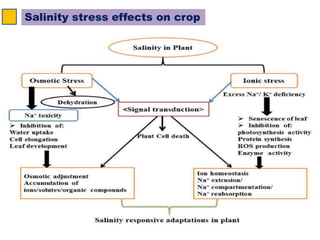
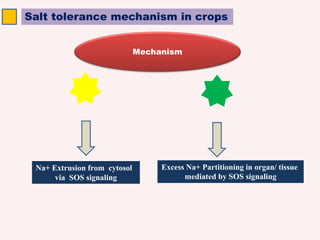
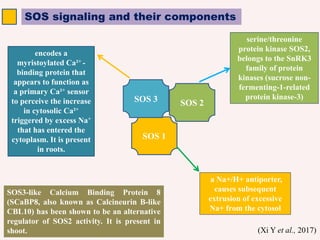
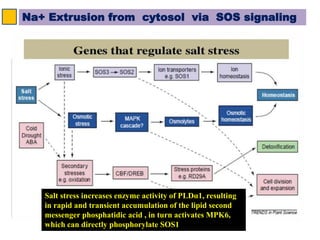
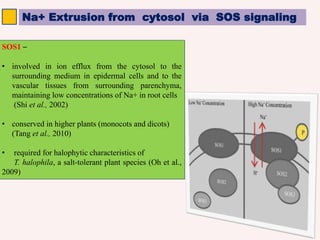
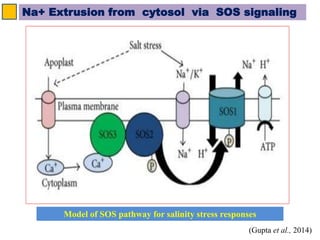
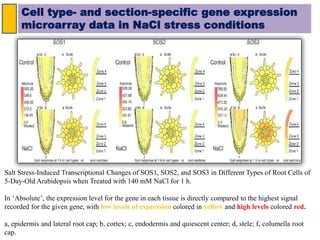
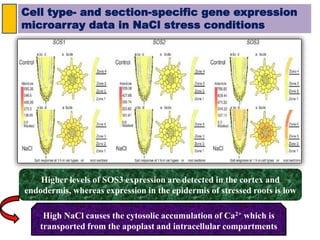
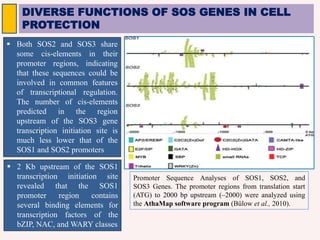
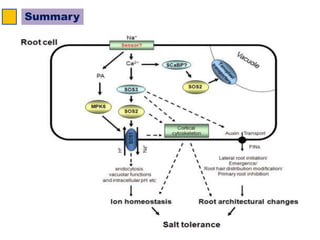
The SOS pathway plays an important role in plant salinity tolerance. It involves the SOS1, SOS2, and SOS3 genes which work together to extrude sodium ions from plant cells. SOS1 encodes a sodium/hydrogen antiporter, SOS2 encodes a protein kinase, and SOS3 encodes a calcium sensor protein. The SOS pathway helps maintain low sodium ion levels in the cytosol and partitions excess sodium to tissues and organs to reduce damage from salinity stress. Recent research also indicates the SOS pathway is involved in cytoskeleton dynamics, root development, and crosstalk with other stress response pathways to help plants withstand salinity stress.