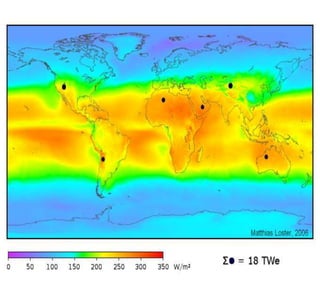
The document discusses recent trends in solar energy. It provides details about how solar panels work by converting sunlight into electrical energy using the photovoltaic effect in semiconductor materials like silicon. It also discusses the construction of different types of solar panels and factors that determine their efficiency. Advantages of solar energy include reduced environmental impact compared to fossil fuels and various applications from powering homes and vehicles to smaller devices.