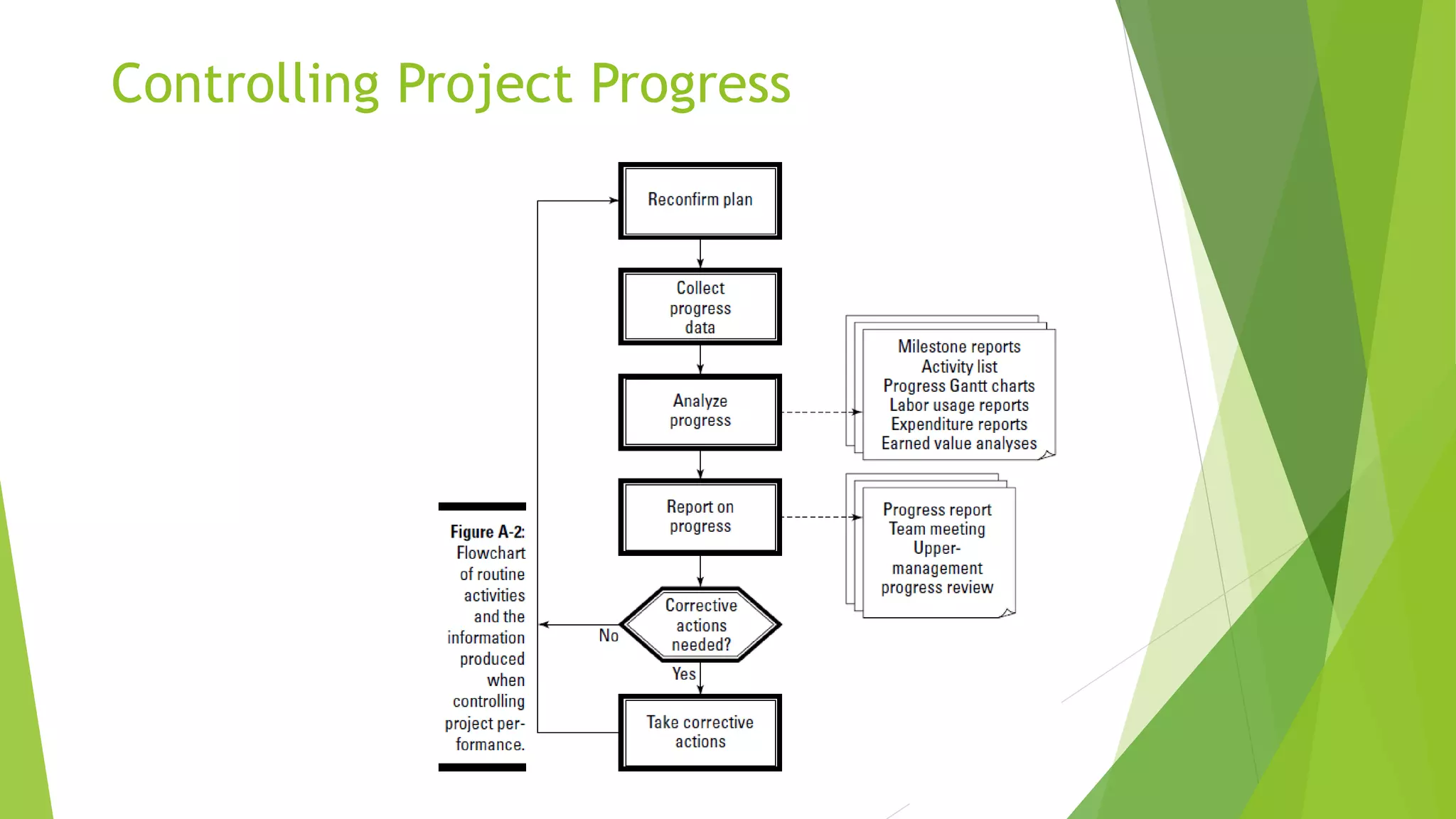
The document provides essential tips and strategies for effective software project management, emphasizing the importance of planning, scheduling, and risk management while highlighting key skills and qualities of successful project managers. It outlines Agile principles that focus on communication, customer satisfaction through early delivery, and maintaining simplicity in development to enhance efficiency. Ultimately, the effectiveness of project management relies on a combination of good practices, proactive approaches, and continuous adaptation to changes.