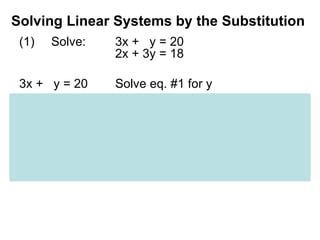
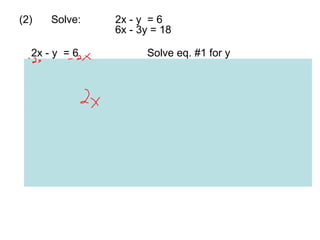
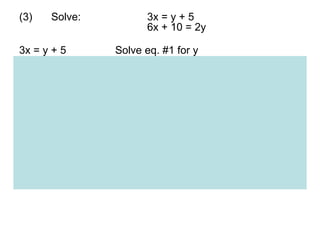
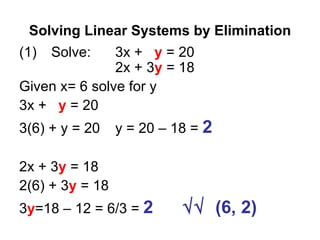
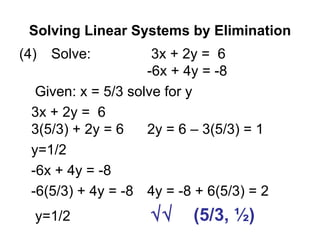
The document discusses solving systems of linear equations using substitution and elimination methods. It provides 4 examples of solving systems of 2 equations with 2 unknowns. The substitution method involves solving one equation for one variable in terms of the other and substituting it into the second equation. The elimination method involves multiplying equations by constants and adding/subtracting them to eliminate one variable. Both methods are shown to yield the solution point that satisfies both equations.