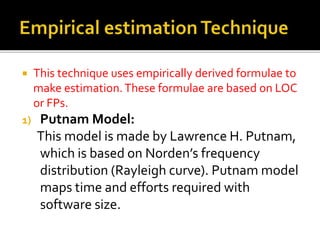
Estimation determines the resources needed to build a system and involves estimating the software size, effort, time, and cost. It is based on past data, documents, assumptions, and risks. The main steps are estimating the software size, effort, time, and cost. Software size can be estimated in lines of code or function points. Effort estimation calculates person-hours or months based on software size using formulas like COCOMO-II. Cost estimation considers additional factors like hardware, tools, personnel skills, and travel. Techniques for estimation include decomposition and empirical models like Putnam and COCOMO, which relate size to time and effort.