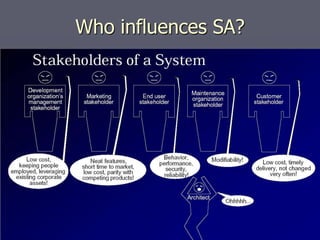
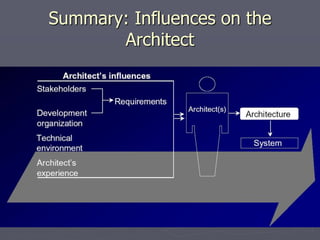
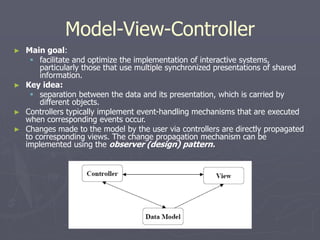
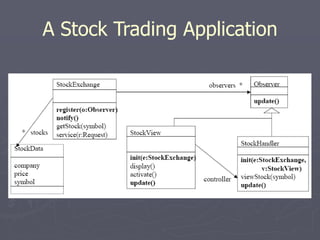
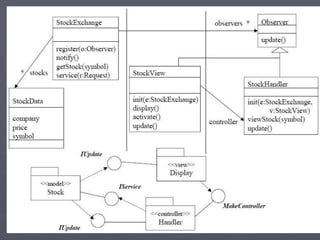
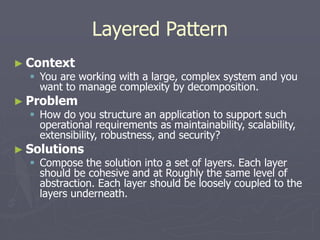
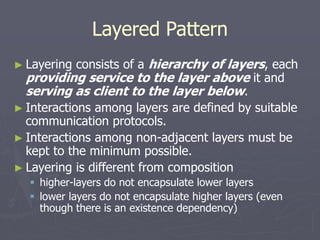
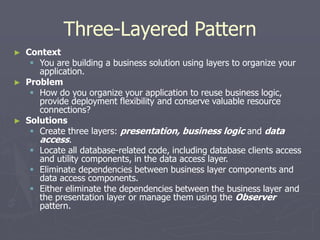
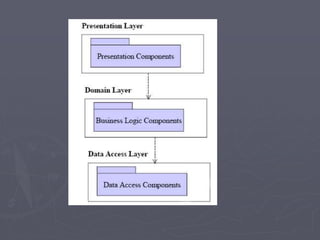
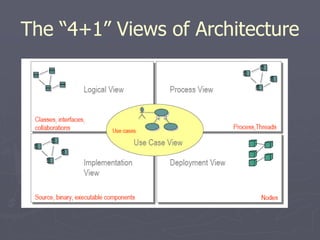
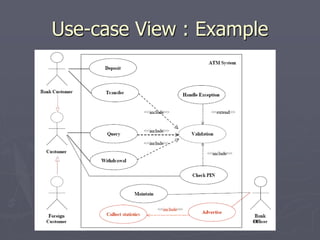
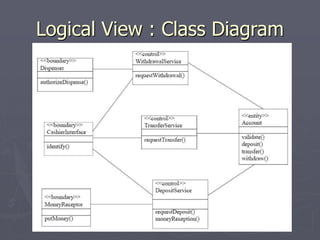
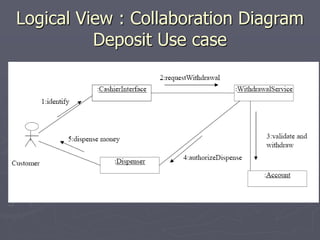
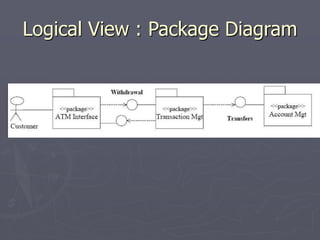
The document introduces software architecture and describes key aspects of documenting a software architecture. It defines software architecture as the structure of components and relationships in a system. It outlines the 4+1 views model for documenting architecture, including use case, logical, process, deployment, and code views. It provides examples of architectural patterns like model-view-controller and layered patterns. It describes how a software architecture document outlines architectural goals, constraints, and quality attributes.