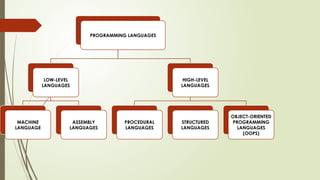
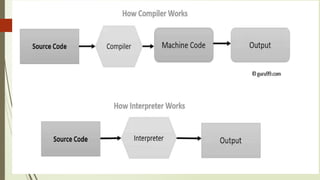
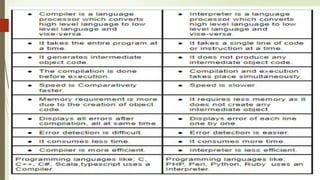
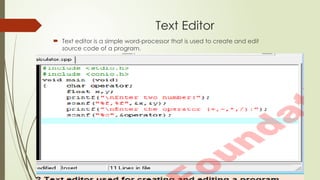
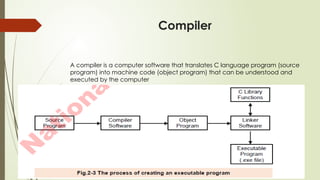
Chapter 2 covers the essentials of programming in C, including the structure of a C program, types of languages, and characteristics of both low and high-level languages. It explains the concepts of syntax, semantics, and programming paradigms like procedural and object-oriented programming, and highlights notable high-level languages such as C, C++, Visual Basic, C#, and Java. Additionally, it details the programming environment and tools like IDEs, compilers, and debuggers used in C programming.