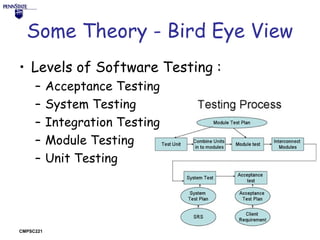
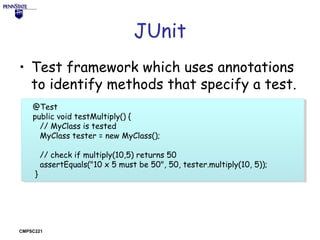
The document discusses the importance of software testing and provides examples of why it is needed. It describes an incident where a radiation therapy machine caused patient deaths due to a lack of software testing. It then lists some of the key benefits of testing such as bug discovery and prevention, improving quality, and gaining confidence in code. The document also provides an overview of different levels of software testing from unit to acceptance testing and describes tools like JUnit that can be used to make testing easier.












![Test Methods
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
fail(String)
assertTrue([message], boolean condition)
assertFalse([message], boolean condition).
assertEquals([String message], expected, actual)
assertEquals([String message], expected, actual,
tolerance)
assertNull([message], object)
assertNotNull([message], object)
assertSame([String], expected, actual)
assertNotSame([String], expected, actual)
CMPSC221](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwaretesting-131210010550-phpapp02/85/Software-testing-15-320.jpg)




