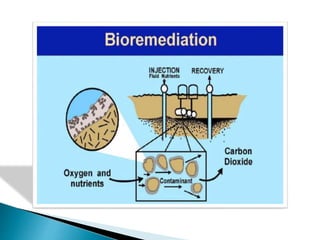
The document discusses soil contamination, its causes from both natural and human activities, and various techniques for soil remediation. It describes how soil can become contaminated from accidental spills, mining, agriculture, transportation, dumping, and landfills. Common soil remediation techniques mentioned include bioremediation, thermal desorption, encapsulation, chemical oxidation, stabilization, soil washing, and soil disposal. The document concludes by recommending banning plastic bags, increasing recycling and plantation programs, and raising awareness to reduce soil contamination.