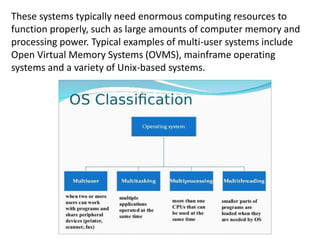
This document provides an overview of software and operating systems. It begins by defining computer software and classifying it into two main categories: system software and application software. System software manages computer hardware and provides a platform for running other software. Application software allows users to perform useful tasks. The document then focuses on operating systems, describing them as the most important system software. It explains the basic functions of operating systems, such as controlling hardware access and managing files, and classifies operating systems based on features like single-user vs multi-user capabilities.