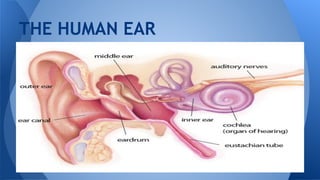
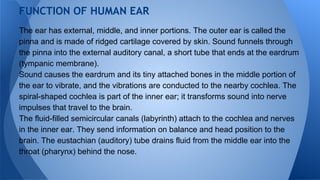
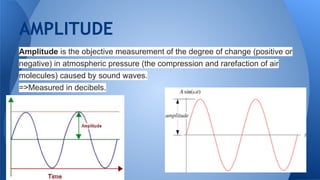
Sound is a form of energy produced by vibration that travels in longitudinal waves faster through solids than liquids or gases. The human ear has external, middle, and inner portions that work together to detect sound. Sound causes the eardrum and tiny bones in the middle ear to vibrate, transmitting the vibrations to the cochlea of the inner ear which transforms them into nerve impulses sent to the brain where they are interpreted. The brain also receives information from the semicircular canals of the inner ear on balance and head position.