Functional testing types include:
- Testing functionality according to requirements
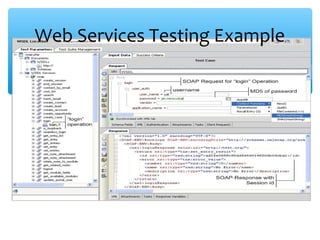
- Testing web services interfaces and compliance with standards
- Conducting testing for software version changes and data migration
Non-functional testing types include:
- Performance testing to ensure systems meet specified performance levels
- Load testing to identify bottlenecks and determine behavior under heavy loads
- Stress testing to detect errors under excessive operational capacity
- Compatibility testing to ensure applications work in different environments
- Security testing to adopt security procedures and probe for vulnerabilities
- Usability testing to evaluate from an end-user perspective


















![• Software maintenance is the modification of a software
product after delivery to correct faults, to improve
performance or other attributes, or to adapt the
product to a modified environment. (IEEE 1219)
• The software product undergoes modification to code
and associated documentation due to a problem or the
need for improvement. The objective is to modify the
existing software product while preserving its integrity.
ISO/IEC [ISO95]
Maintenance Testing](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwarequalityandtestingfunc-170402091552/85/Software-quality-and-testing-func-amp-non-func-20-320.jpg)





















