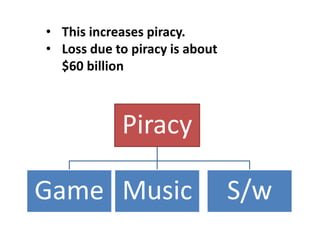
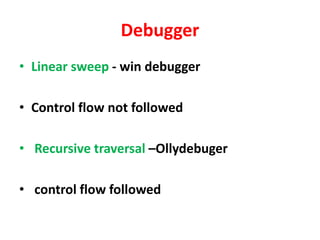
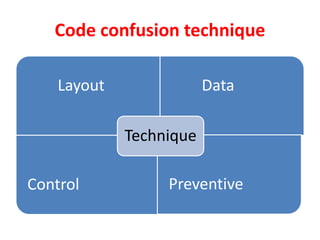
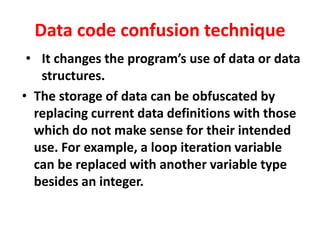
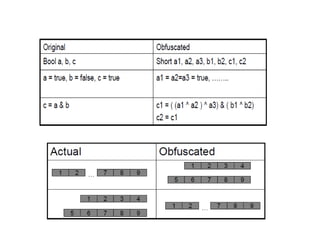
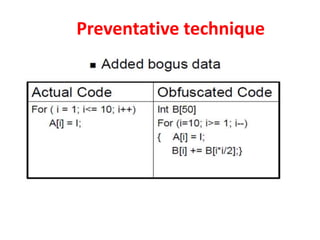
The document summarizes various techniques for copy protection and preventing software cracking, including hardware-based protection using USB devices, serial key generation, encryption, debug blocking, and code confusion techniques. Code confusion involves obfuscating source code through renaming identifiers, removing debugging information, modifying data and control flow, and inserting confusing code to make the software difficult for humans and debuggers to understand and reverse engineer. The goal is to prevent piracy and protect against $60 billion in estimated annual losses.