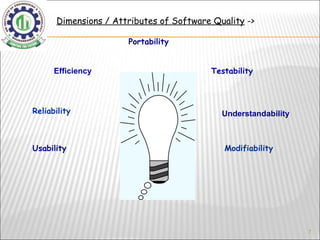
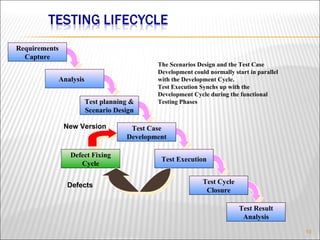
The document discusses software testing fundamentals including what testing is, why it's important, the testing lifecycle, principles, and process. It explains that testing verifies requirements are implemented correctly, finds defects before deployment, and improves quality and reliability. Various testing techniques are covered like unit, integration, system, manual and automation testing along with popular testing tools like Mercury WinRunner, TestDirector, and LoadRunner.