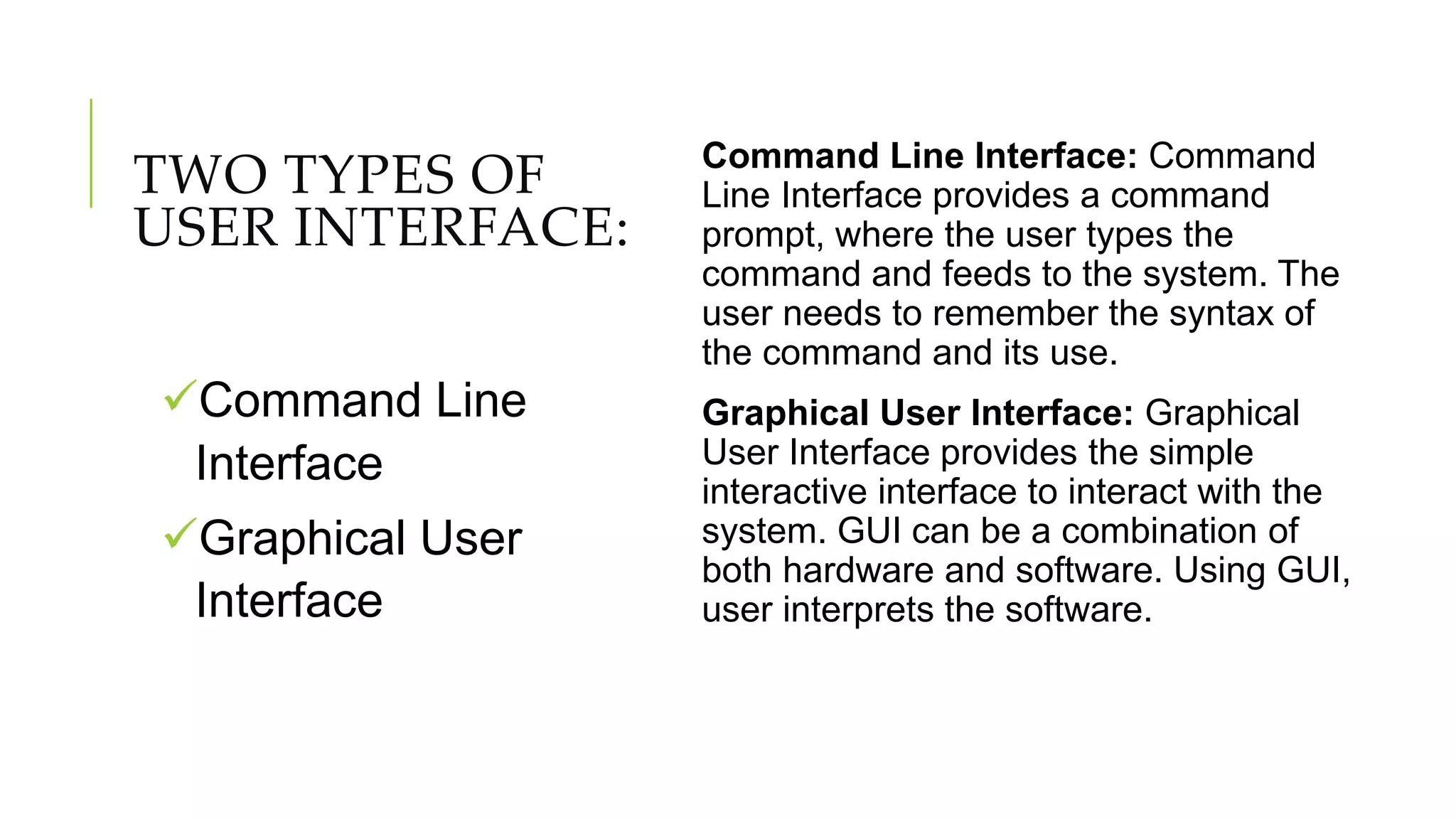
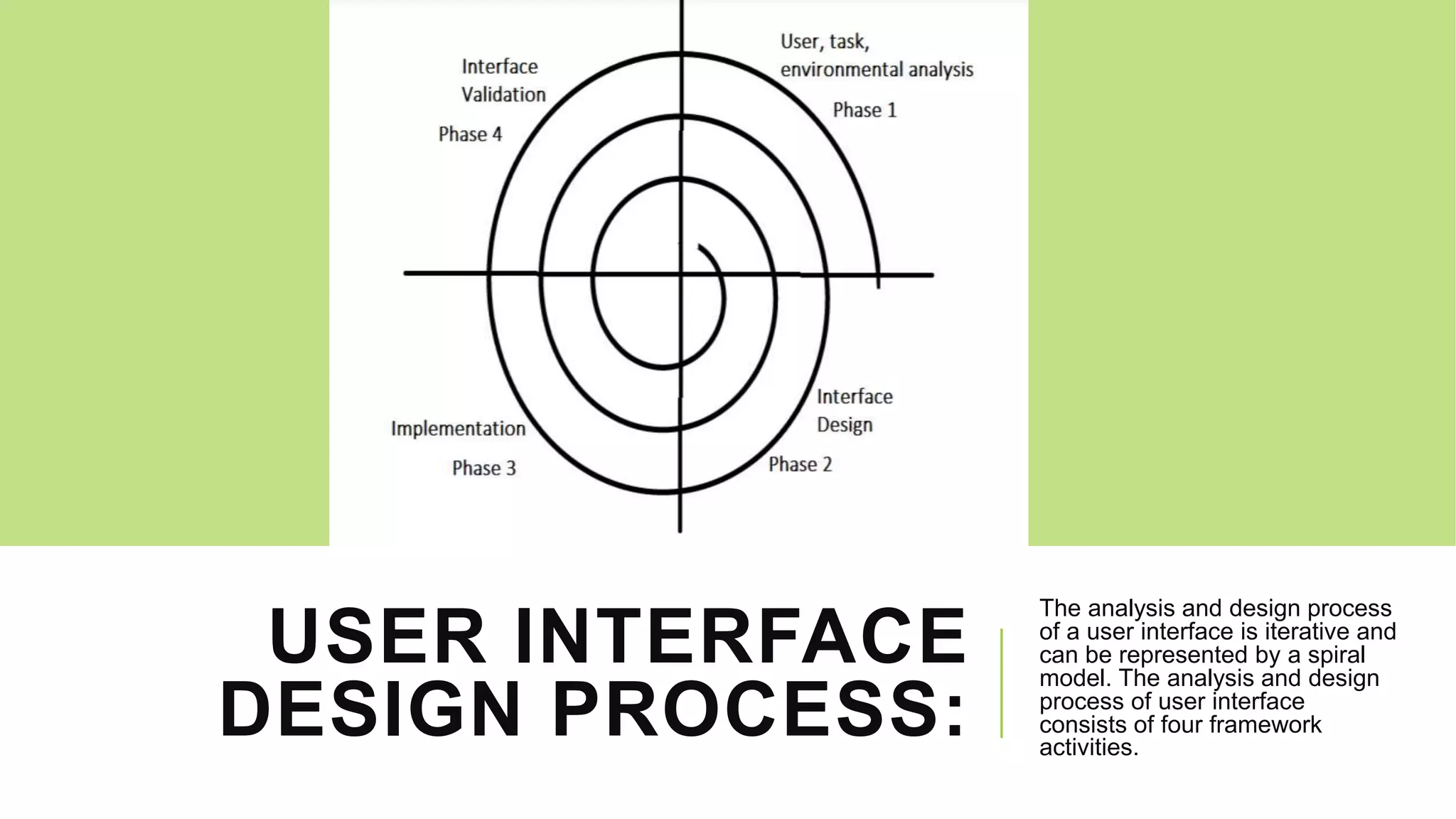
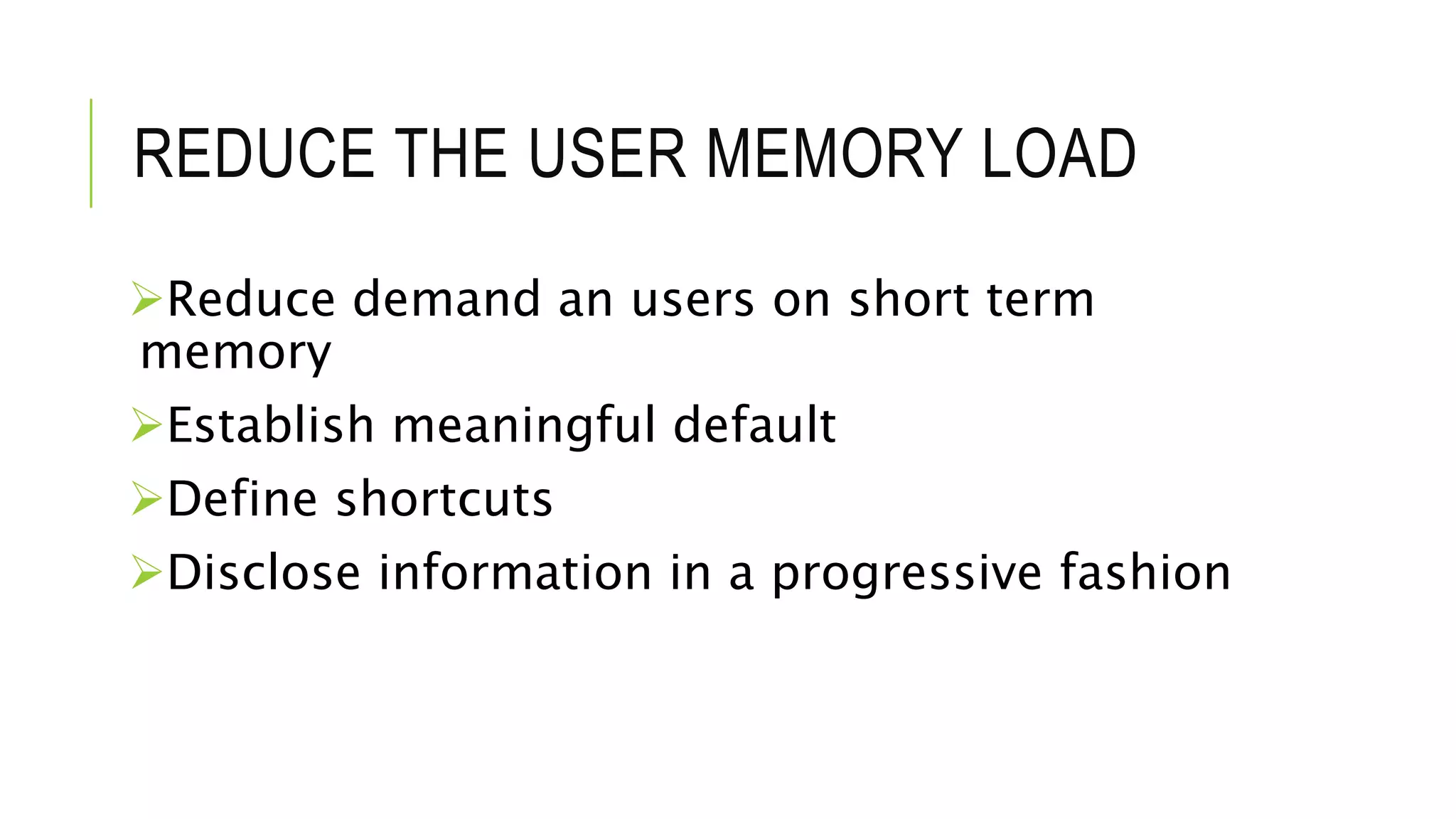
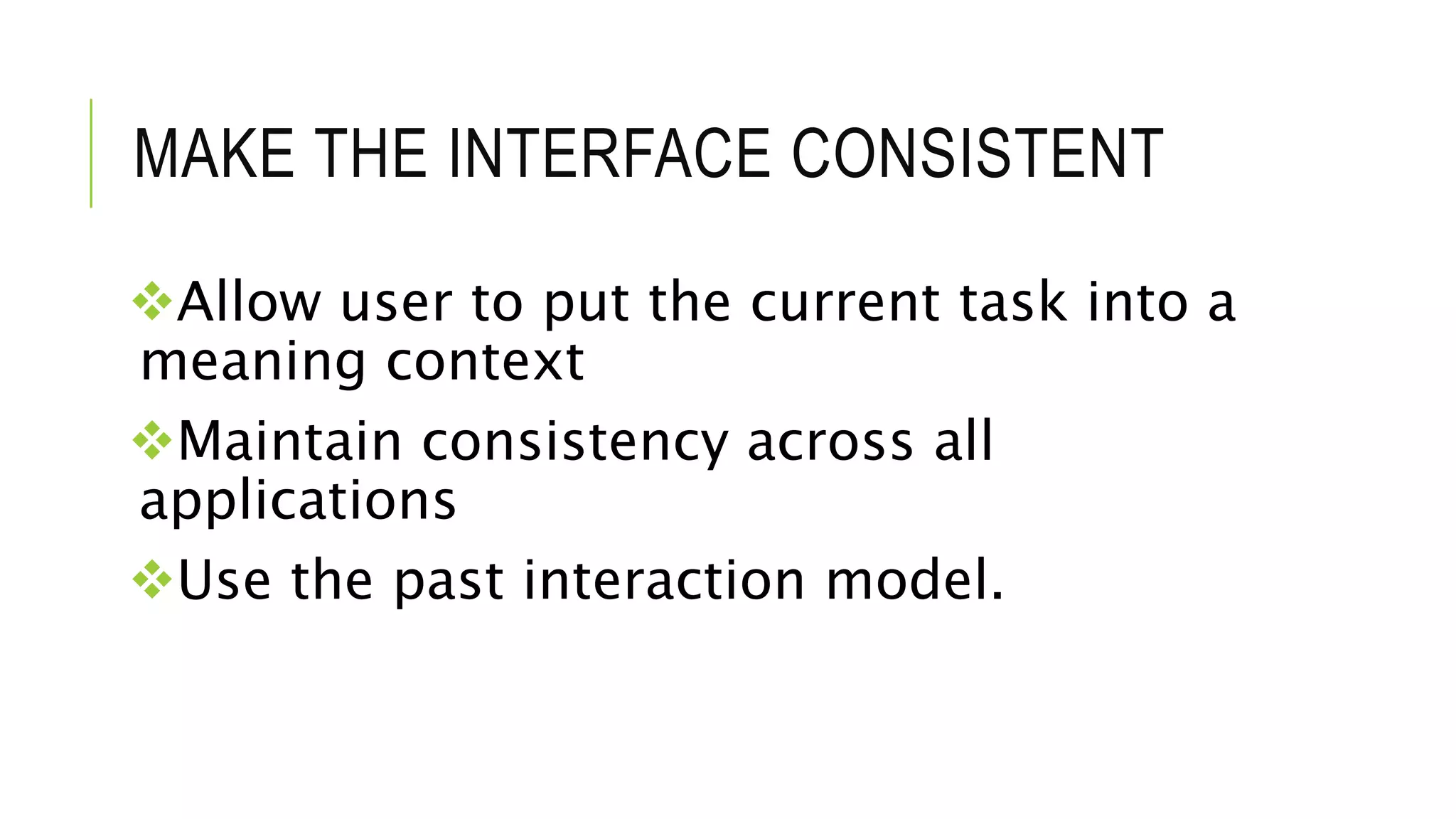
The document discusses user interface (UI) design in software engineering, highlighting the importance of attractive, simple, responsive, clear, and consistent UIs. It outlines two types of UIs: command-line interfaces and graphical user interfaces, and details the iterative design process, which includes user analysis, interface design, implementation, and validation. Key techniques for effective UI include placing the user in control, reducing memory load, and ensuring consistency across interfaces.