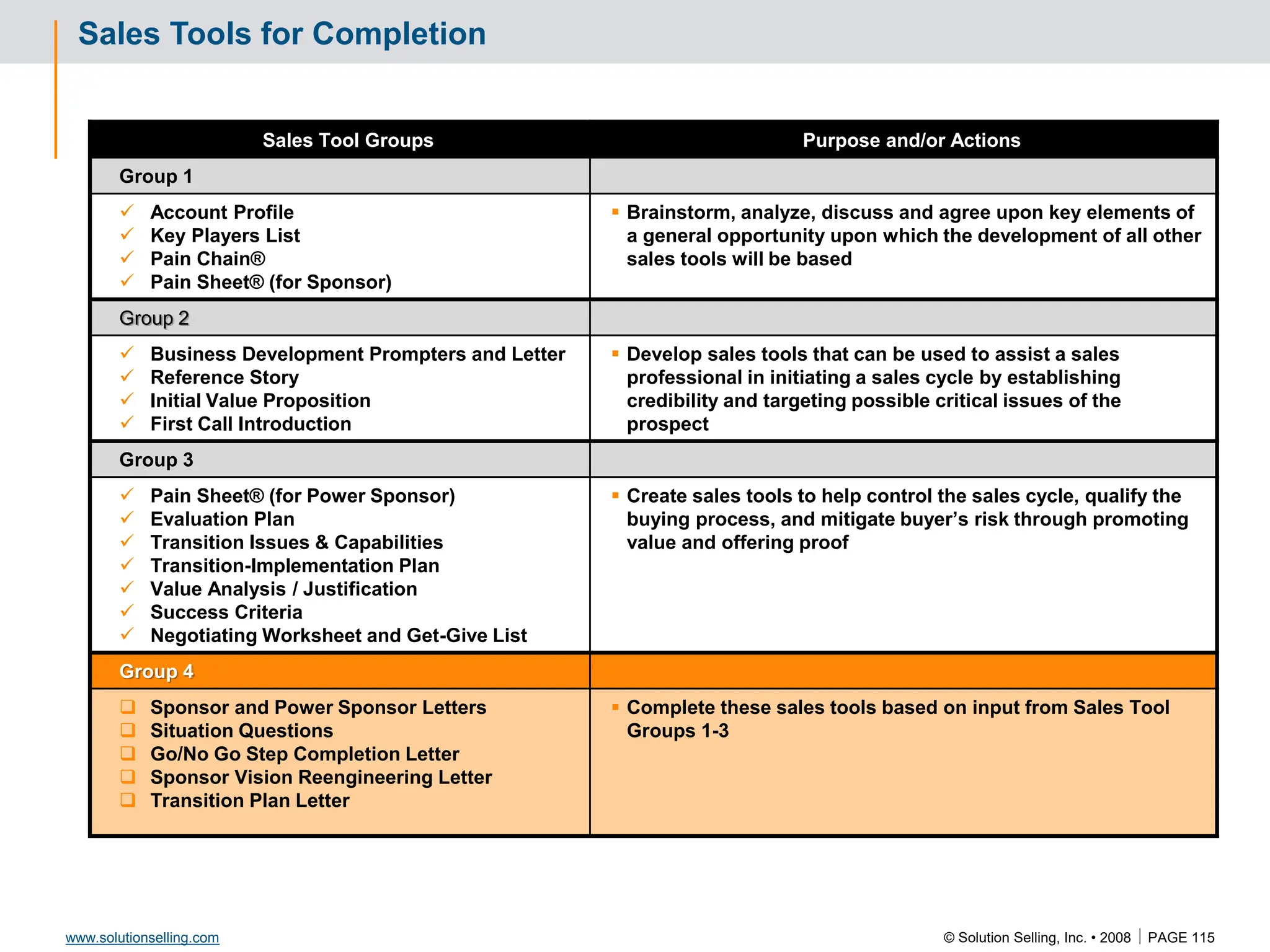
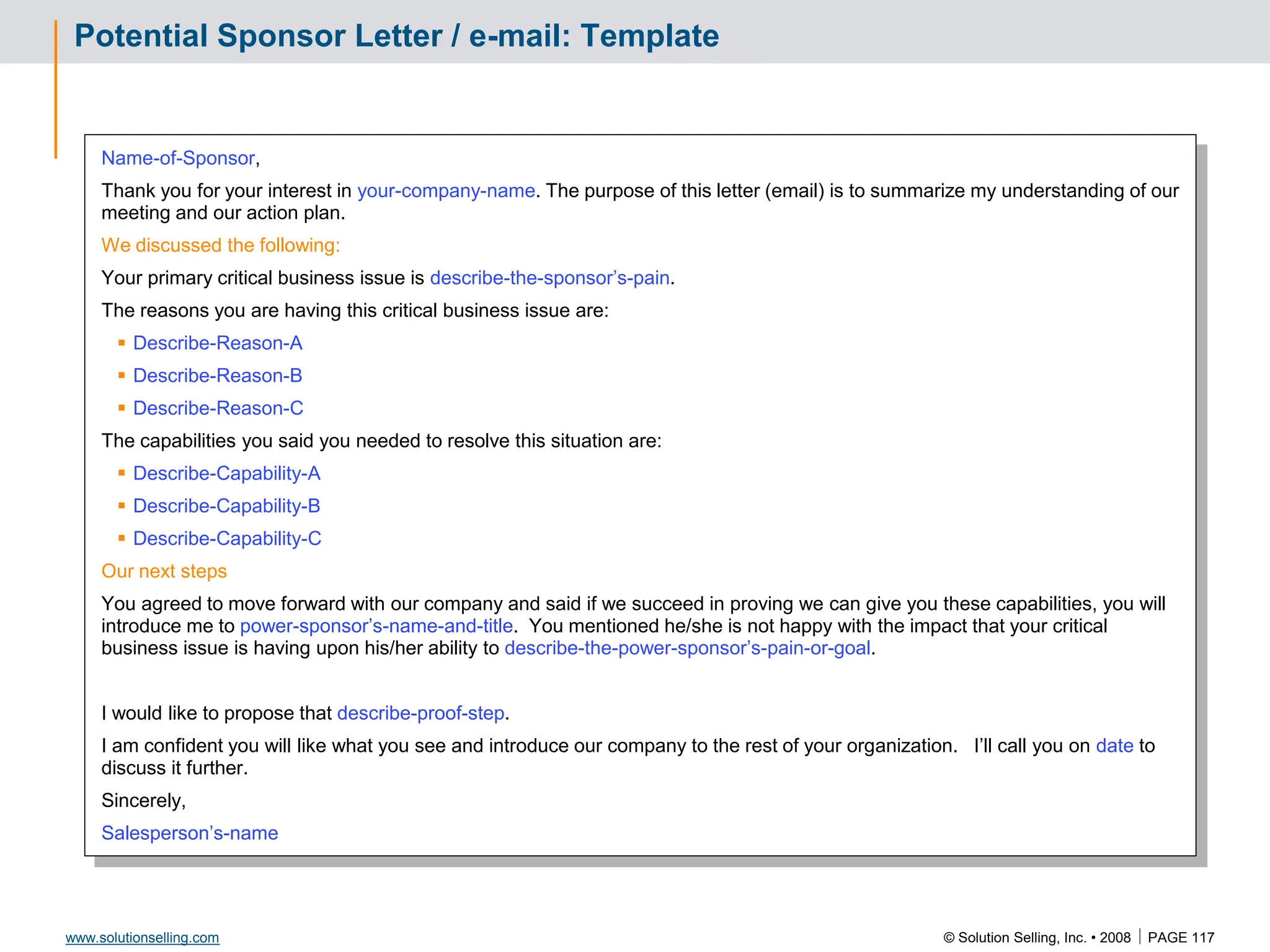
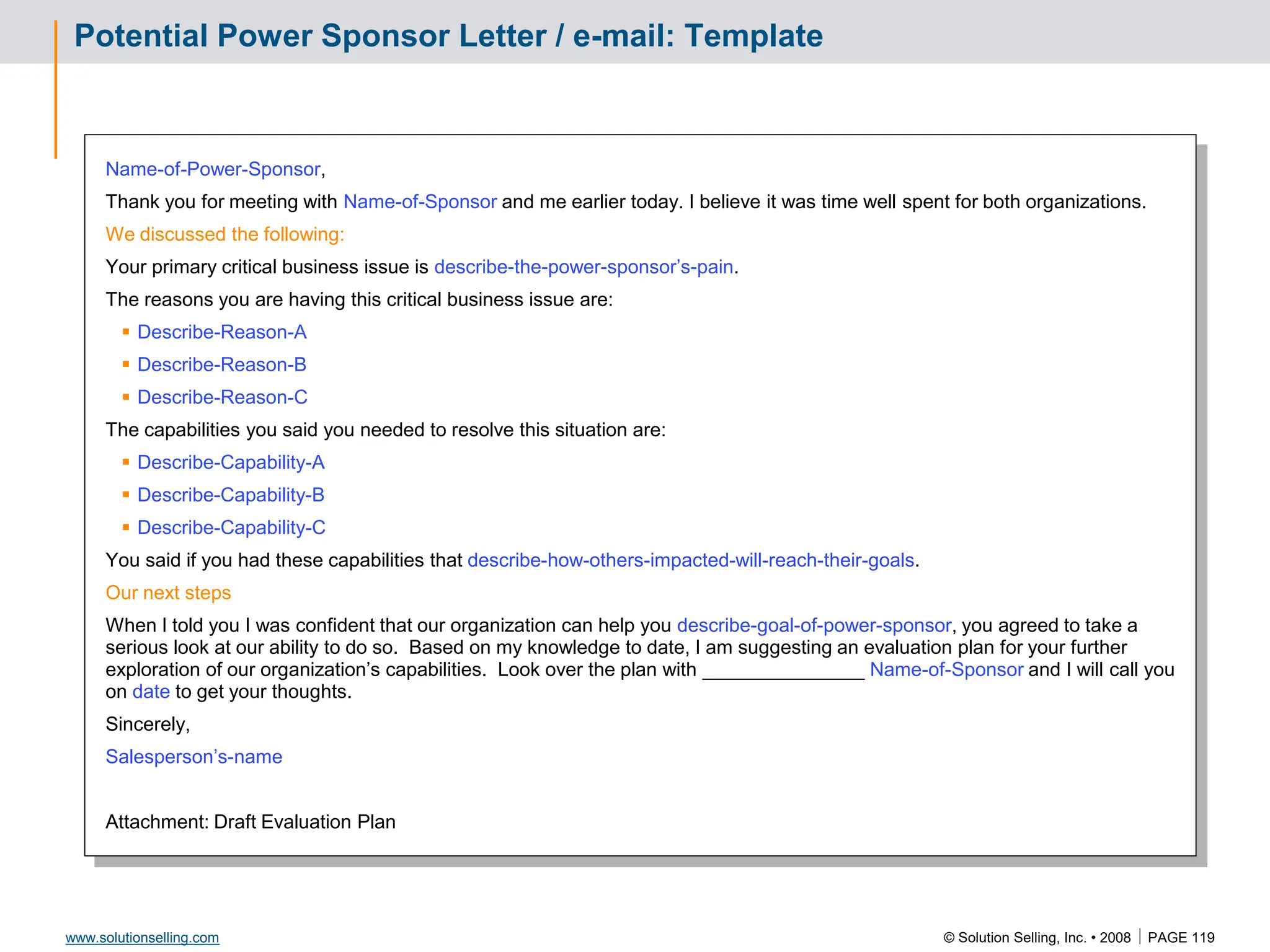
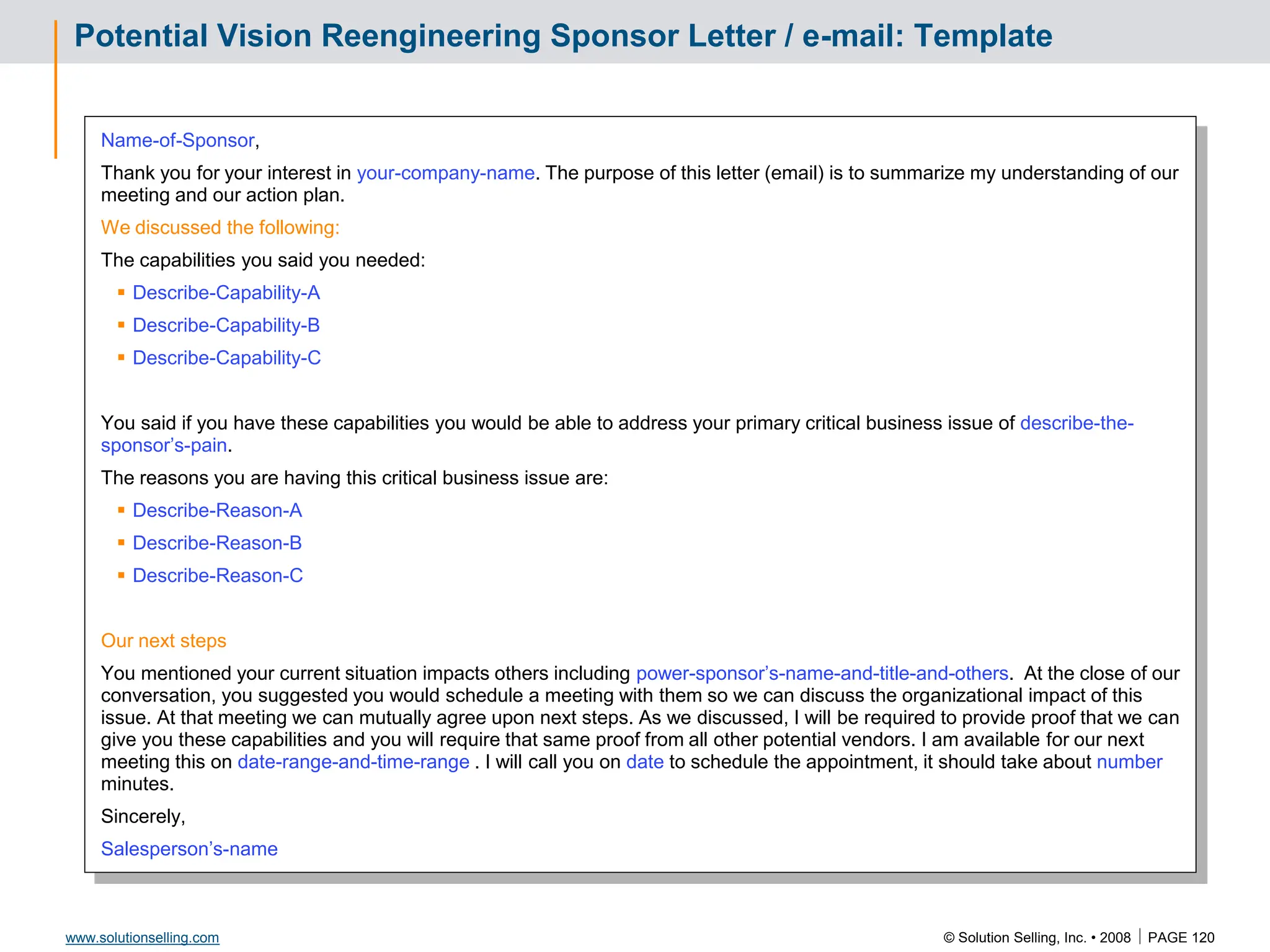
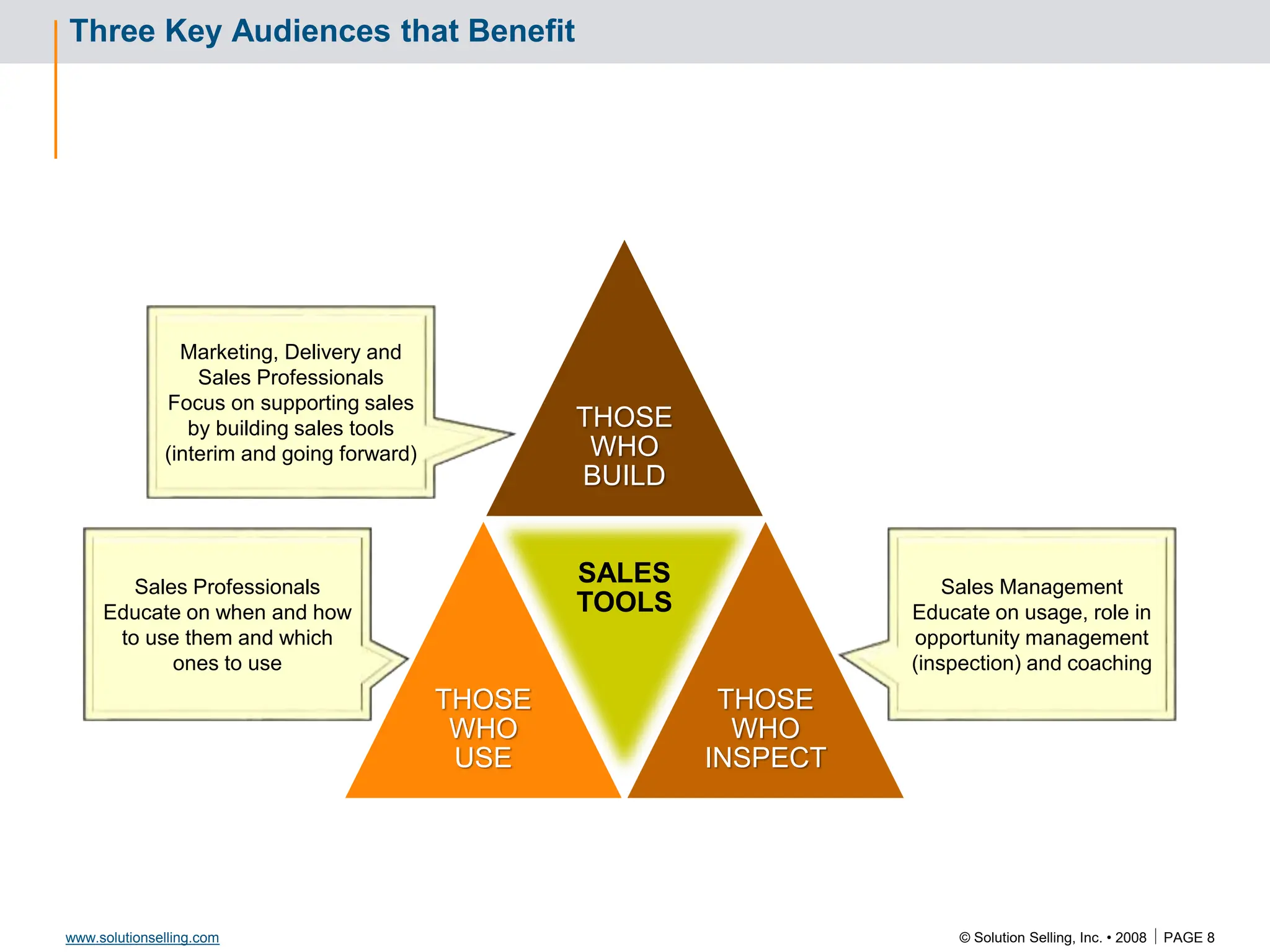
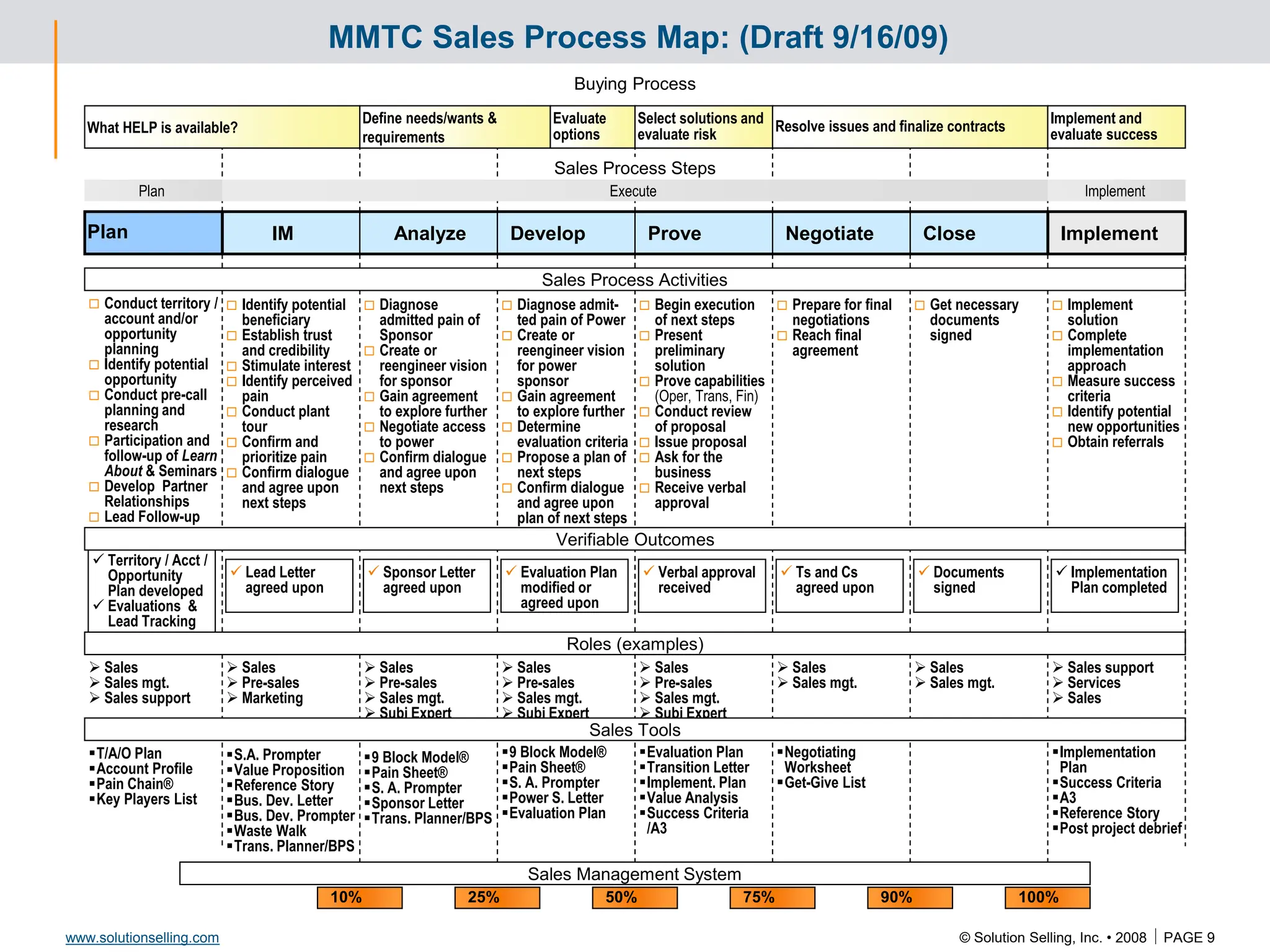
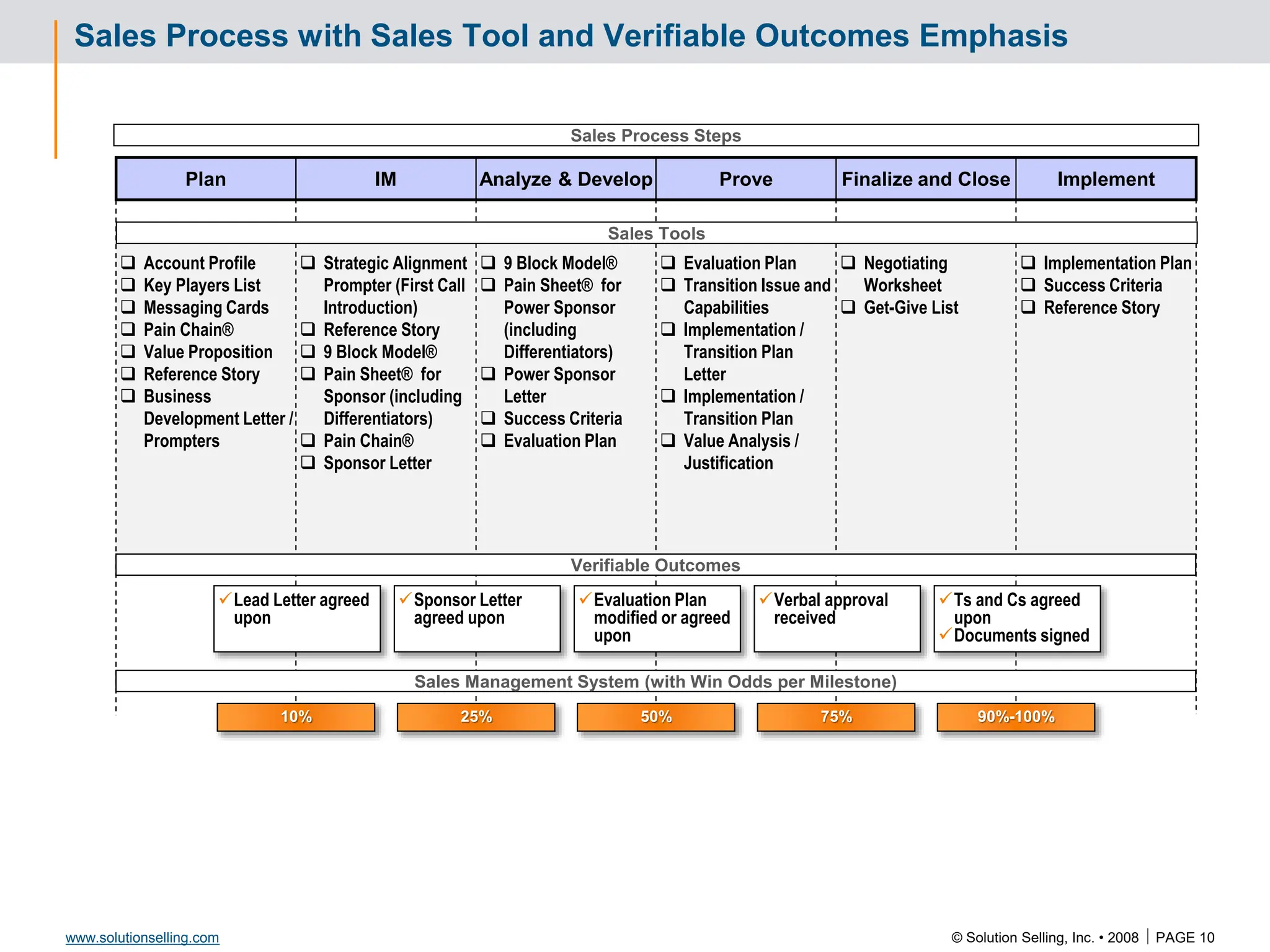
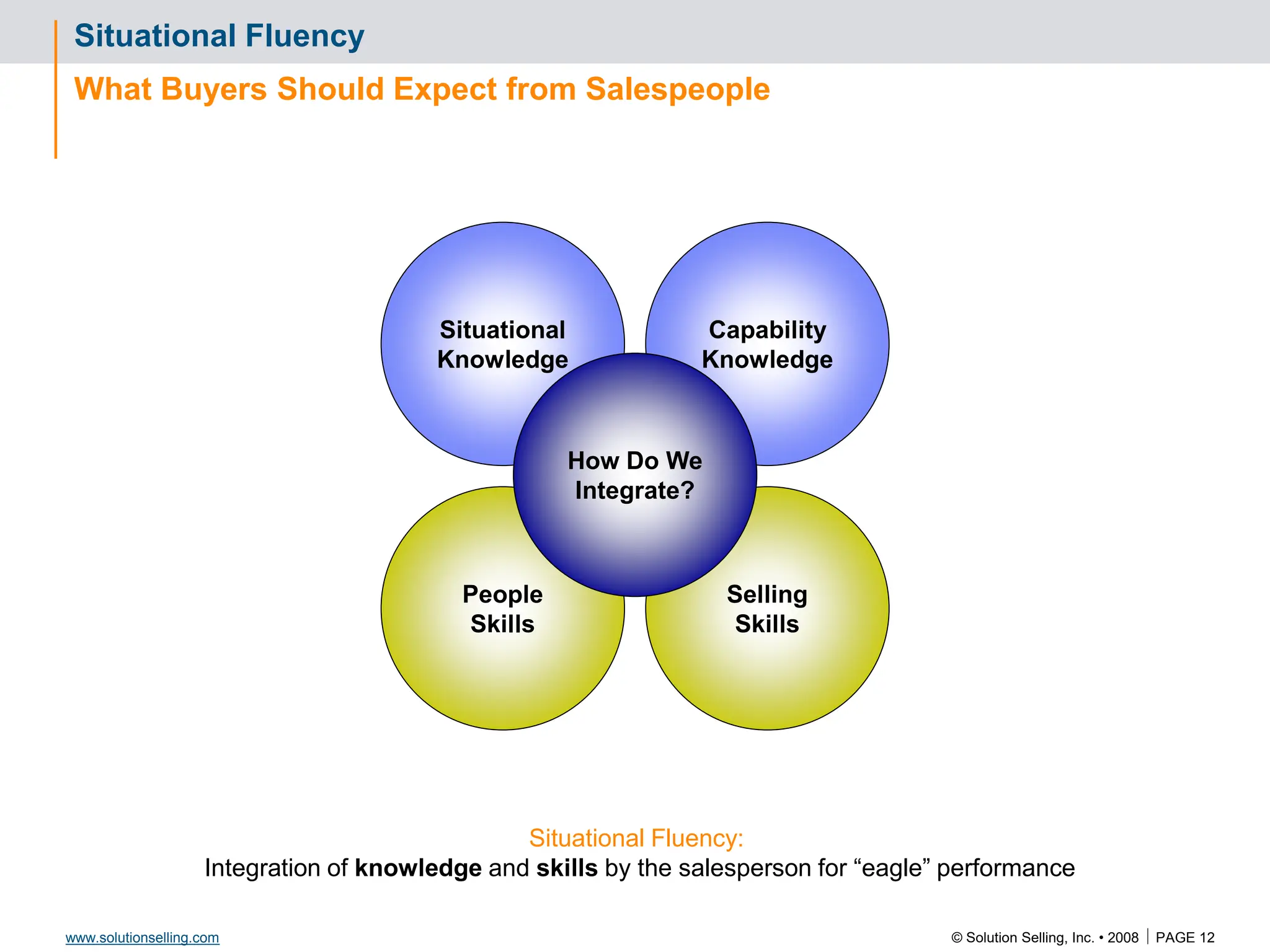
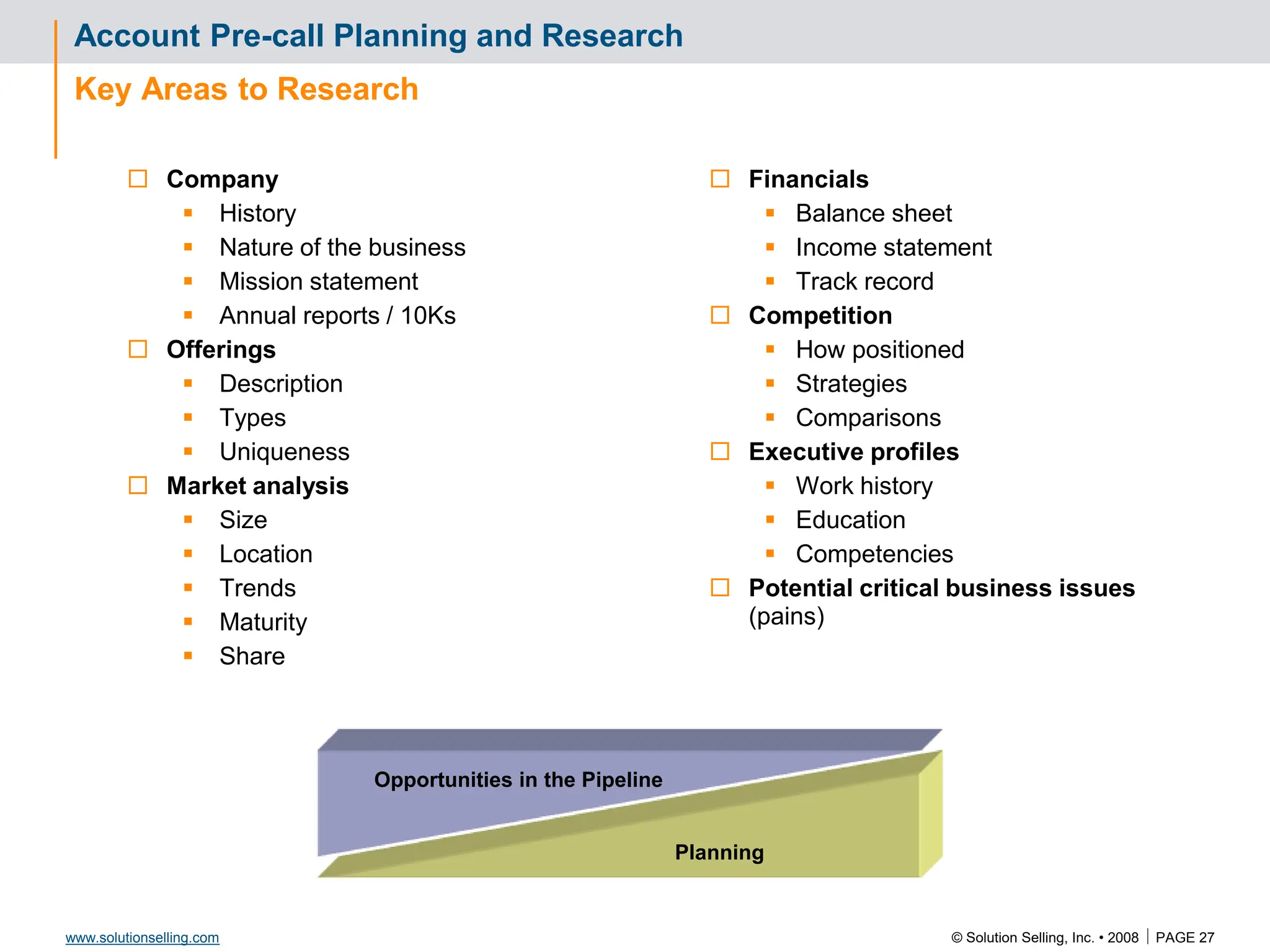
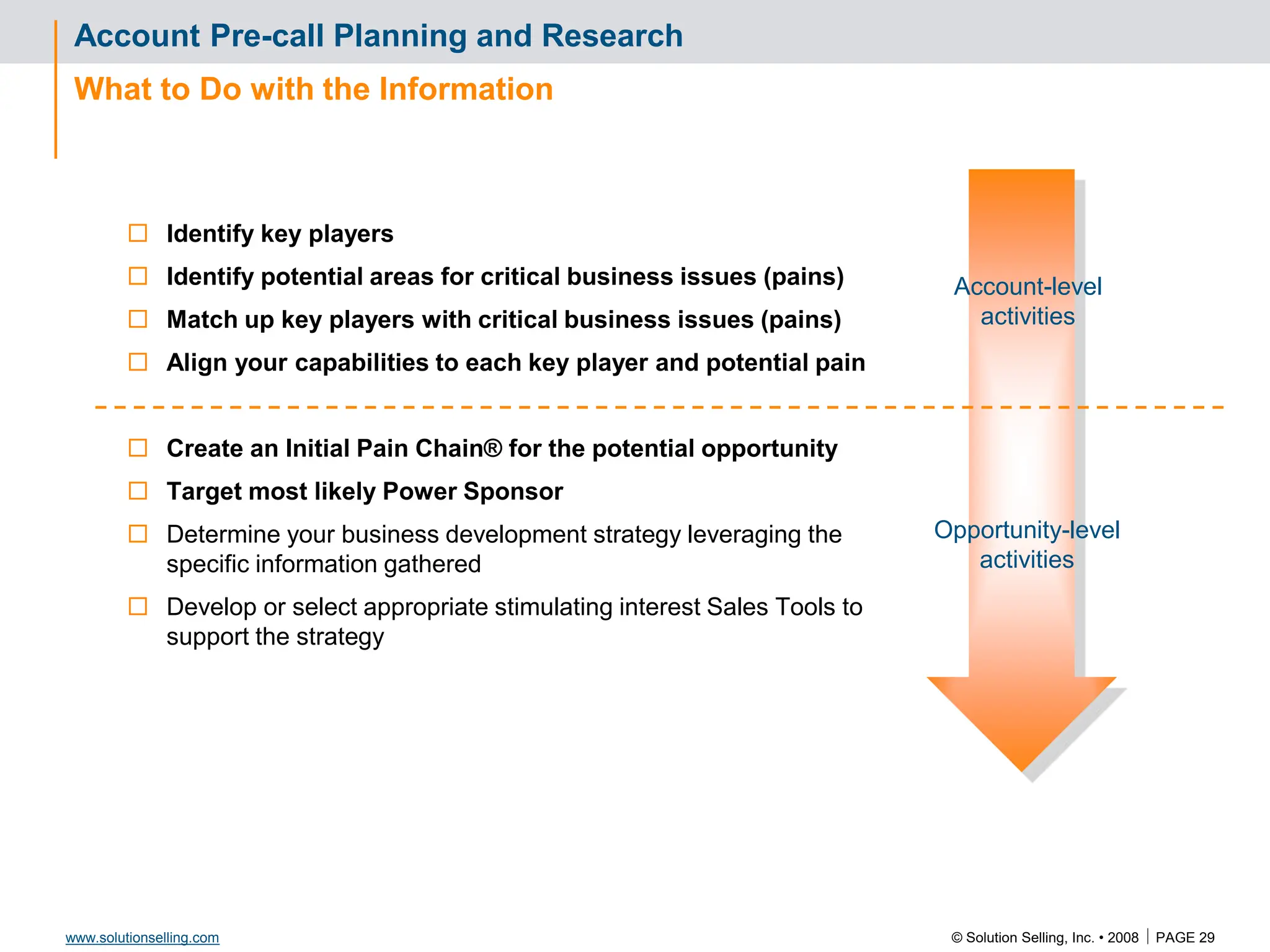
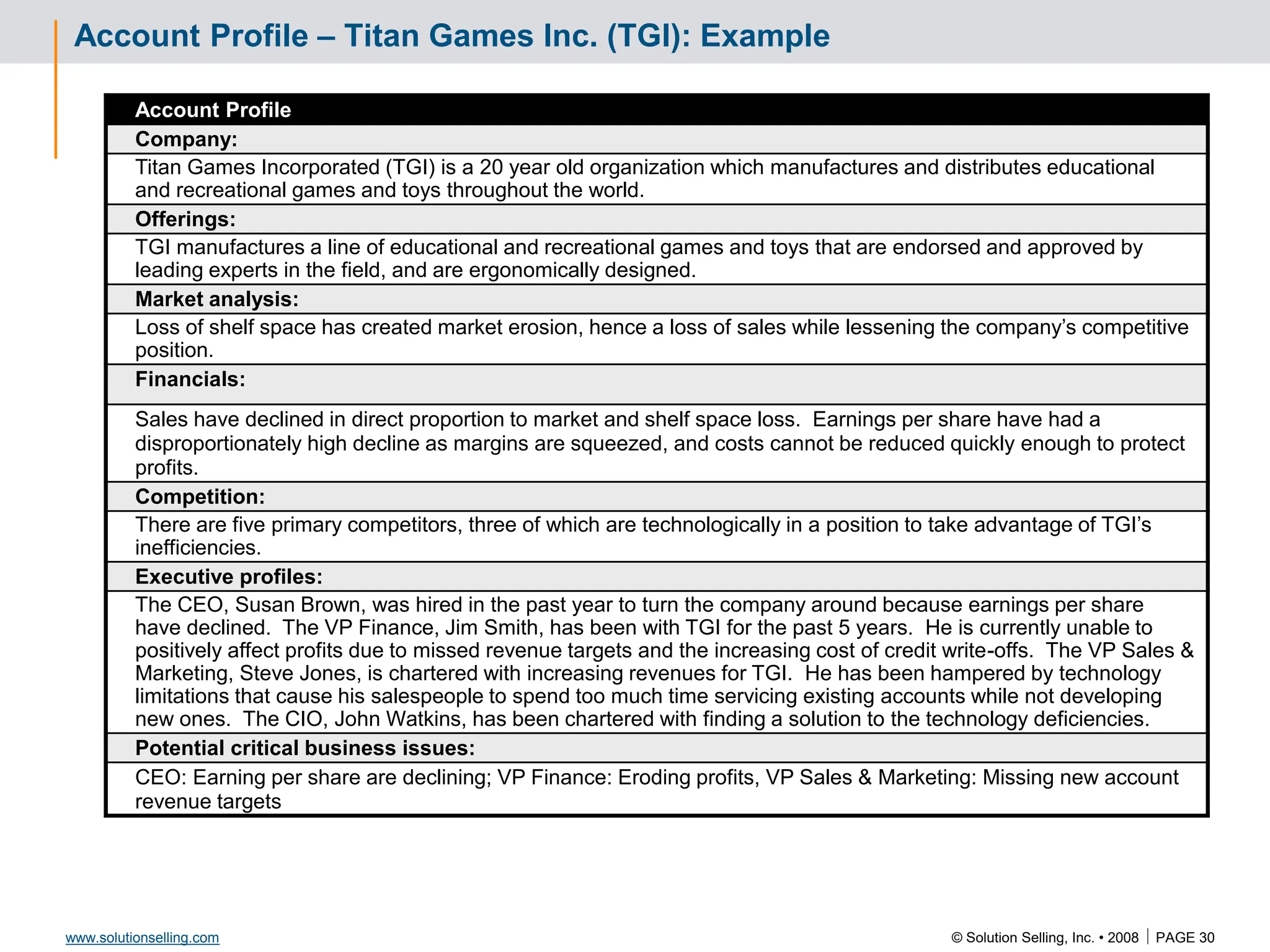
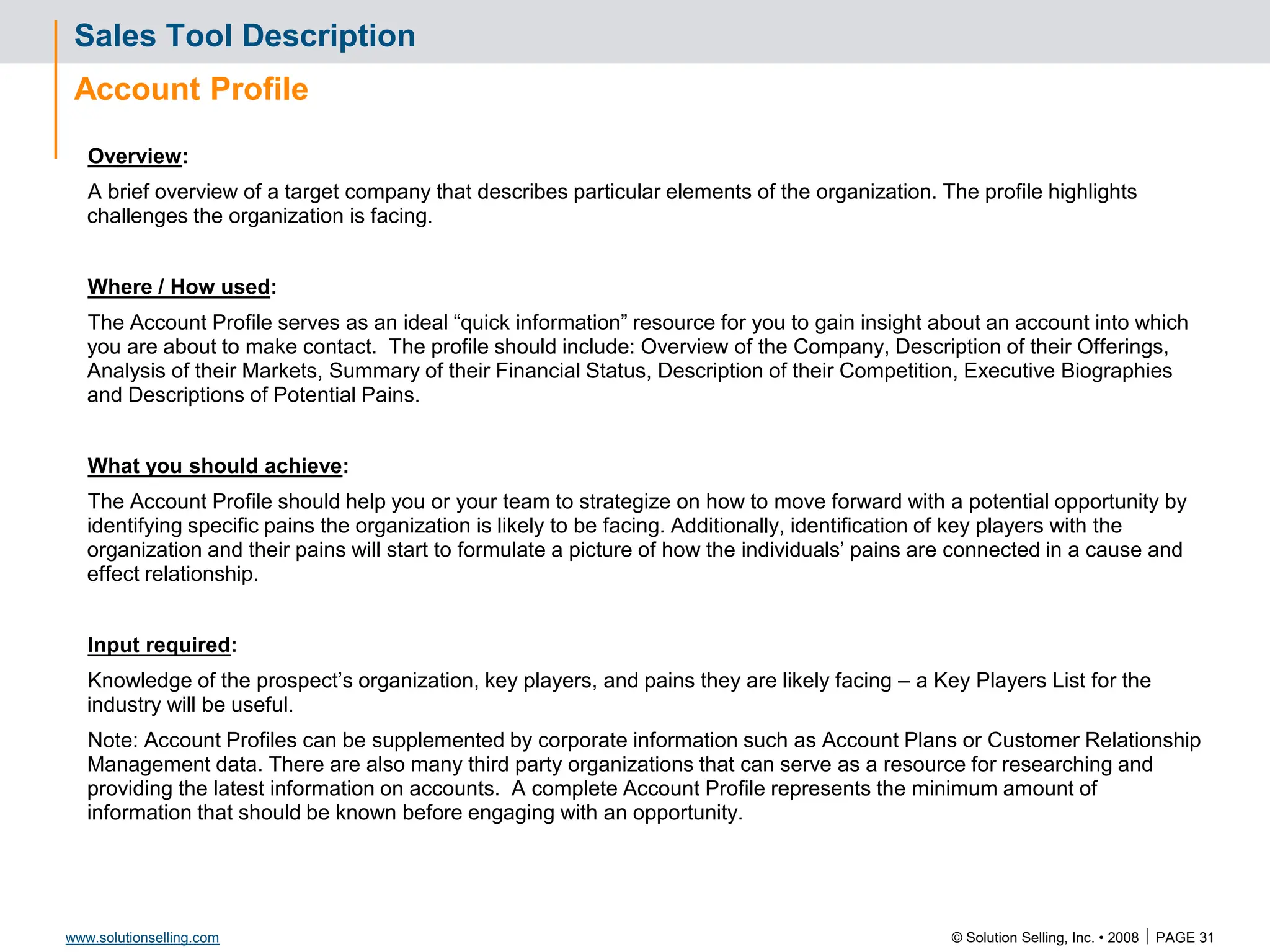
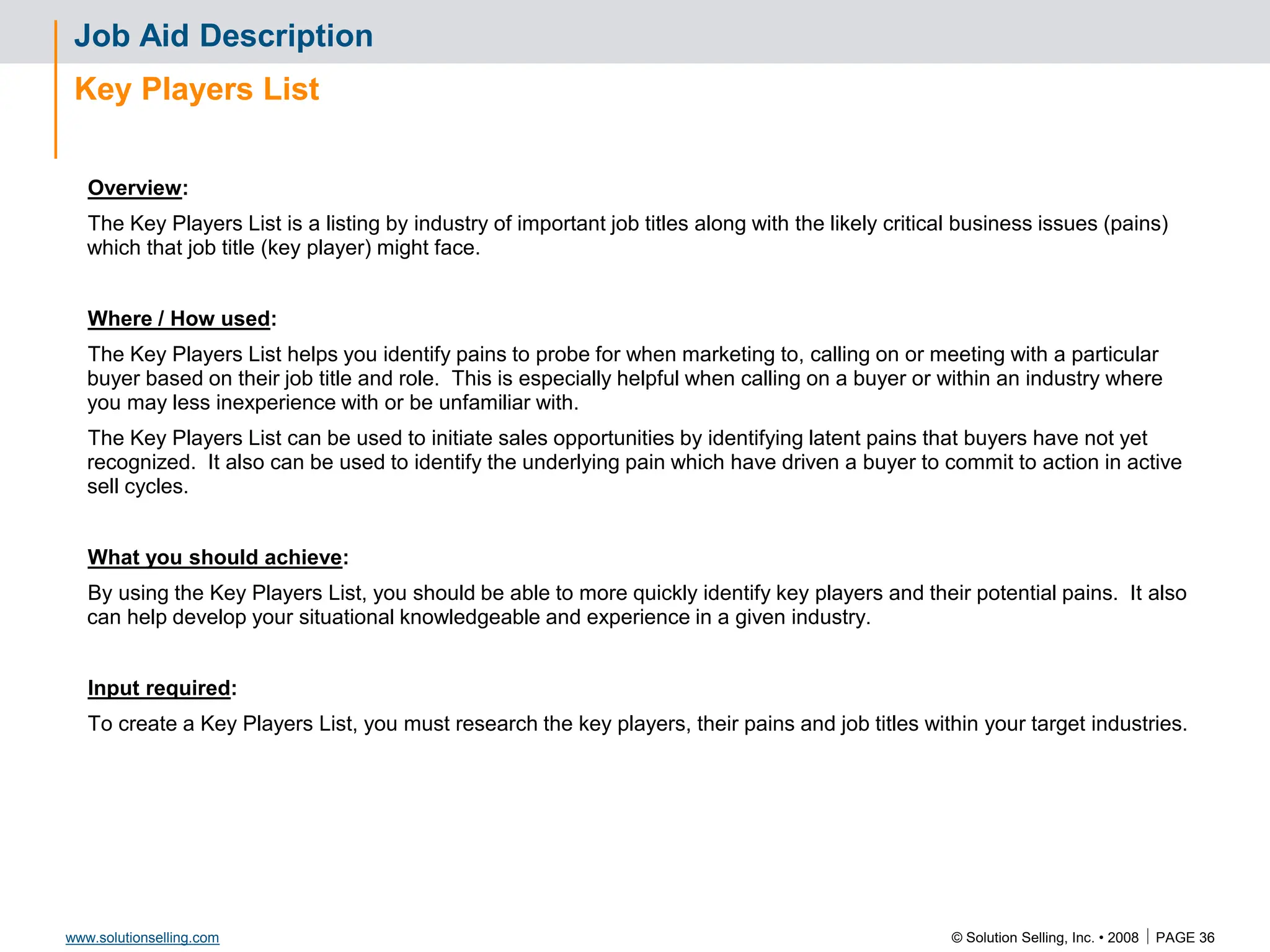
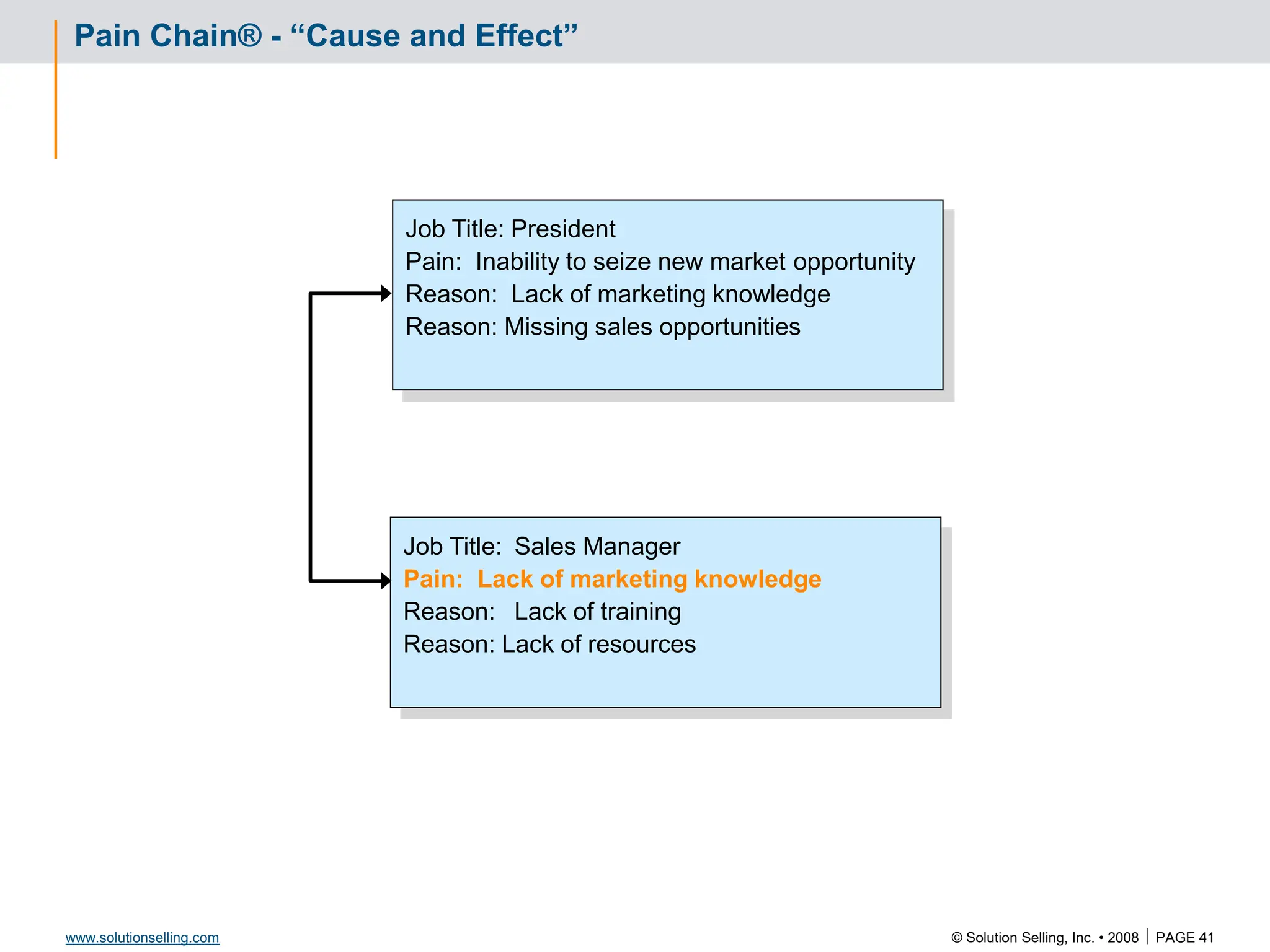
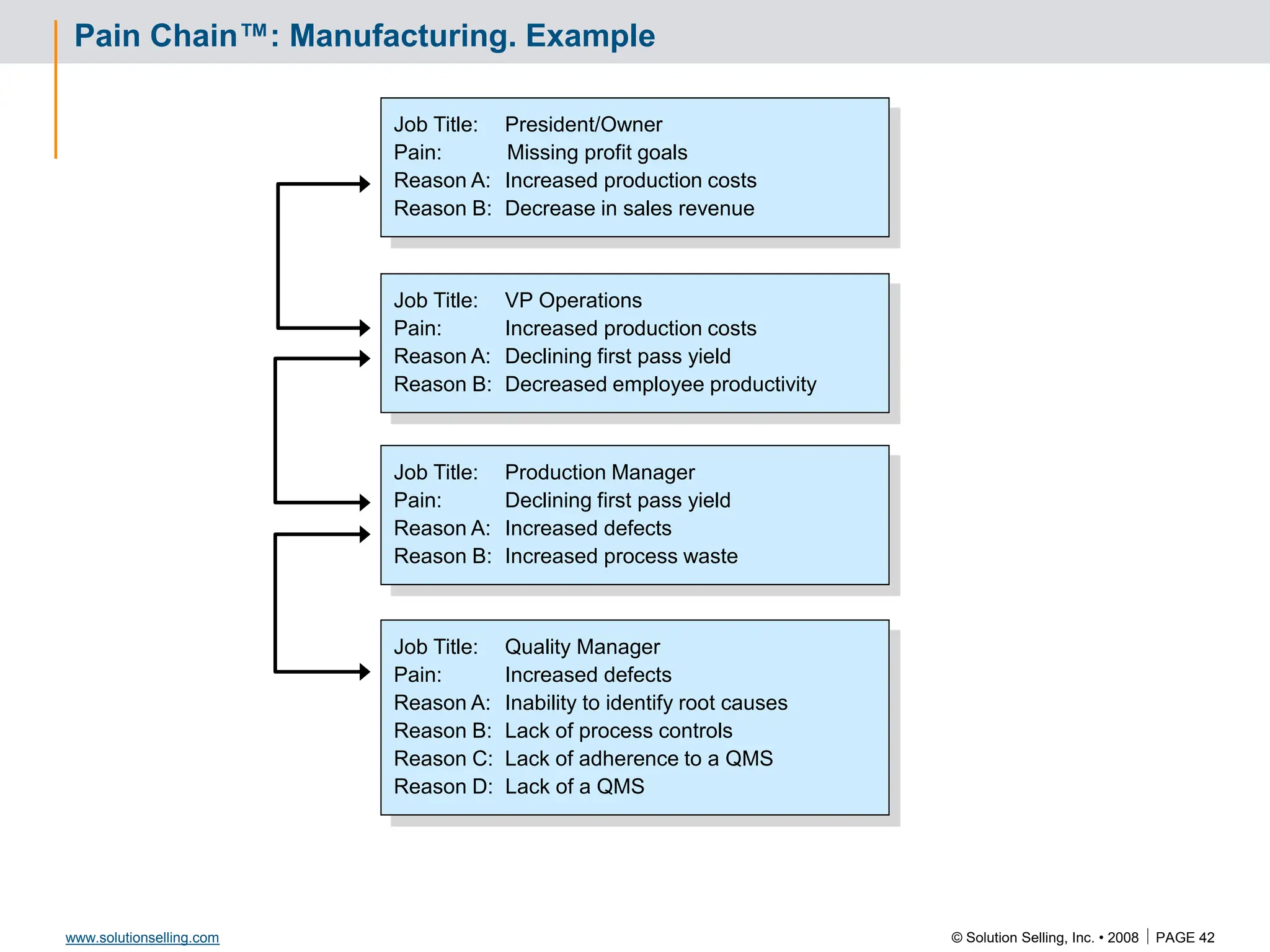
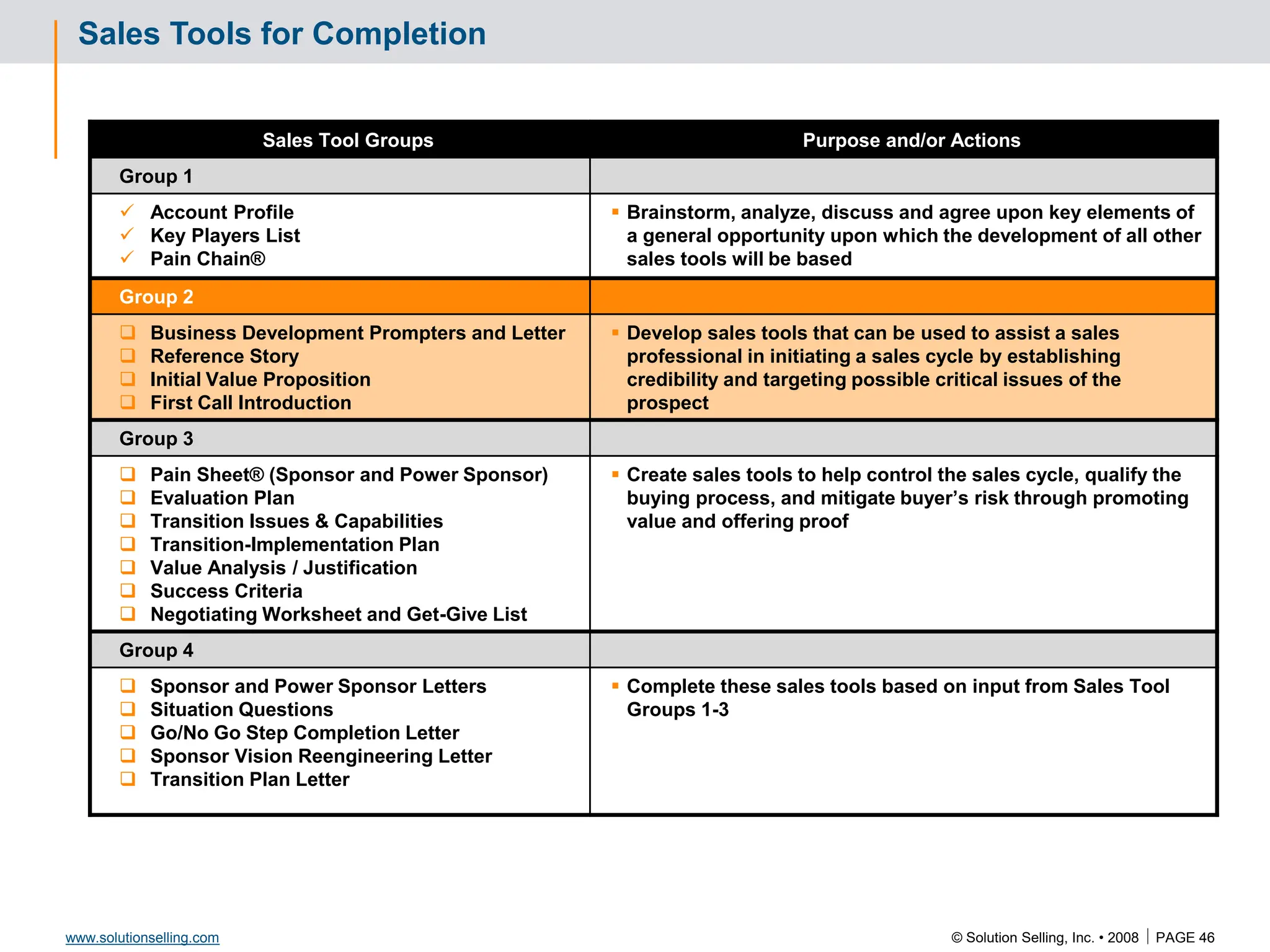
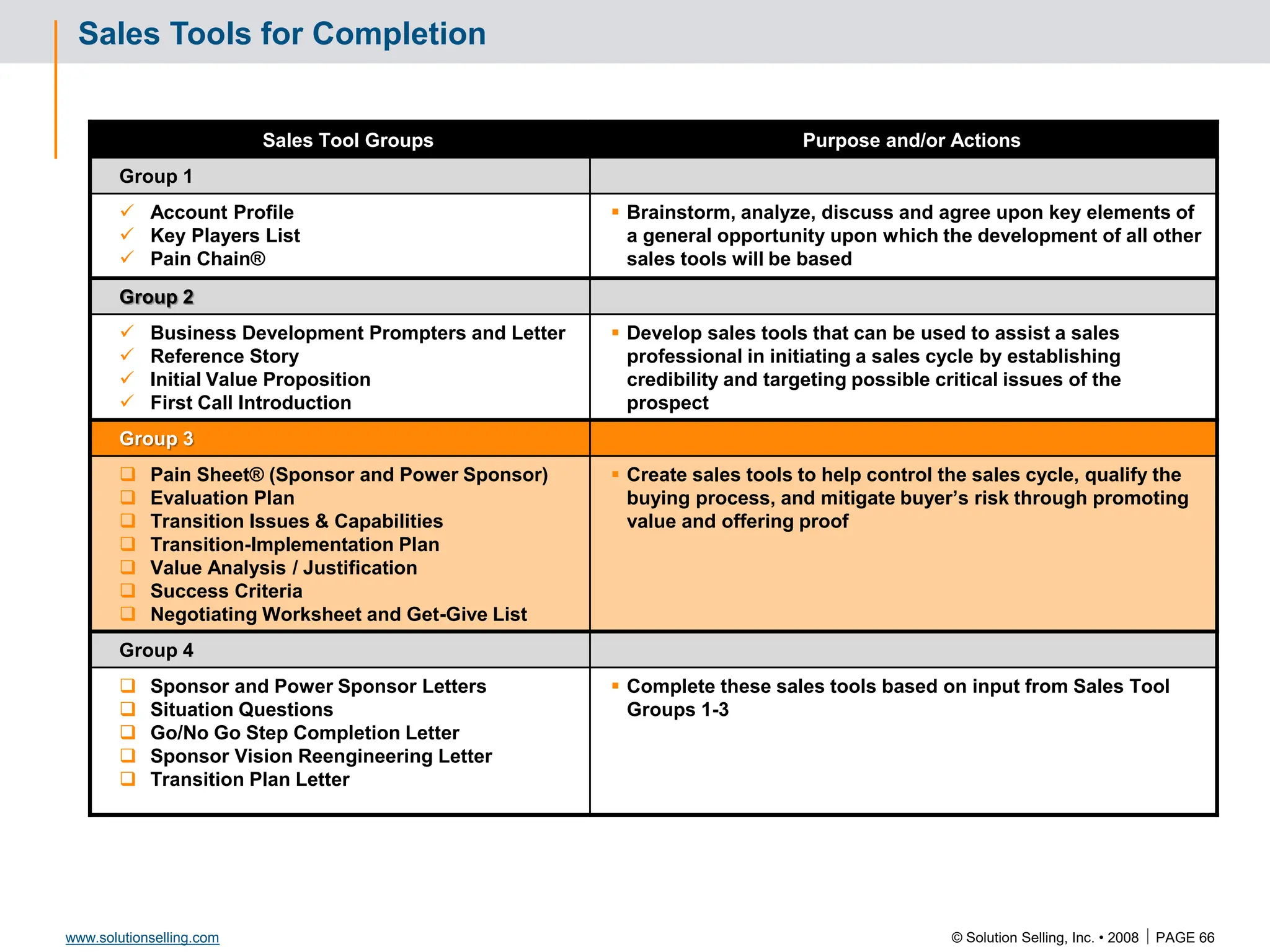
This document contains information about copyrights, trademarks, and contacts for Solution Selling Inc. It provides templates and definitions for developing sales tools to guide salespeople through each step of the sales process. These tools are meant to help salespeople integrate their knowledge and skills to have conversations with customers, understand their needs and pain points, and ultimately help the customer select and implement an appropriate solution.






















![© Solution Selling, Inc. • 2008 PAGE 61
www.solutionselling.com
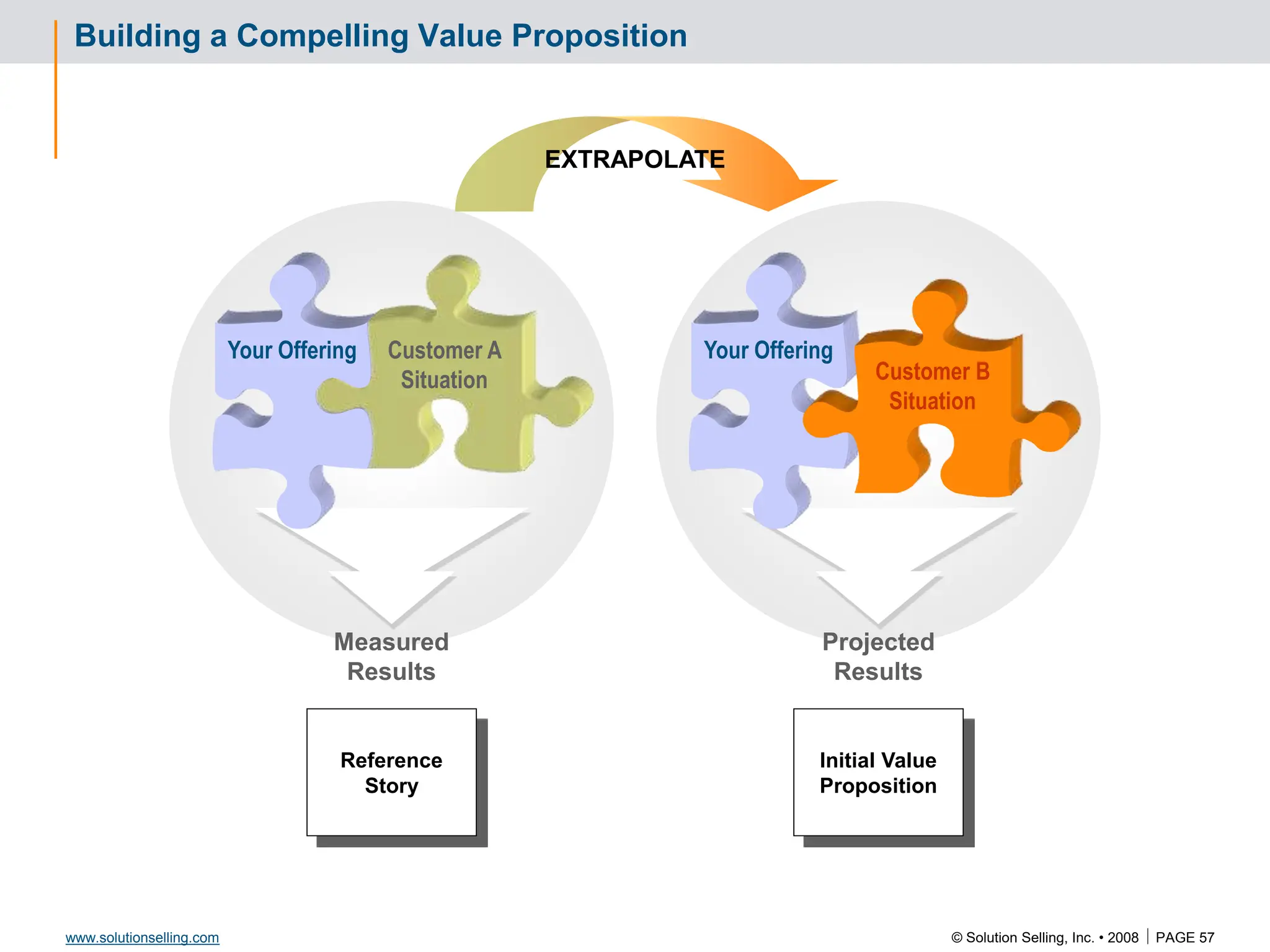
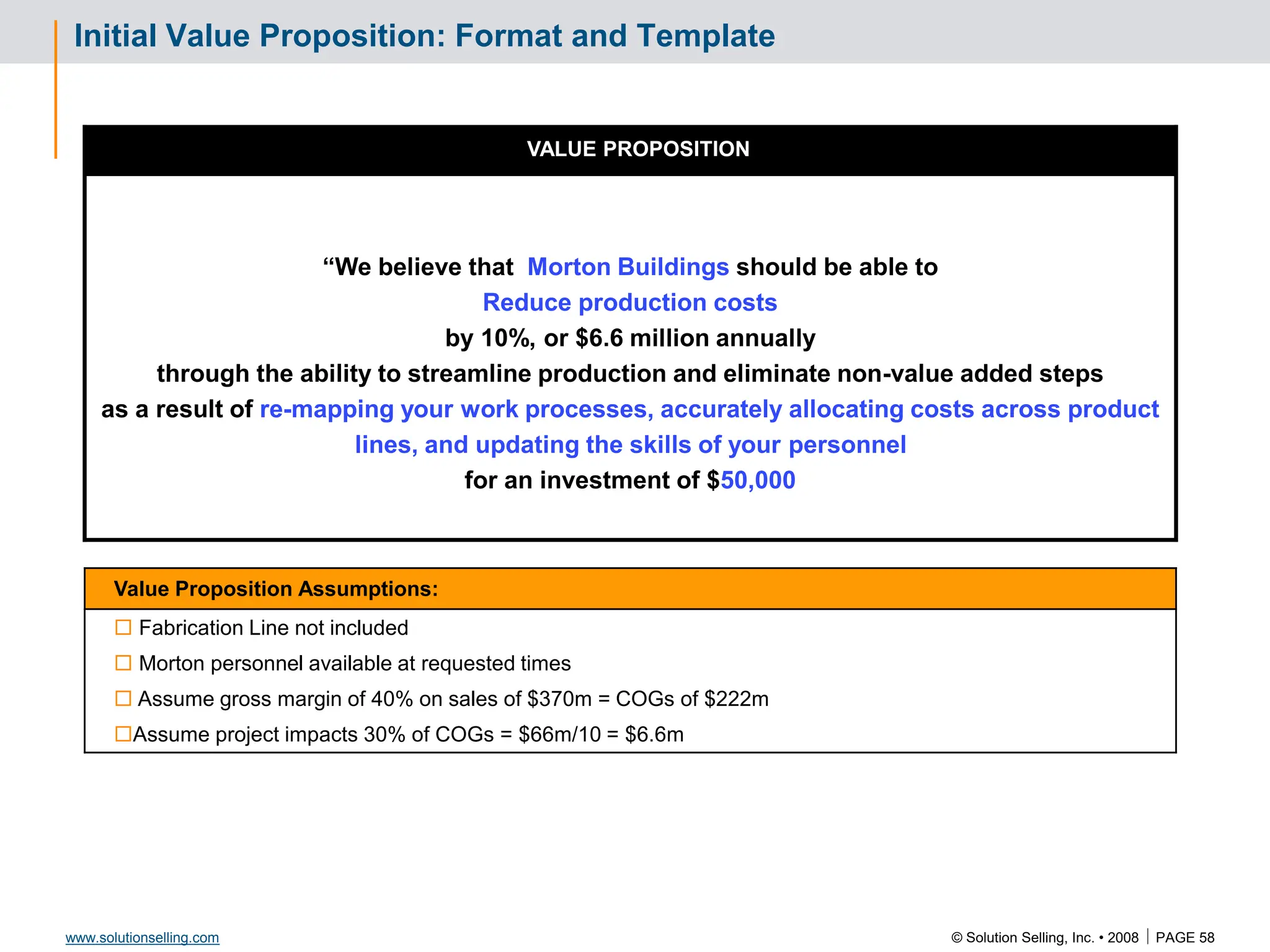
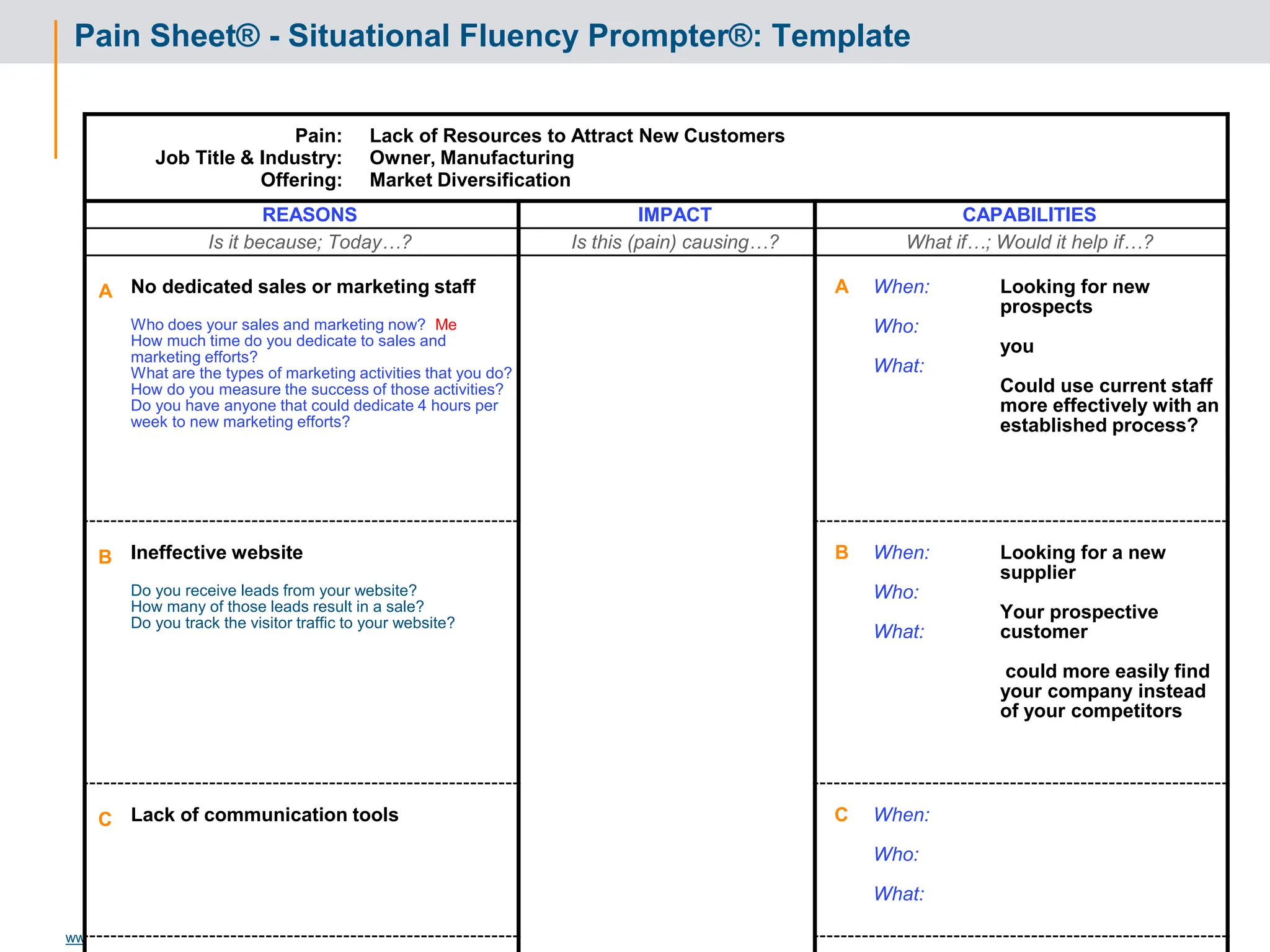
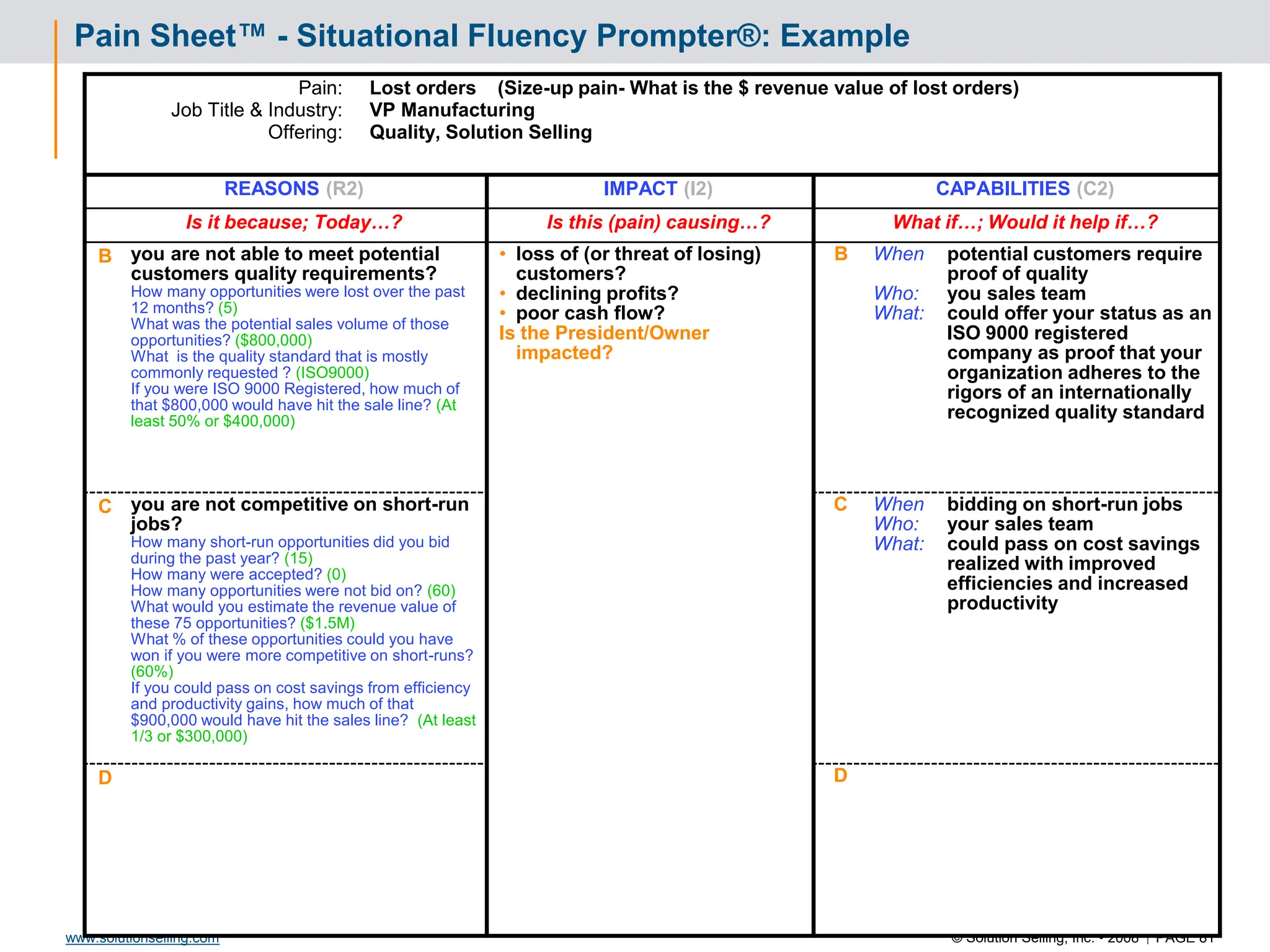
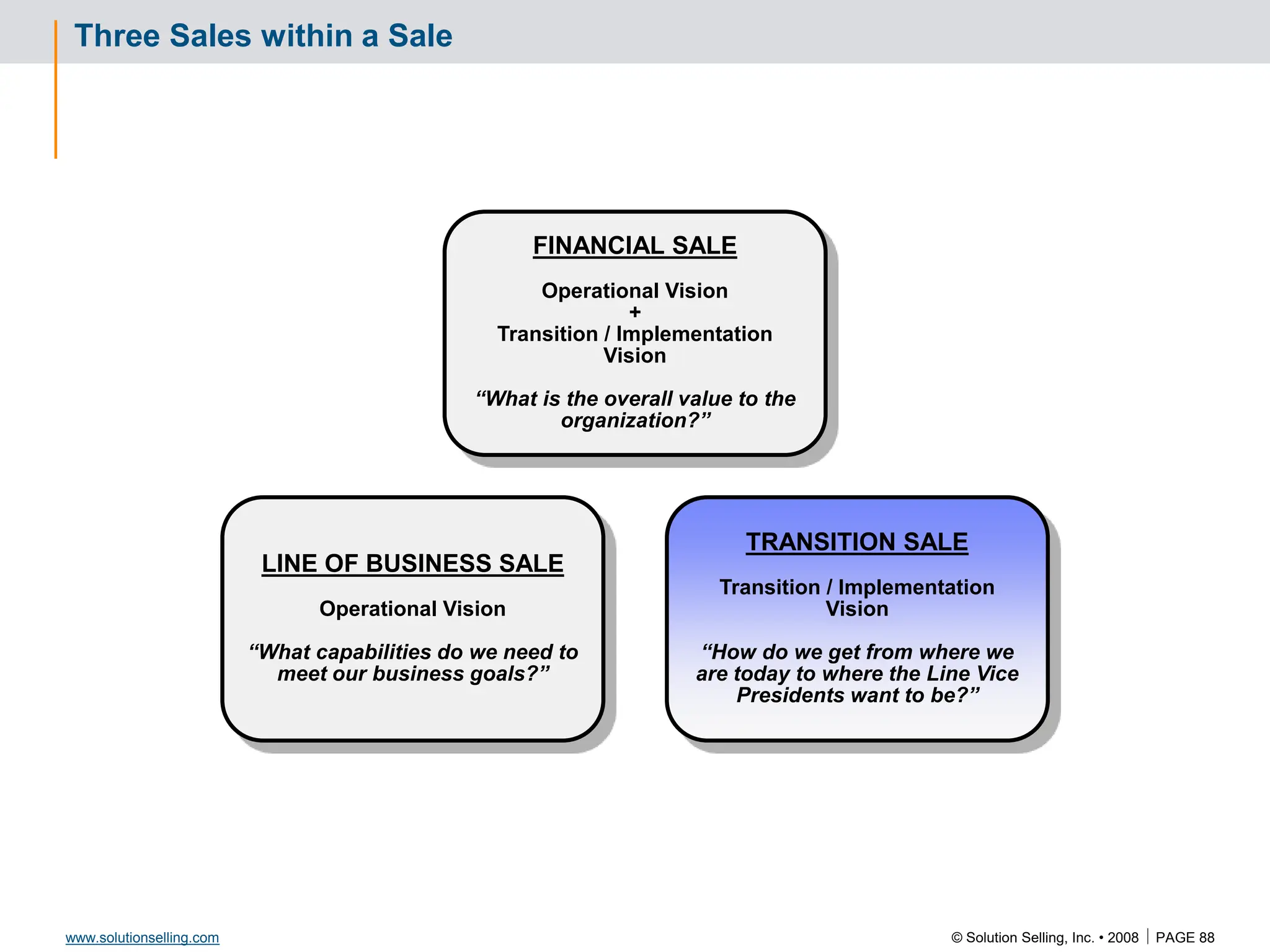
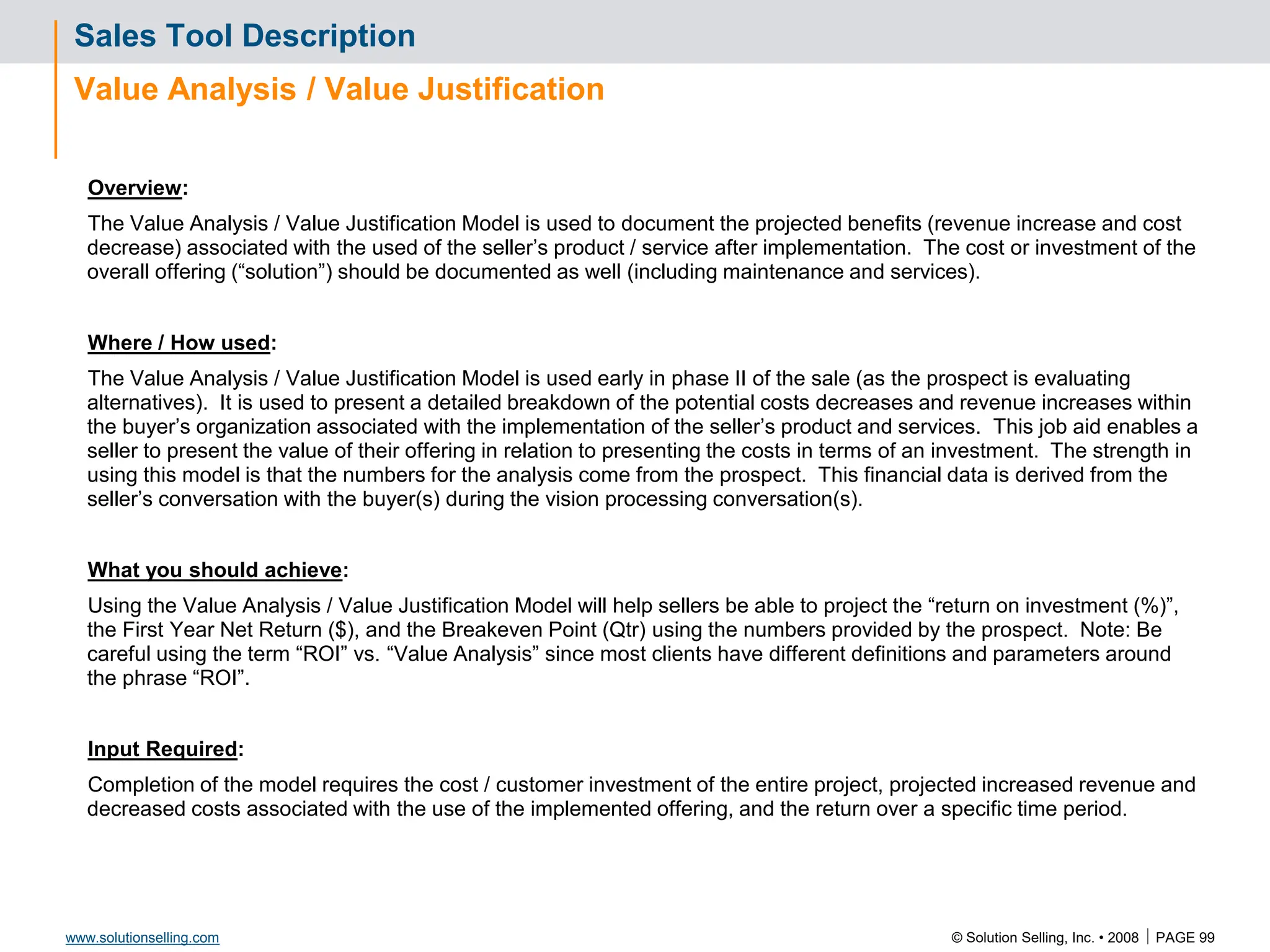
Initial Value Proposition: Format and Template
VALUE PROPOSITION
“We believe that TC Sports should be able to increase sales by $500,000
through the ability to market effectively, drive new RFQ opportunities, and
infiltrate new markets as a result of updating personnel skill sets and
website enhancement, for an investment of $ 22,000”
Value Proposition assumptions being made:
Average sale amount = $20,000
Closing ratio = 15%
24 hour response to all quote opportunities
Personnel available at requested times
Value Proposition Format:
We believe that [ Client name ]
should be able to [ improve what ]
by [ how much, what %? ]
through the ability to [ do what? ]
as a result of [ what enabling capabilities? ]
for an investment of [ what relative cost? ] .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3266826-240213232649-a441385e/75/Solution-Selling-Principles-Primer-Content-62-2048.jpg)





![© Solution Selling, Inc. • 2008 PAGE 84
www.solutionselling.com
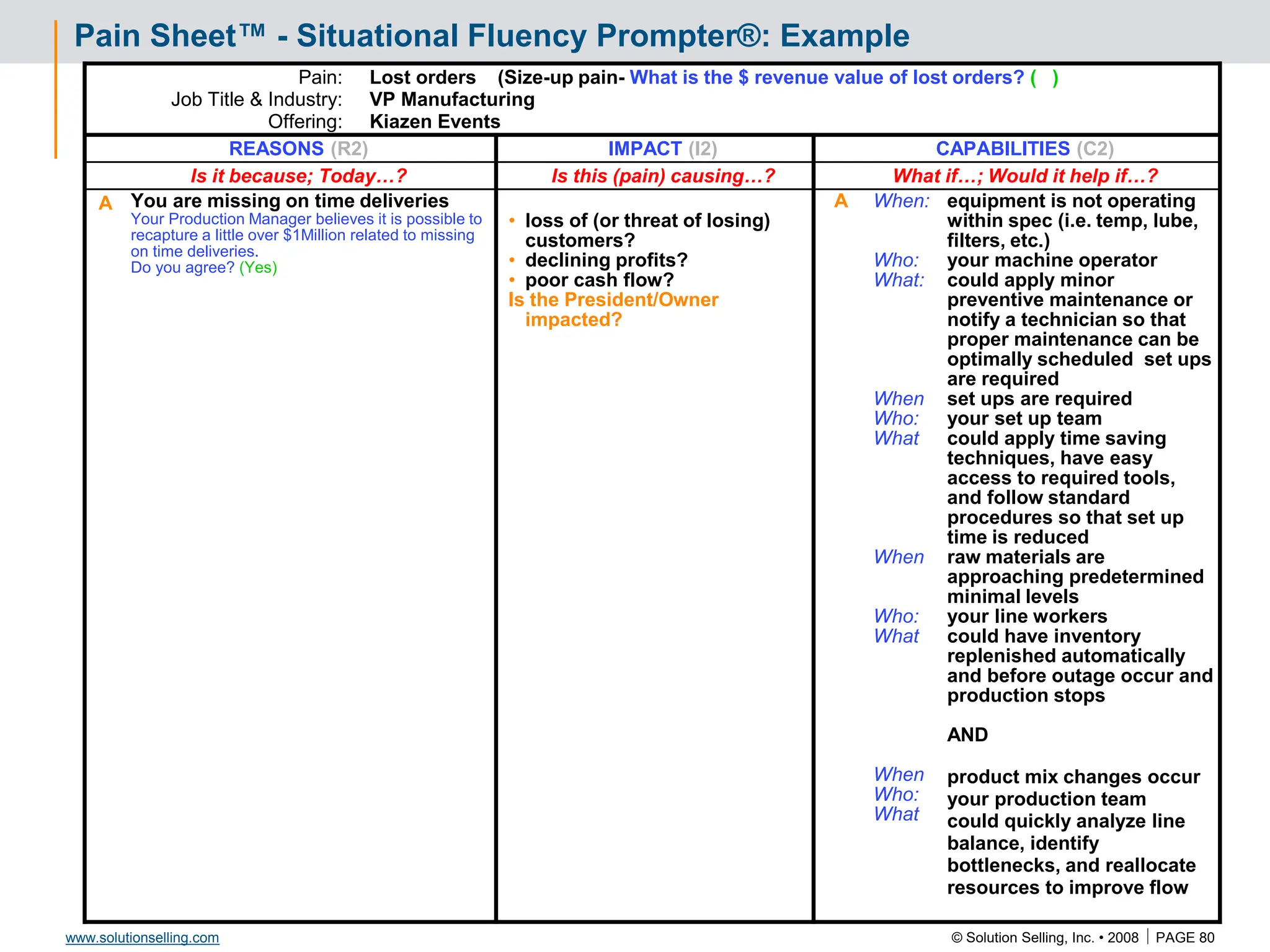
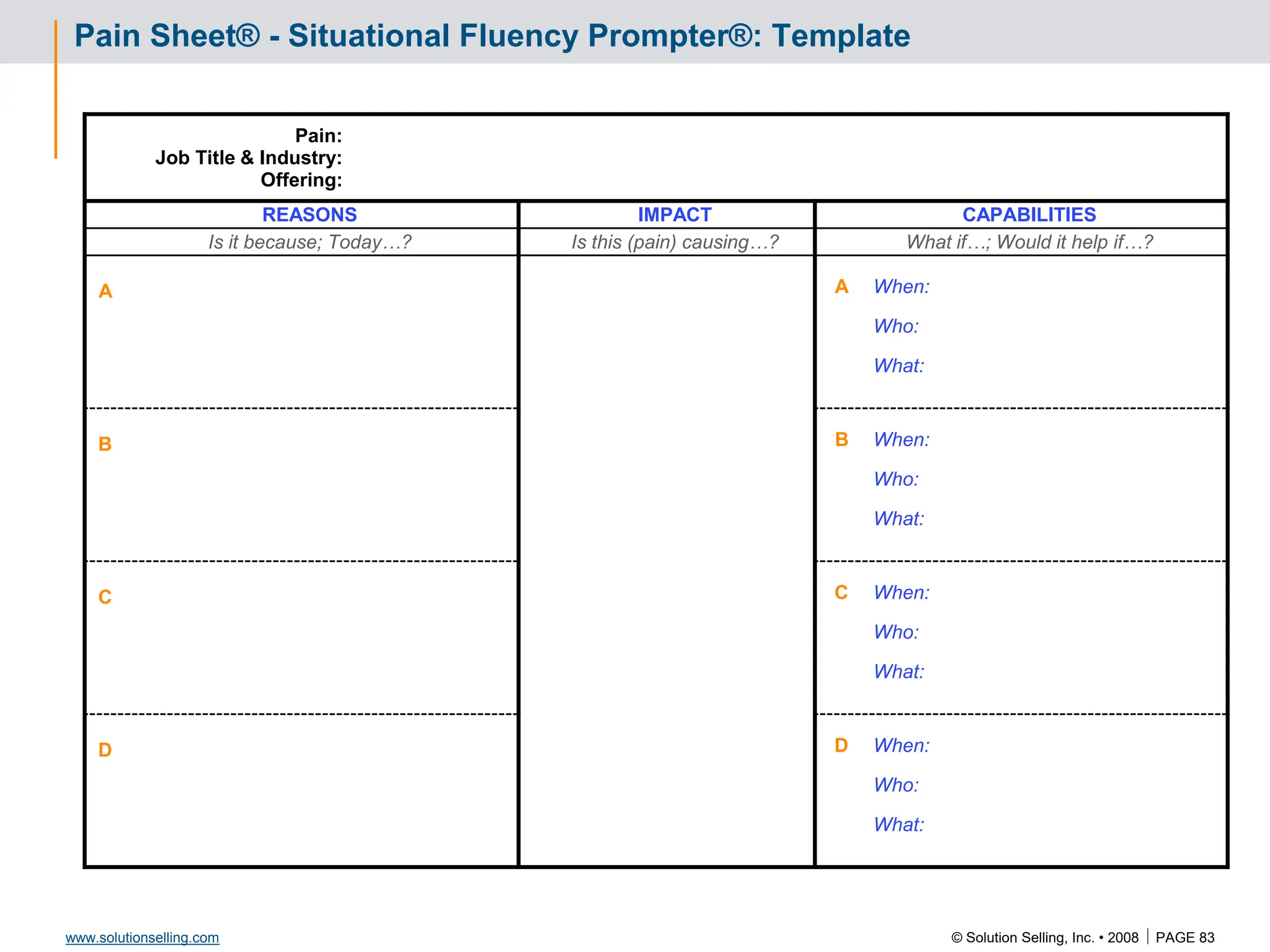
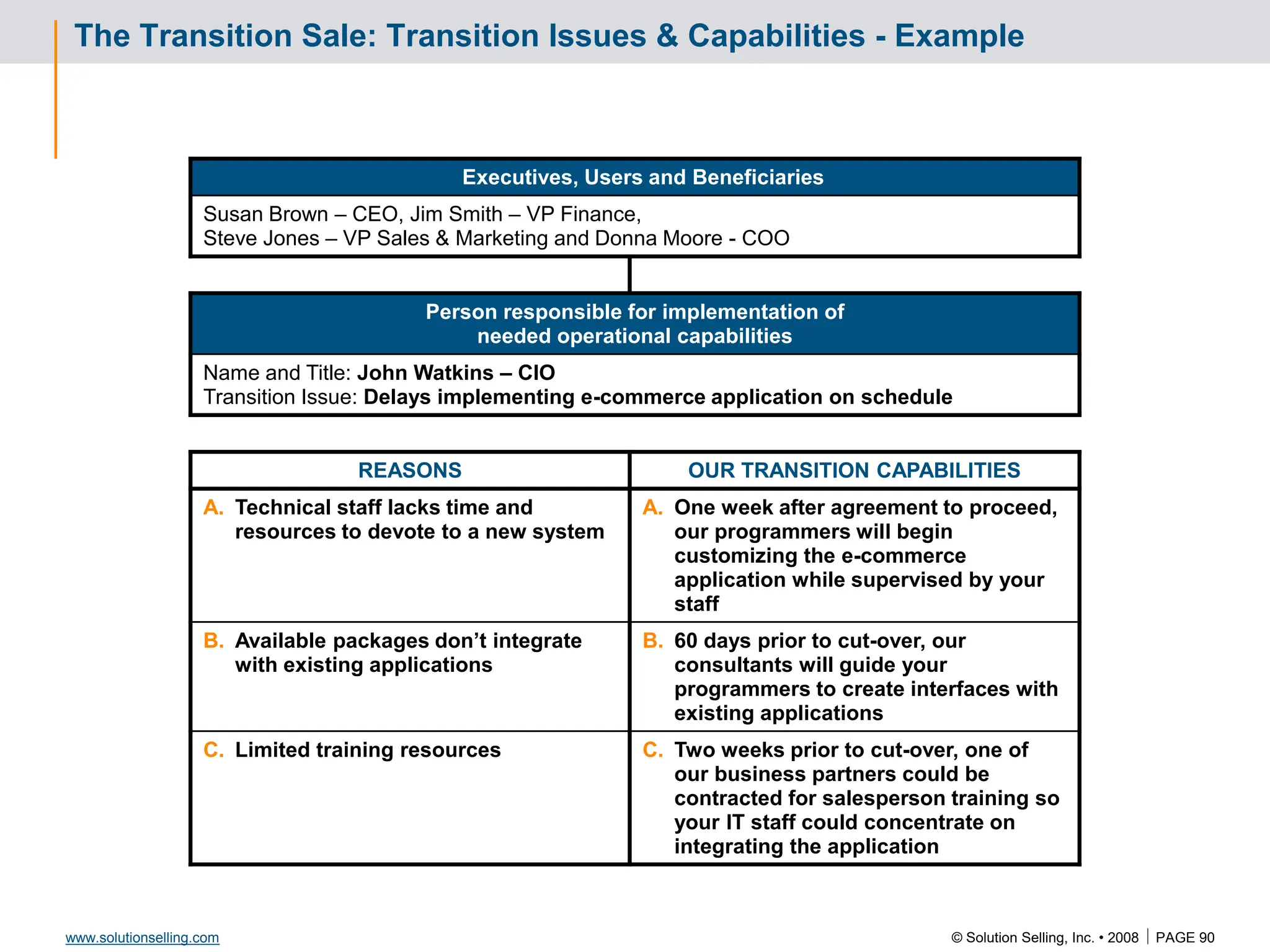
Draft Evaluation Plan: Example
Attachment to Power Sponsor Letter / e-mail
[DRAFT]
Event Week of √ Responsible
Go/No
Go
Billable
Phone interview John Watkins (CIO) Feb 14 Us/TGI
Phone interview Donna Moore (COO) Feb 14 Us/TGI
Summarize findings to management team
and agree to evaluation plan
Feb 21 Us/TGI *
Prove capabilities to management team Feb 28 Us *
Perform detailed survey of current systems (2 days) March 4 Us yes
Present preliminary solution/design March 11 Us *
Implementation plan approval by IT department March 18 TGI *
Determine / present value justification March 18 Us/TGI *
Agree on preliminary success criteria March 18 Us/TGI
Send our license agreement to legal March 18 Us
Gain legal approval (Terms & Conditions) April 4 TGI *
Visit Corporate HQ April 11 Us
Pre-proposal review meeting April 18 Us
Present proposal for approval April 25 Us *
Transition kickoff & finalize success criteria May 10 Us/TGI
Measure success criteria Ongoing TGI
* Mutual decision to proceed](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3266826-240213232649-a441385e/75/Solution-Selling-Principles-Primer-Content-85-2048.jpg)
![© Solution Selling, Inc. • 2008 PAGE 87
www.solutionselling.com
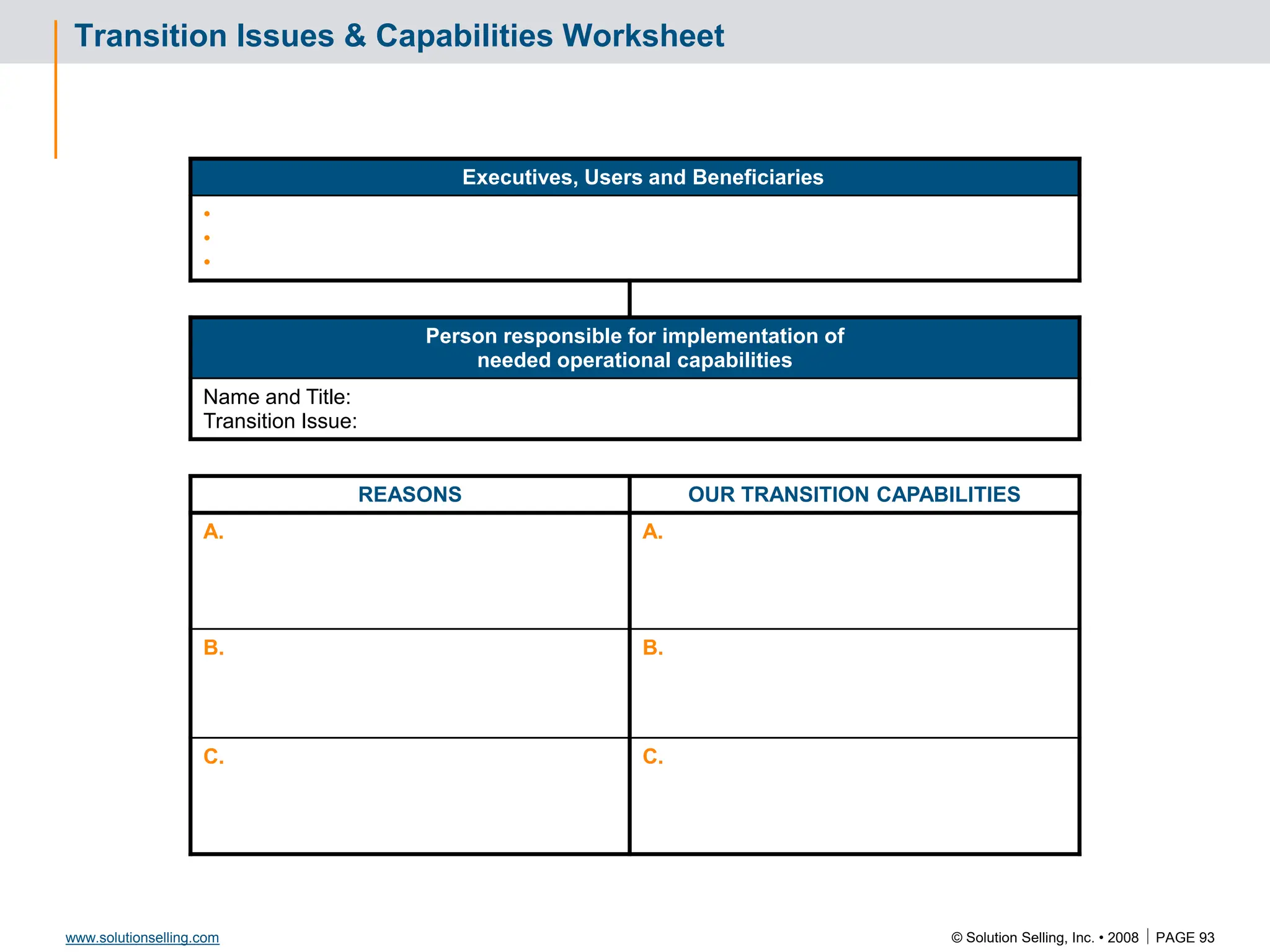
Draft Evaluation Plan: Template
[DRAFT]
Event Week of √ Responsible
Go/No
Go
Billable
* Mutual decision to proceed](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3266826-240213232649-a441385e/75/Solution-Selling-Principles-Primer-Content-88-2048.jpg)
![© Solution Selling, Inc. • 2008 PAGE 89
www.solutionselling.com
Draft Evaluation Plan: Example
Attachment to Power Sponsor Letter / e-mail
[DRAFT]
Event Week of √ Responsible
Go/No
Go
Billable
Phone interview John Watkins (CIO) Feb 14 Us/TGI
Phone interview Donna Moore (COO) Feb 14 Us/TGI
Summarize findings to management team
and agree to evaluation plan
Feb 21 Us/TGI *
Prove capabilities to management team Feb 28 Us *
Perform detailed survey of current systems (2 days) March 4 Us yes
Present preliminary solution/design March 11 Us *
Implementation plan approval by IT department March 18 TGI *
Determine / present value justification March 18 Us/TGI *
Agree on preliminary success criteria March 18 Us/TGI
Send our license agreement to legal March 18 Us
Gain legal approval (Terms & Conditions) April 4 TGI *
Visit Corporate HQ April 11 Us
Pre-proposal review meeting April 18 Us
Present proposal for approval April 25 Us *
Transition kickoff & finalize success criteria May 10 Us/TGI
Measure success criteria Ongoing TGI
* Mutual decision to proceed](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3266826-240213232649-a441385e/75/Solution-Selling-Principles-Primer-Content-90-2048.jpg)

![© Solution Selling, Inc. • 2008 PAGE 95
www.solutionselling.com
Draft Evaluation Plan: Example
Attachment to Power Sponsor Letter / e-mail
[DRAFT]
Event Week of √ Responsible
Go/No
Go
Billable
Phone interview John Watkins (CIO) Feb 14 Us/TGI
Phone interview Donna Moore (COO) Feb 14 Us/TGI
Summarize findings to management team
and agree to evaluation plan
Feb 21 Us/TGI *
Prove capabilities to management team Feb 28 Us *
Perform detailed survey of current systems (2 days) March 4 Us yes
Present preliminary solution/design March 11 Us *
Implementation plan approval by IT department March 18 TGI *
Determine / present value justification March 18 Us/TGI *
Agree on preliminary success criteria March 18 Us/TGI
Send our license agreement to legal March 18 Us
Gain legal approval (Terms & Conditions) April 4 TGI *
Visit Corporate HQ April 11 Us
Pre-proposal review meeting April 18 Us
Present proposal for approval April 25 Us *
Transition kickoff & finalize success criteria May 10 Us/TGI
Measure success criteria Ongoing TGI
* Mutual decision to proceed](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3266826-240213232649-a441385e/75/Solution-Selling-Principles-Primer-Content-96-2048.jpg)
![© Solution Selling, Inc. • 2008 PAGE 104
www.solutionselling.com
Draft Evaluation Plan: Example
Attachment to Power Sponsor Letter / e-mail
[DRAFT]
Event Week of √ Responsible
Go/No
Go
Billable
Phone interview John Watkins (CIO) Feb 14 Us/TGI
Phone interview Donna Moore (COO) Feb 14 Us/TGI
Summarize findings to management team
and agree to evaluation plan
Feb 21 Us/TGI *
Prove capabilities to management team Feb 28 Us *
Perform detailed survey of current systems (2 days) March 4 Us yes
Present preliminary solution/design March 11 Us *
Implementation plan approval by IT department March 18 TGI *
Determine / present value justification March 18 Us/TGI *
Agree on preliminary success criteria March 18 Us/TGI
Send our license agreement to legal March 18 Us
Gain legal approval (Terms & Conditions) April 4 TGI *
Visit Corporate HQ April 11 Us
Pre-proposal review meeting April 18 Us
Present proposal for approval April 25 Us *
Transition kickoff & finalize success criteria May 10 Us/TGI
Measure success criteria Ongoing TGI
* Mutual decision to proceed](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3266826-240213232649-a441385e/75/Solution-Selling-Principles-Primer-Content-105-2048.jpg)
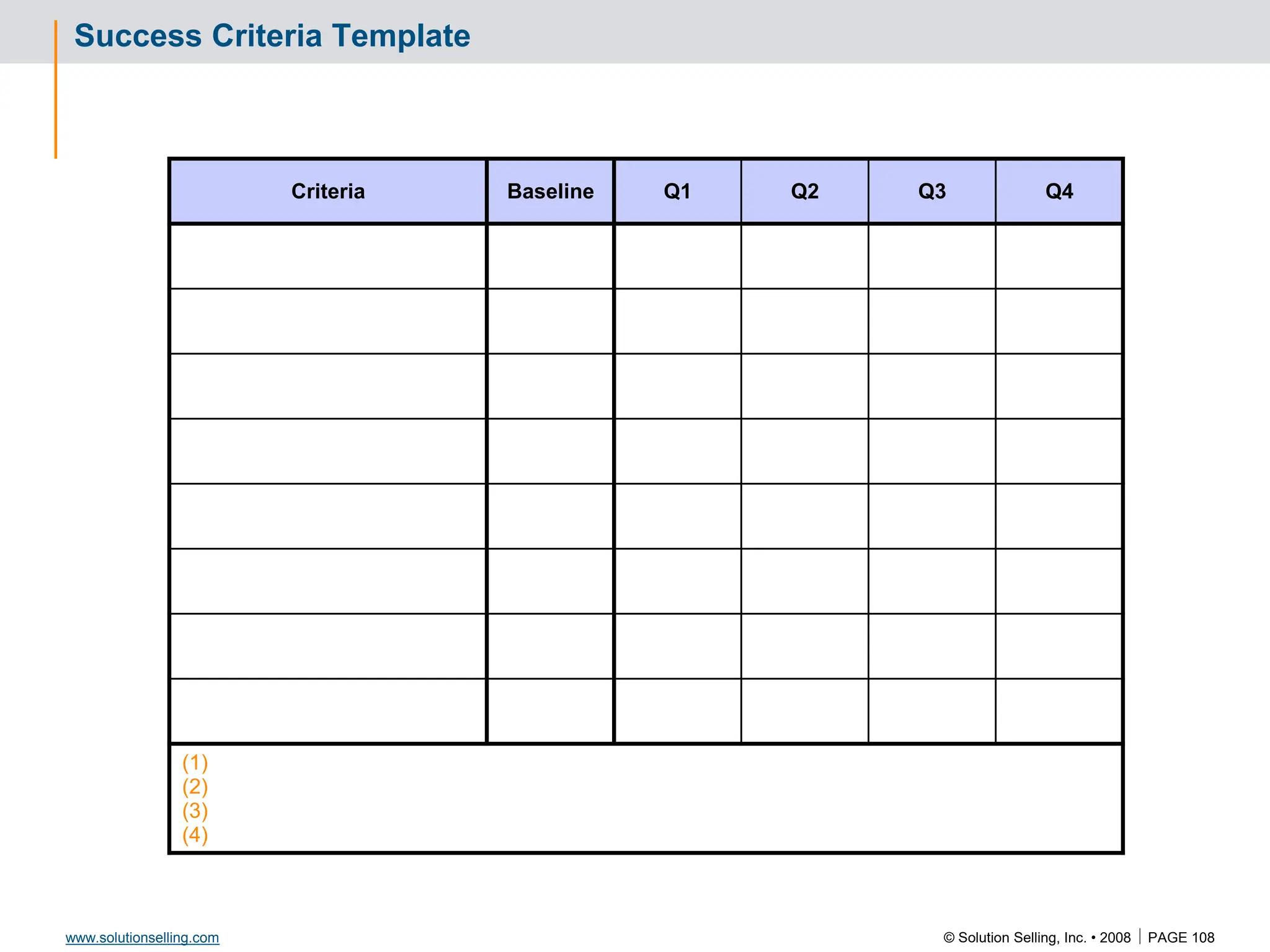
![© Solution Selling, Inc. • 2008 PAGE 105
www.solutionselling.com
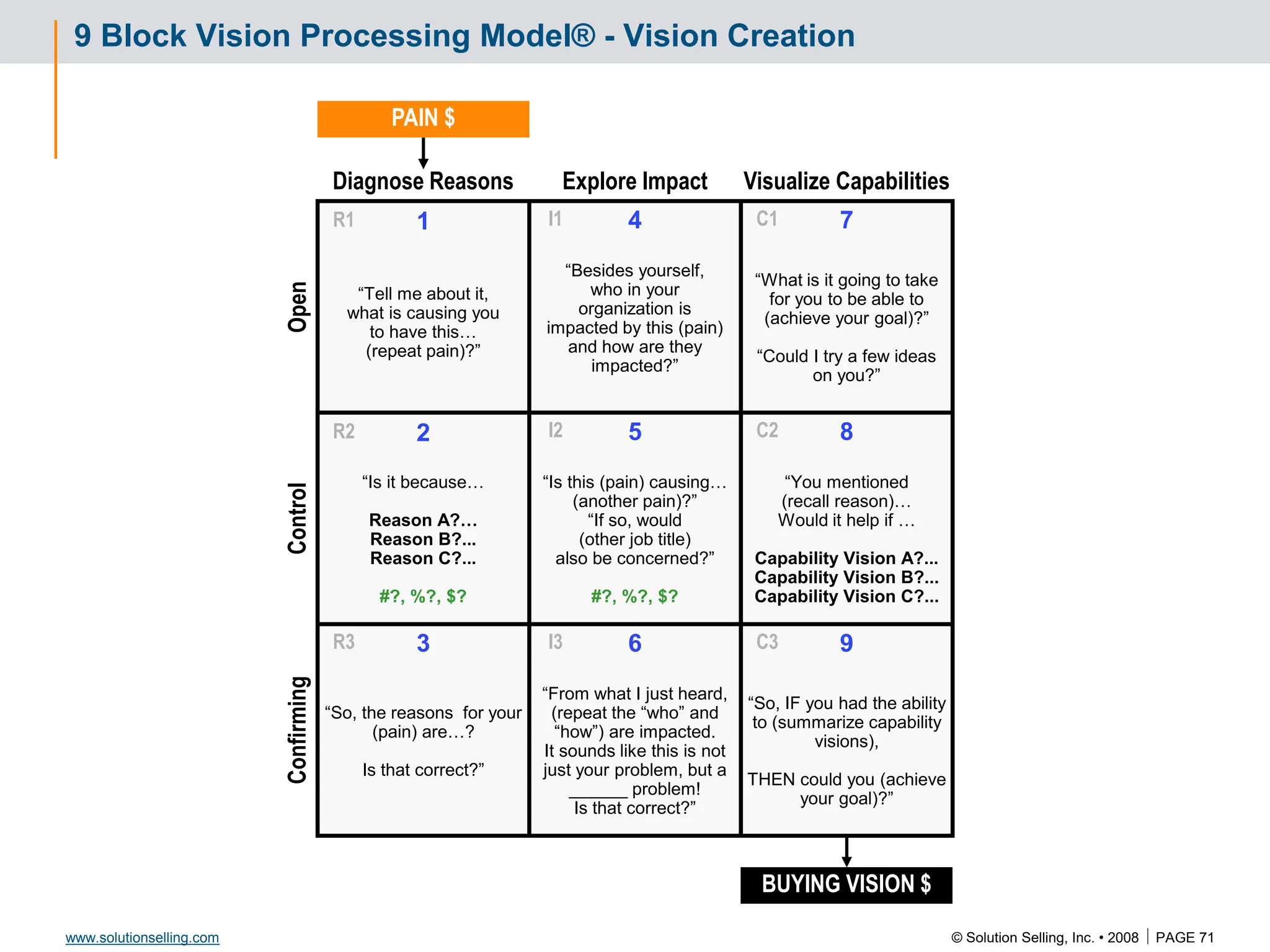
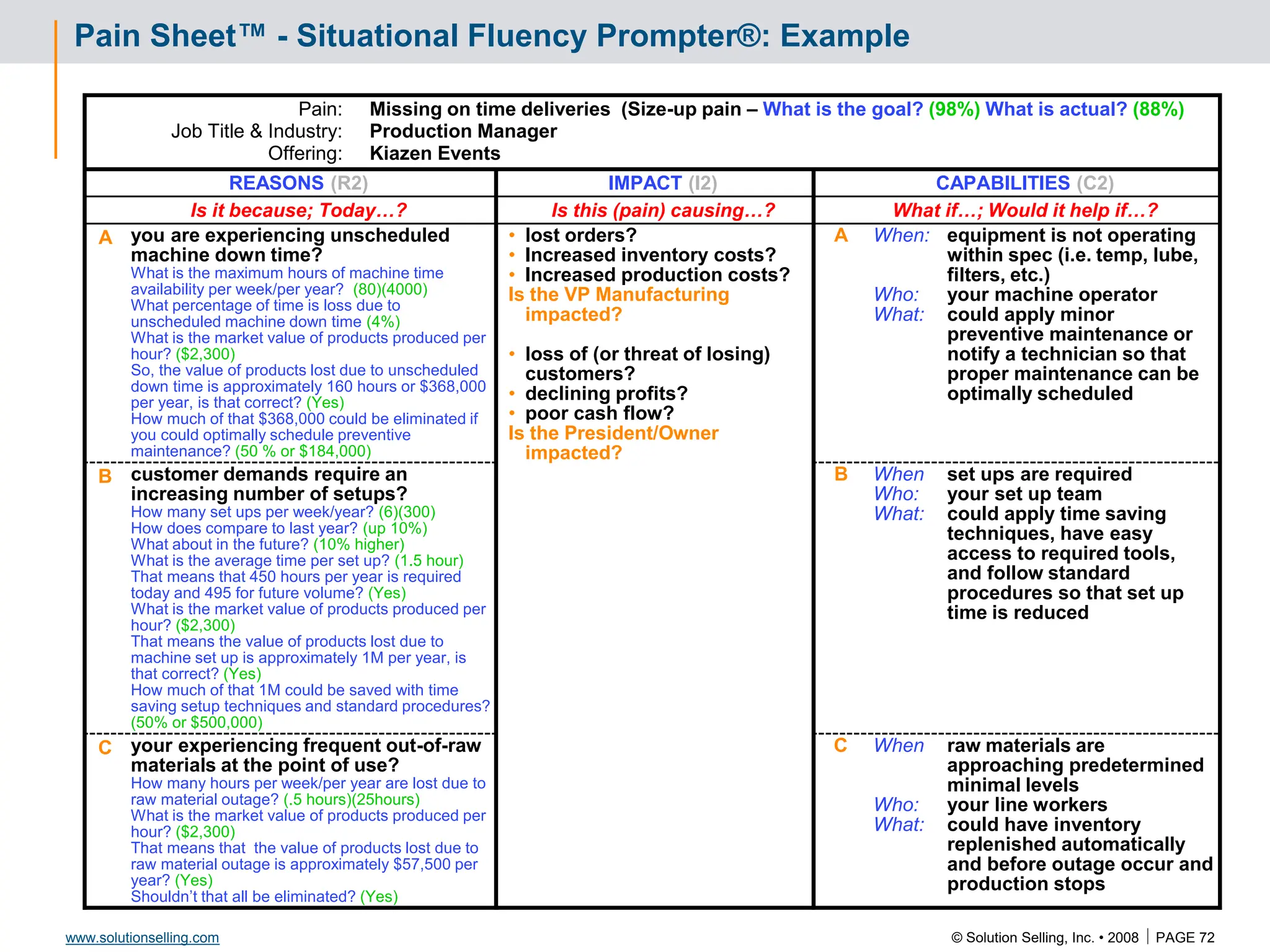
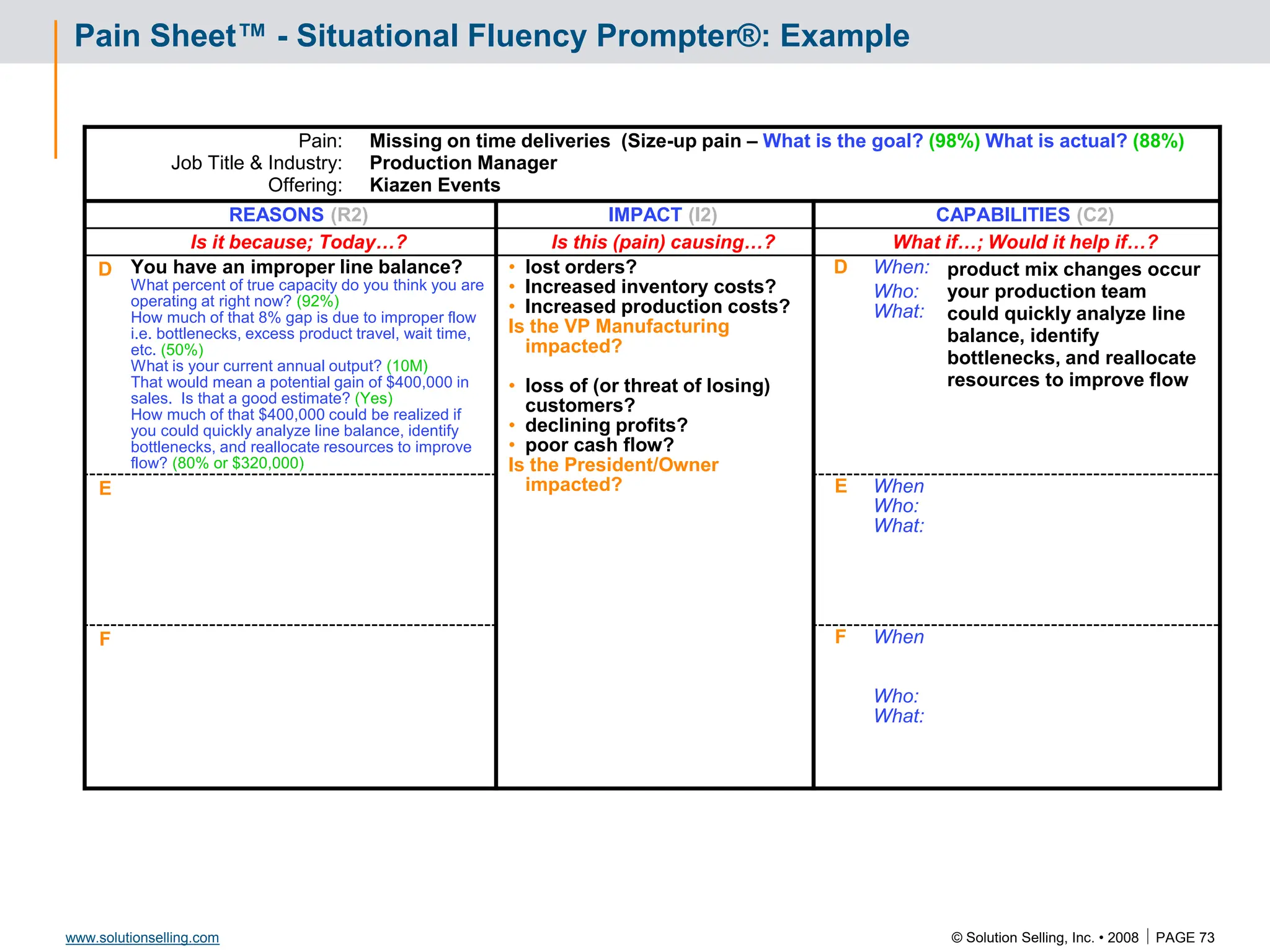
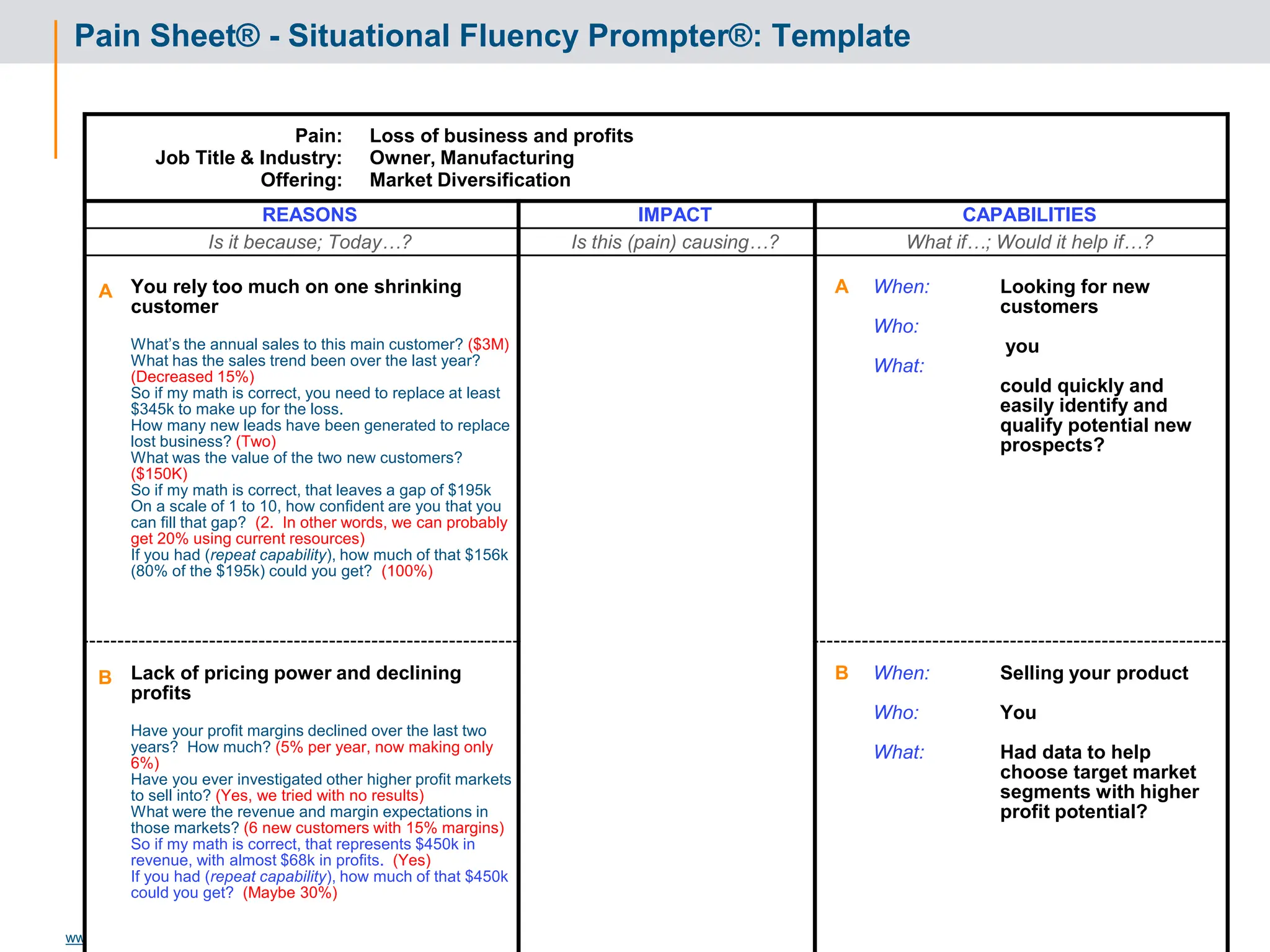
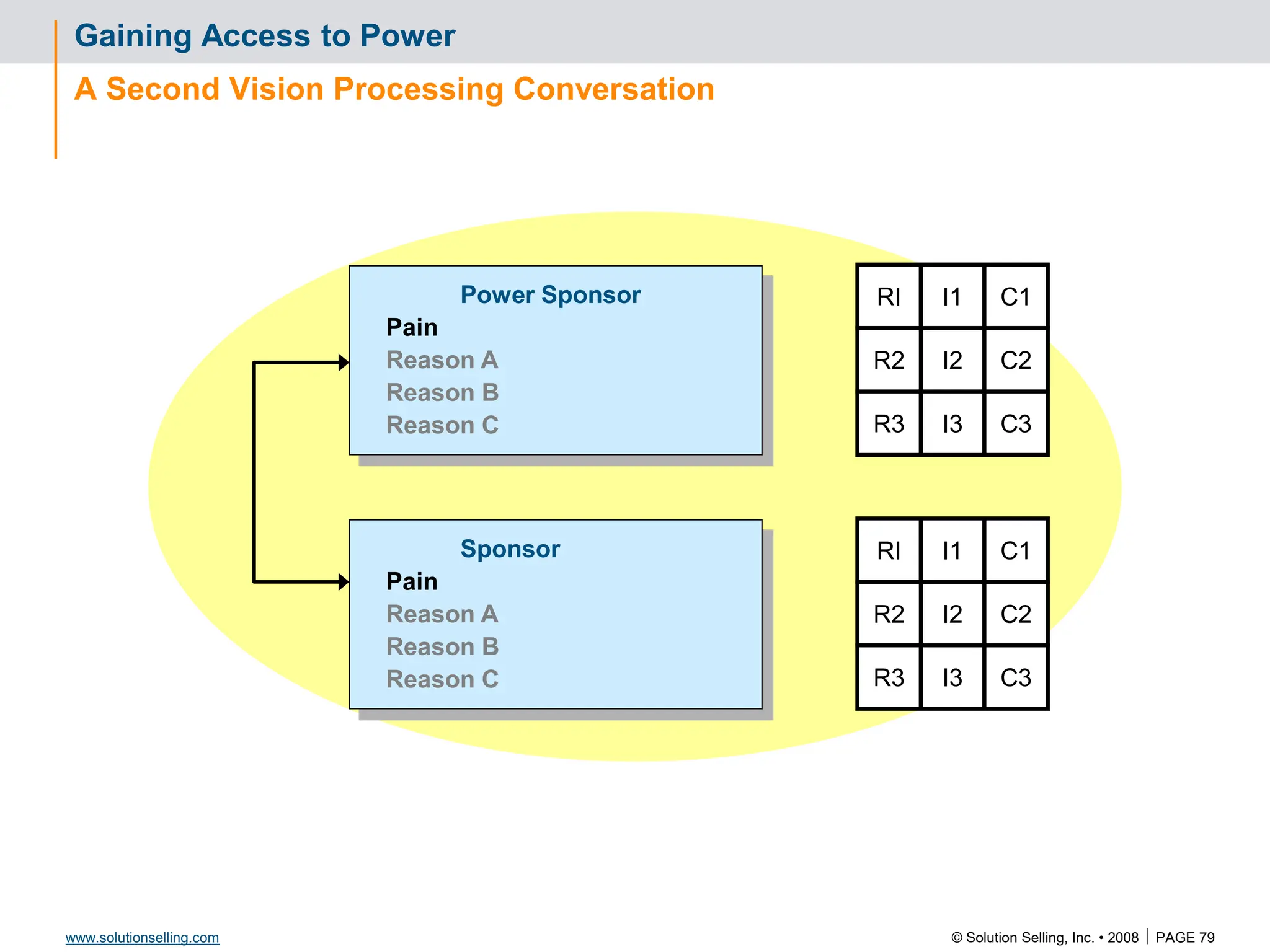
Success Criteria: Leveraging Success
Criteria Baseline Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4
I2 C2
RI
R2
I1 C1
R3 I3 C3
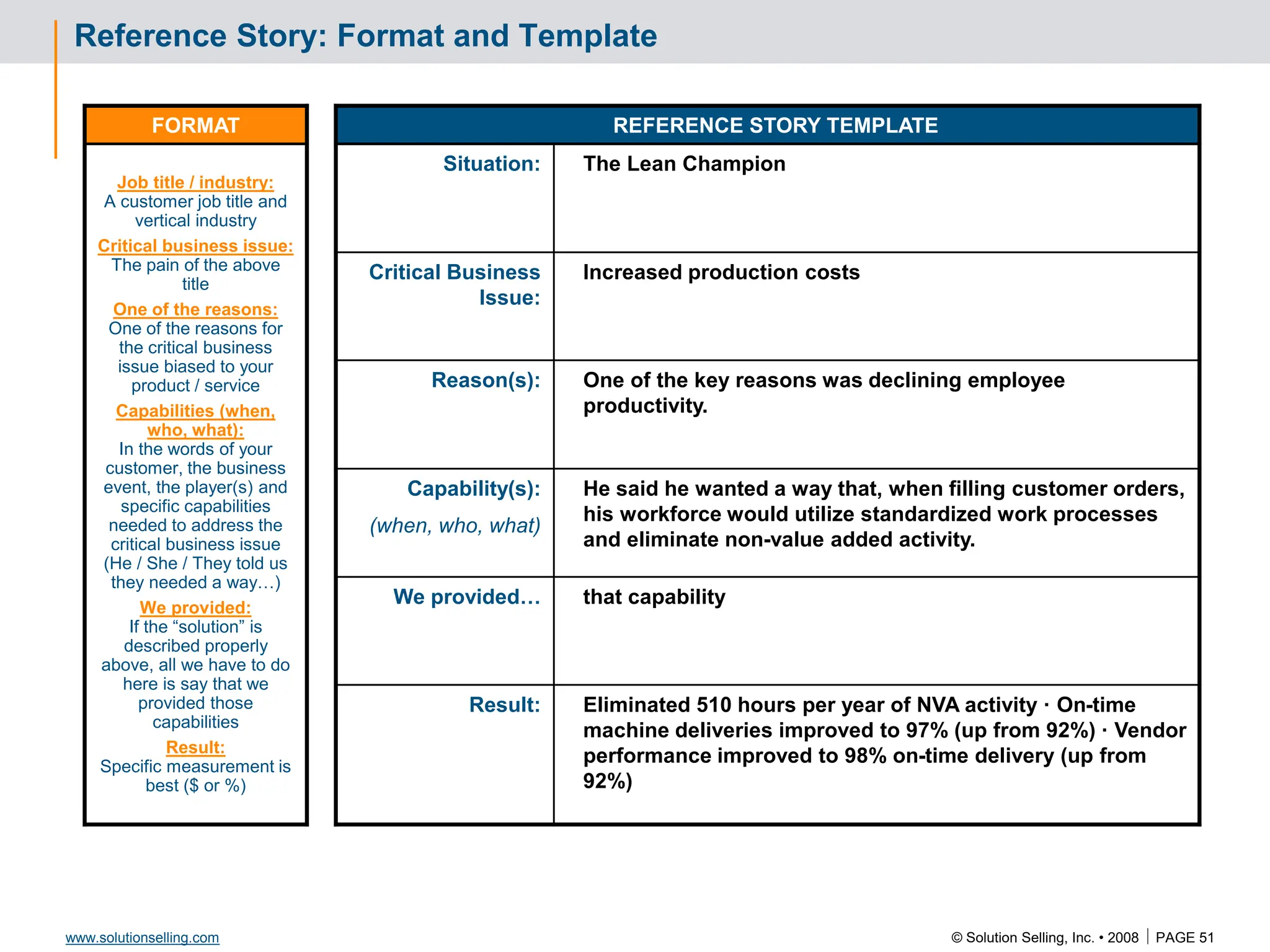
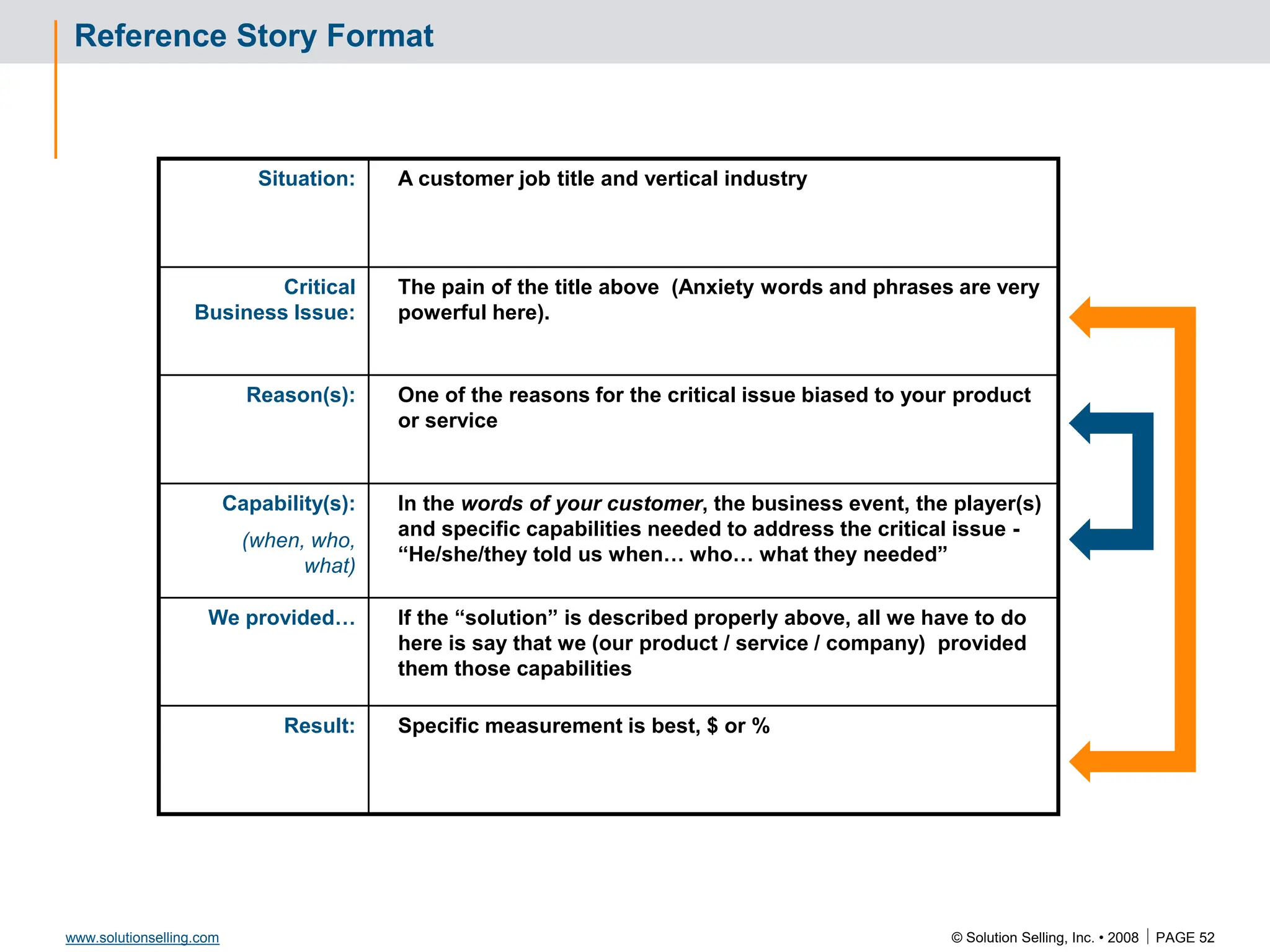
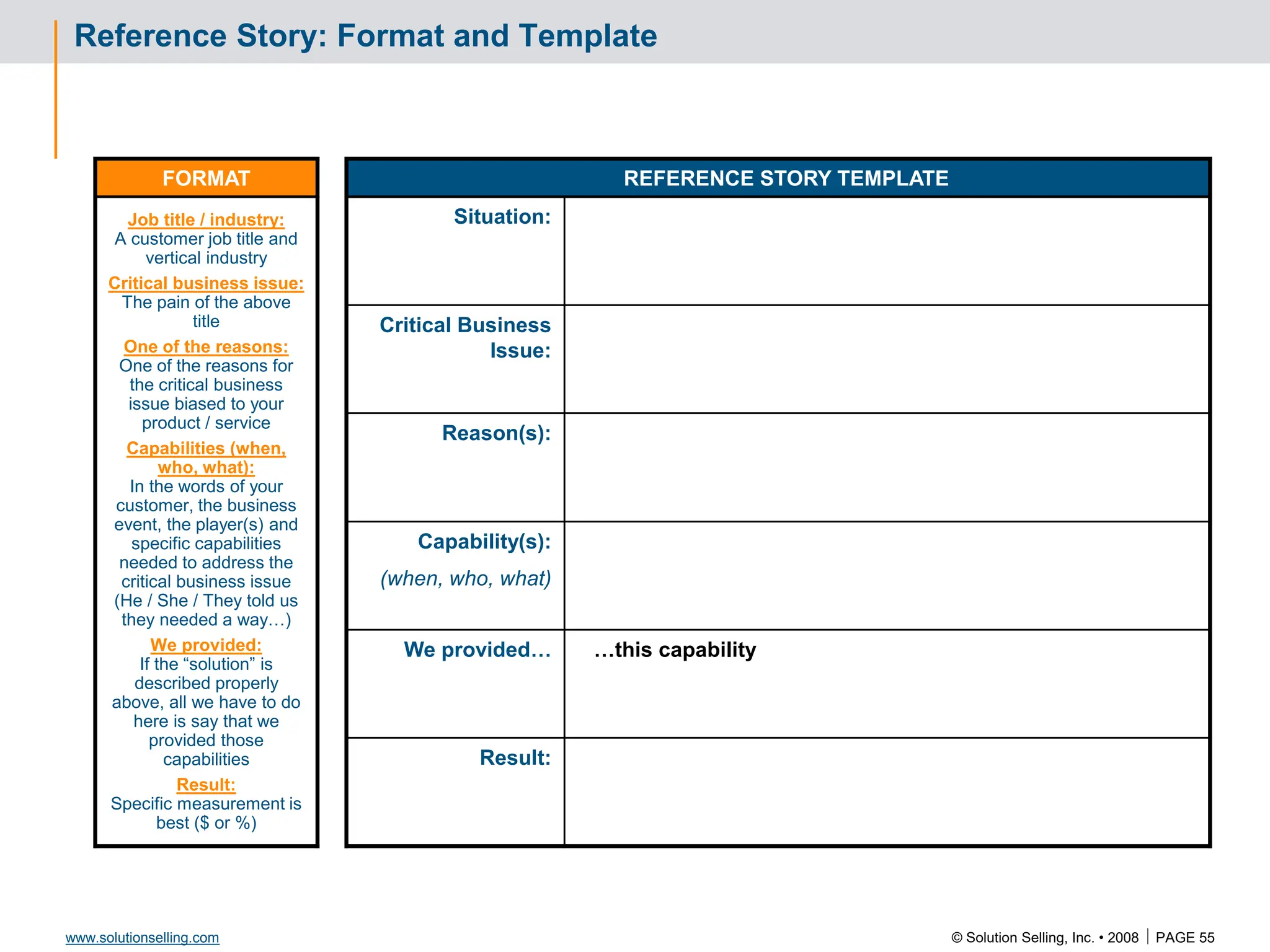
Reference Story
Situation:
Critical issue:
Reasons:
Capabilities:
We provided:
Results:
Business Development Prompter: New Opportunity
This is __________ (salesperson name) with __________ (your company). You and I
haven’t spoken before, but we have been working with __________ (specific industry)
organizations for the last ___ (#) years. A common trend we are hearing lately from other
__________ (job title) is their frustration (difficulty) with _______________ (job title’s likely
critical issue / pain) [resulting from ______ (articulate common reasons)]. We have been
able to help our customers address this issue. Would you like to know how?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3266826-240213232649-a441385e/75/Solution-Selling-Principles-Primer-Content-106-2048.jpg)