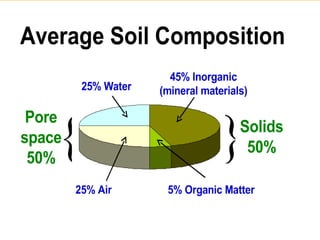
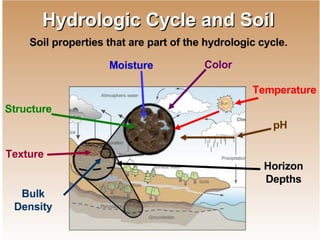
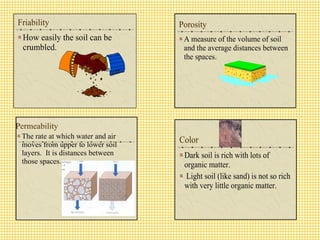
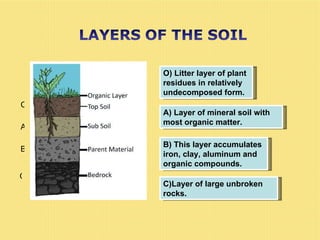
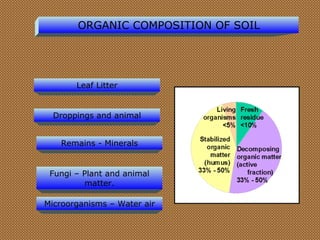
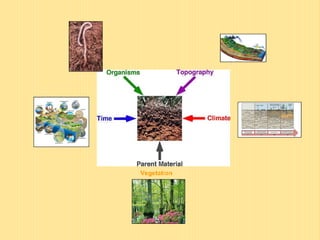
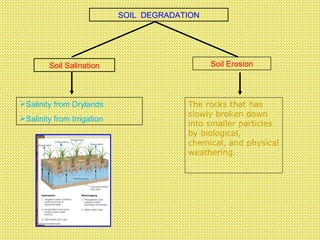
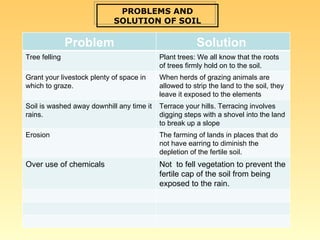
The document discusses the use and importance of soil as a natural resource, highlighting its various layers, properties, and roles in supporting life. It emphasizes the necessity of soil conservation practices due to problems like erosion, degradation, and contamination. Solutions for maintaining healthy soil include sustainable agricultural methods, tree planting, and managing livestock grazing.