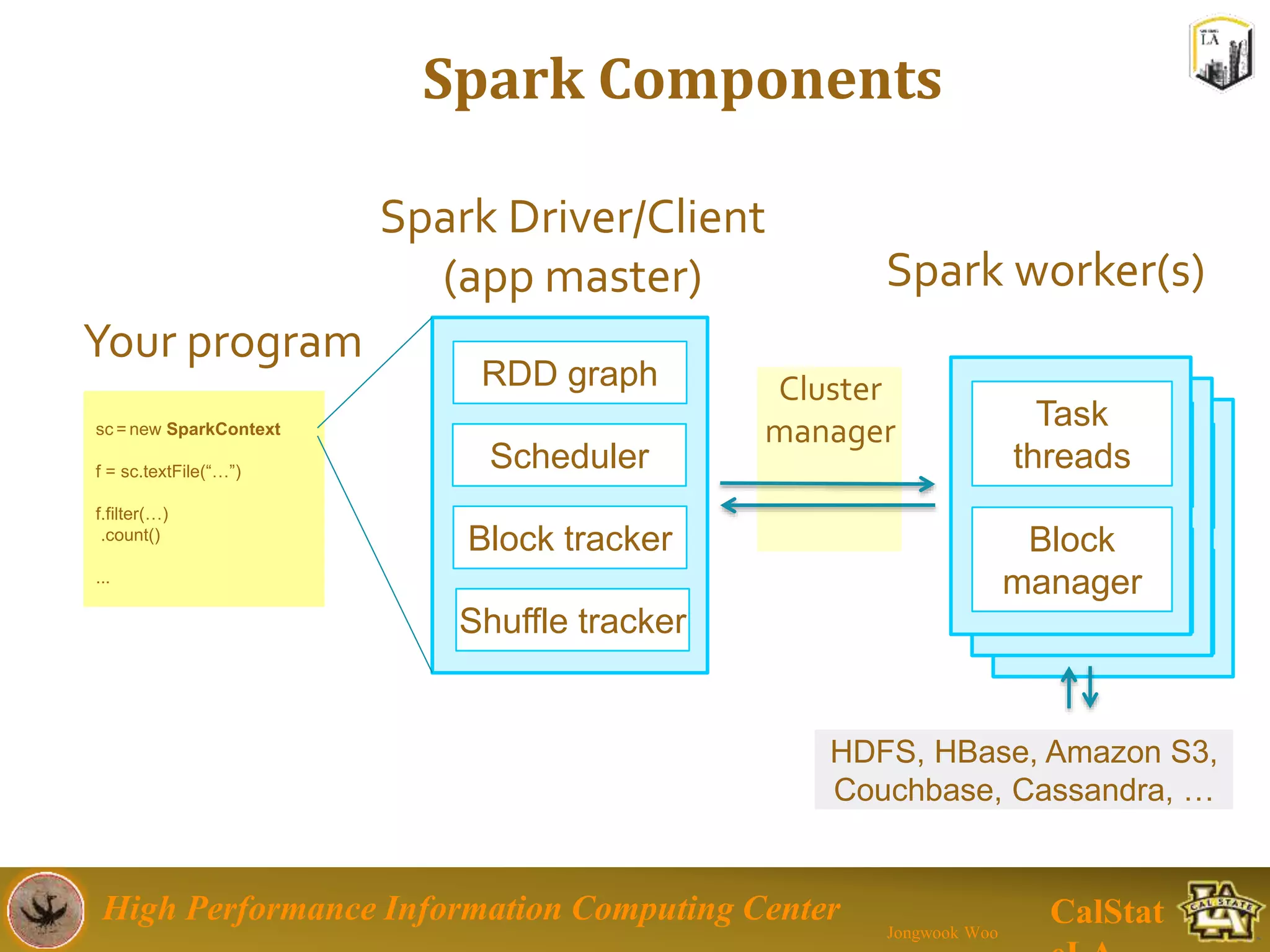
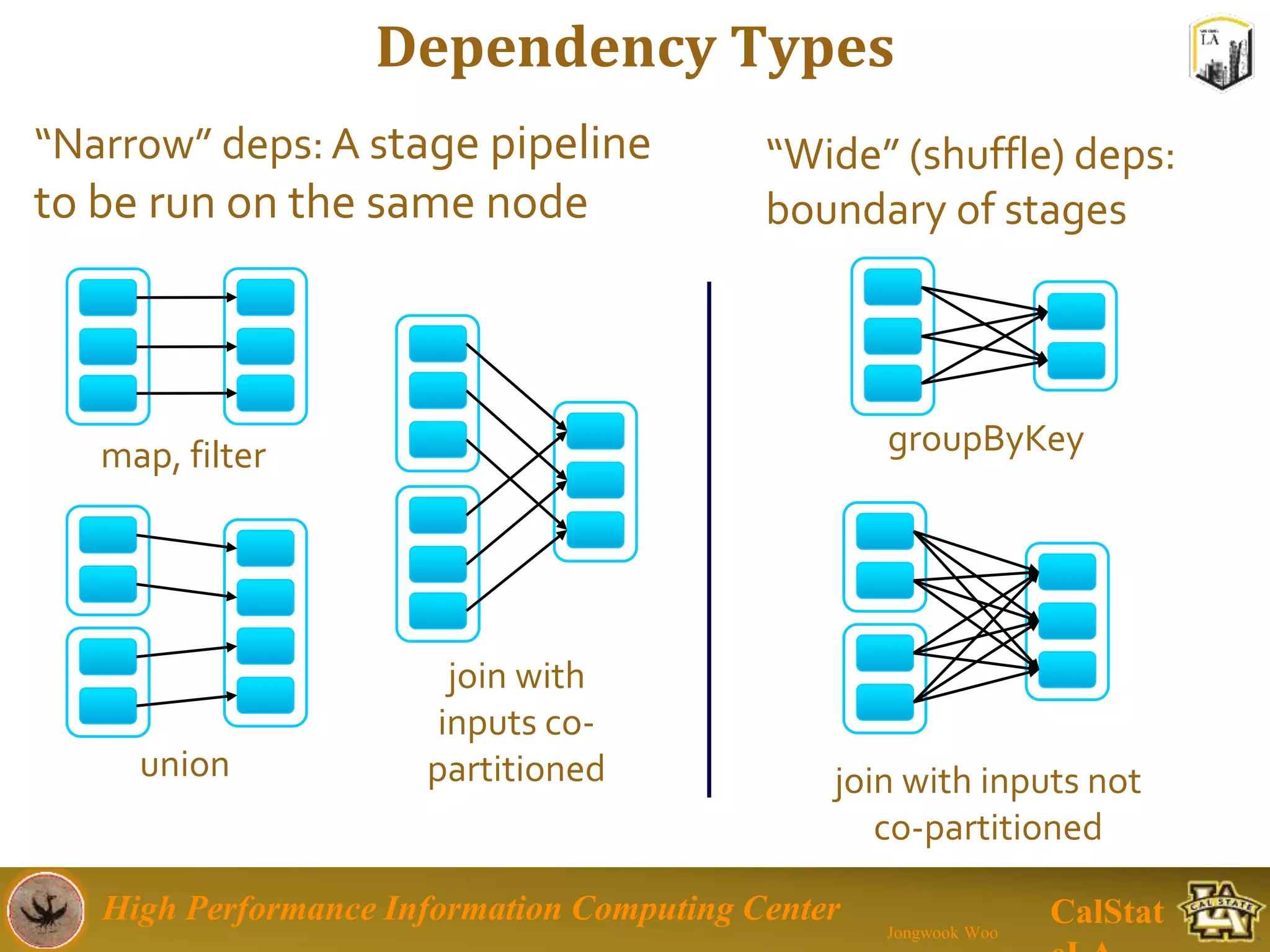
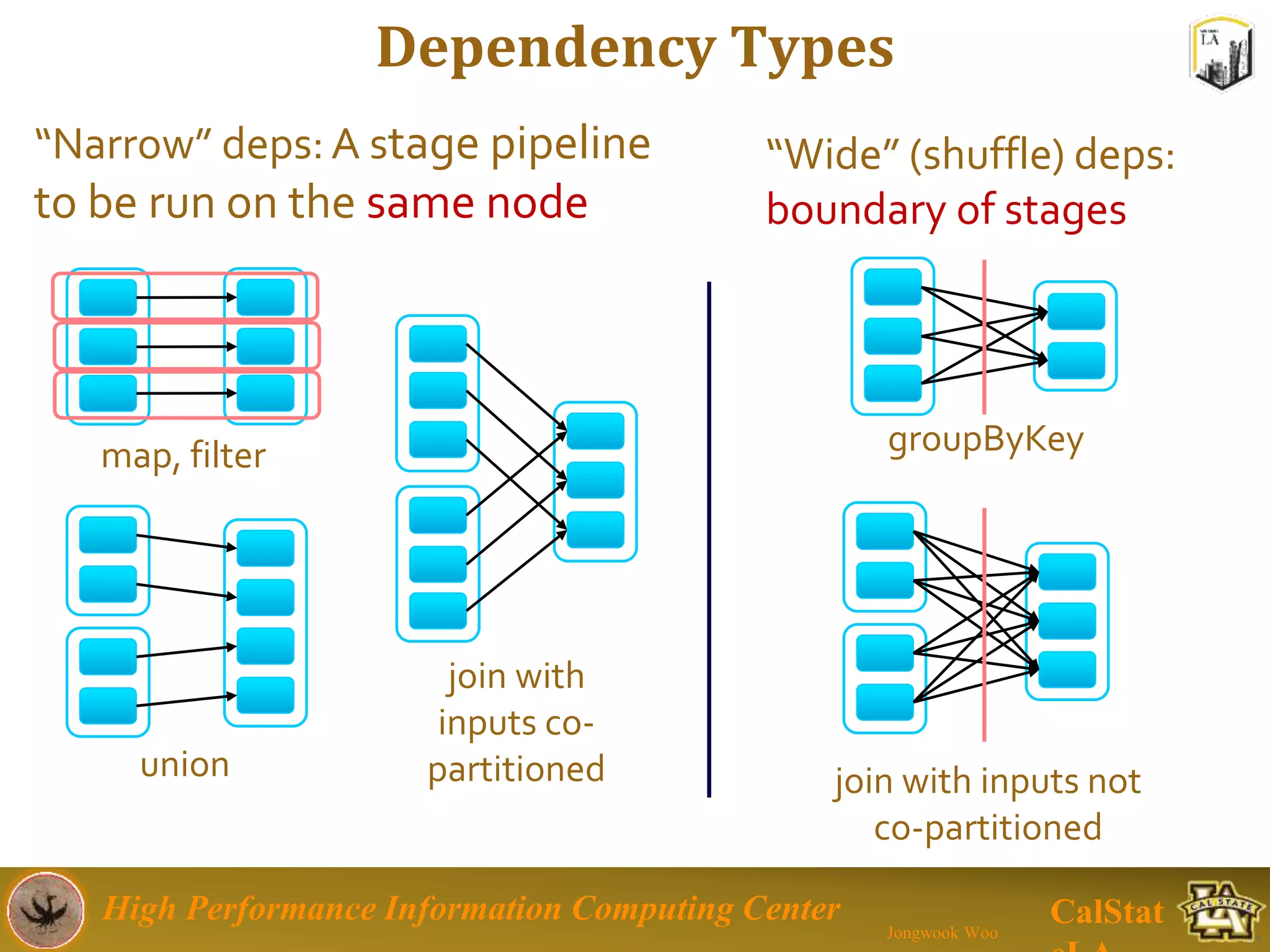
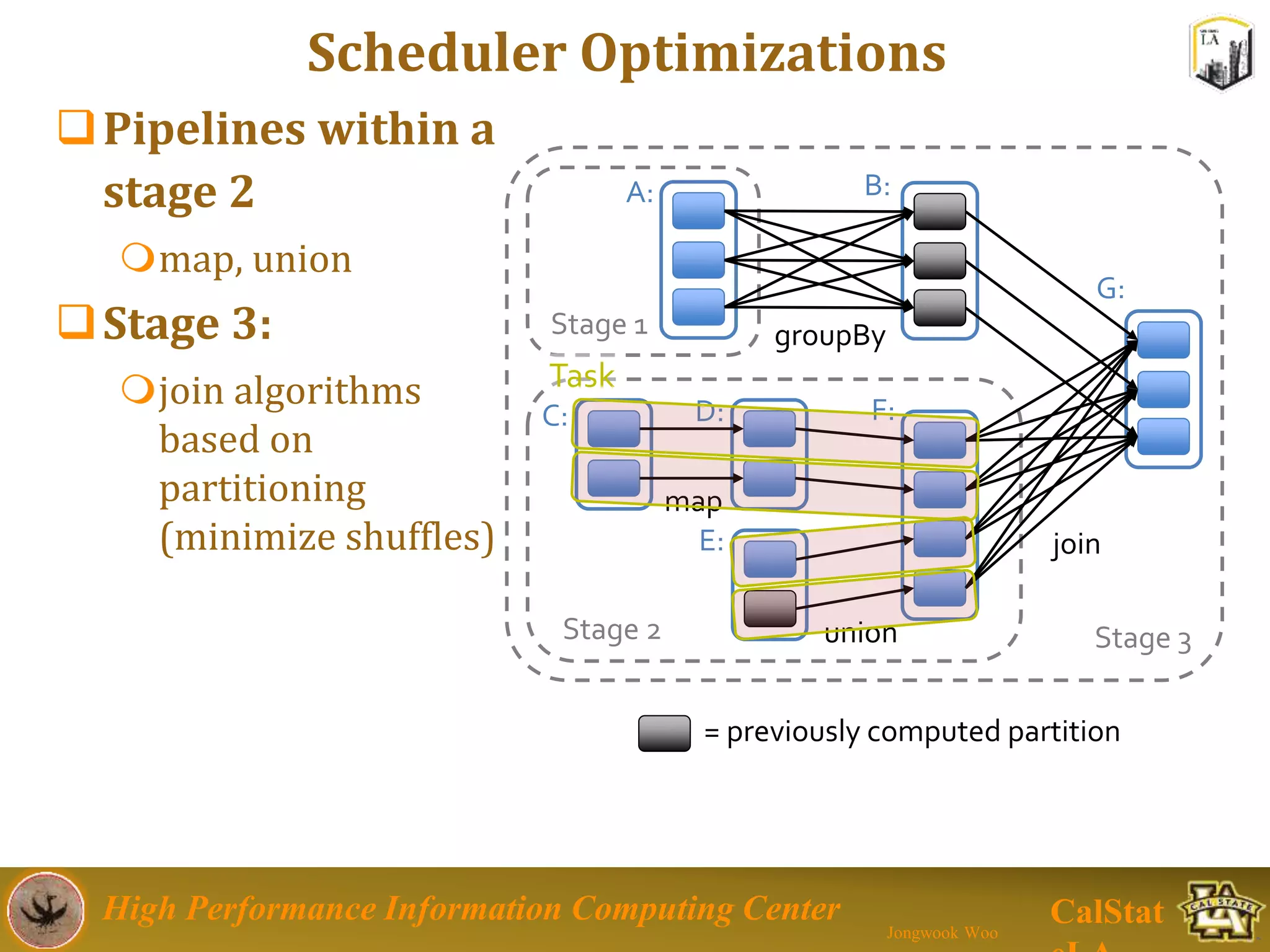
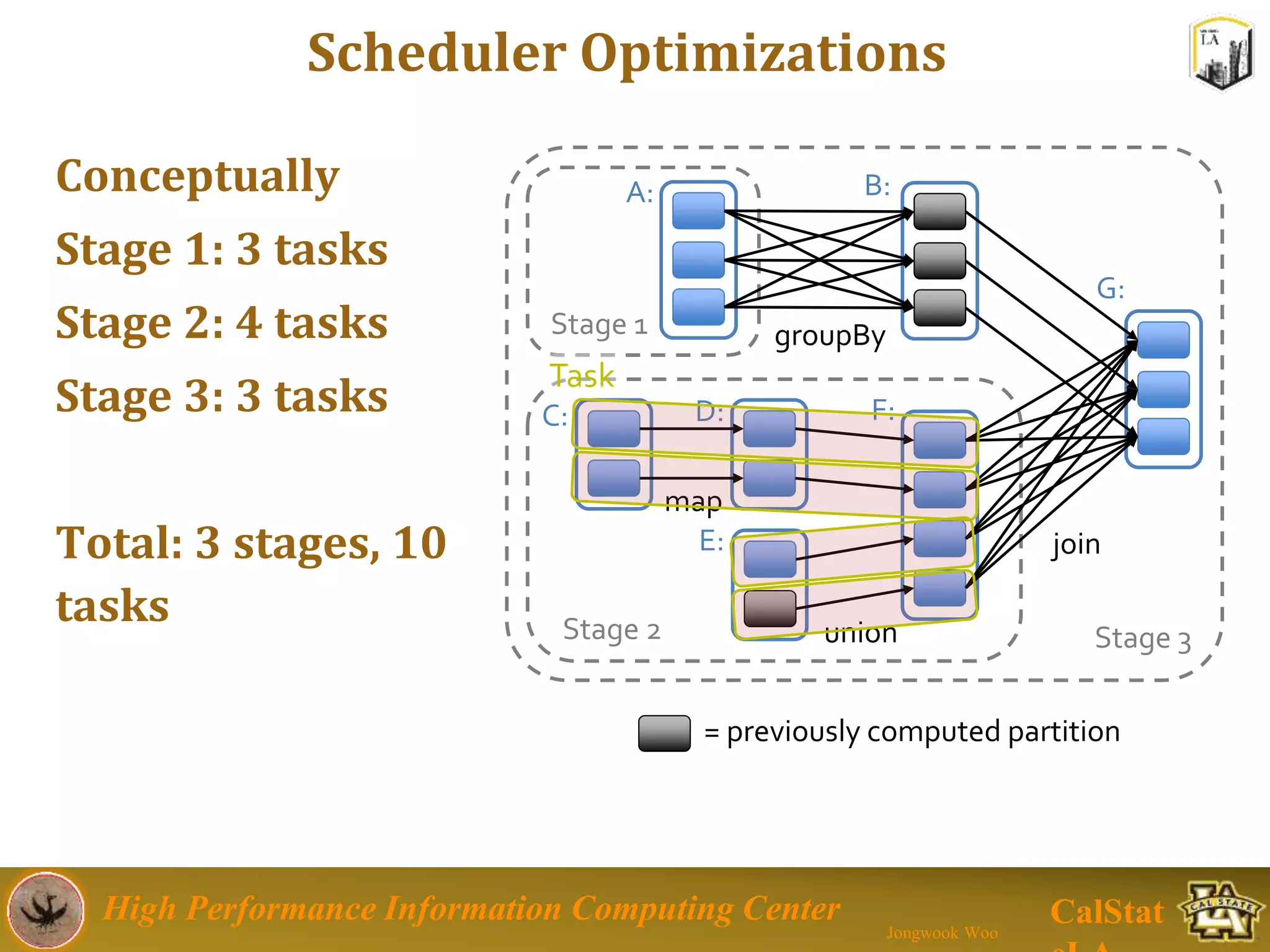
This document summarizes a presentation on big data trends and open data. It introduces the speaker, Jongwook Woo, and his experience in big data. It then covers topics including what is big data, Hadoop and Spark frameworks, using open data for analysis, and examples of analyzing Twitter data on AlphaGo and government airline and crime data sets.