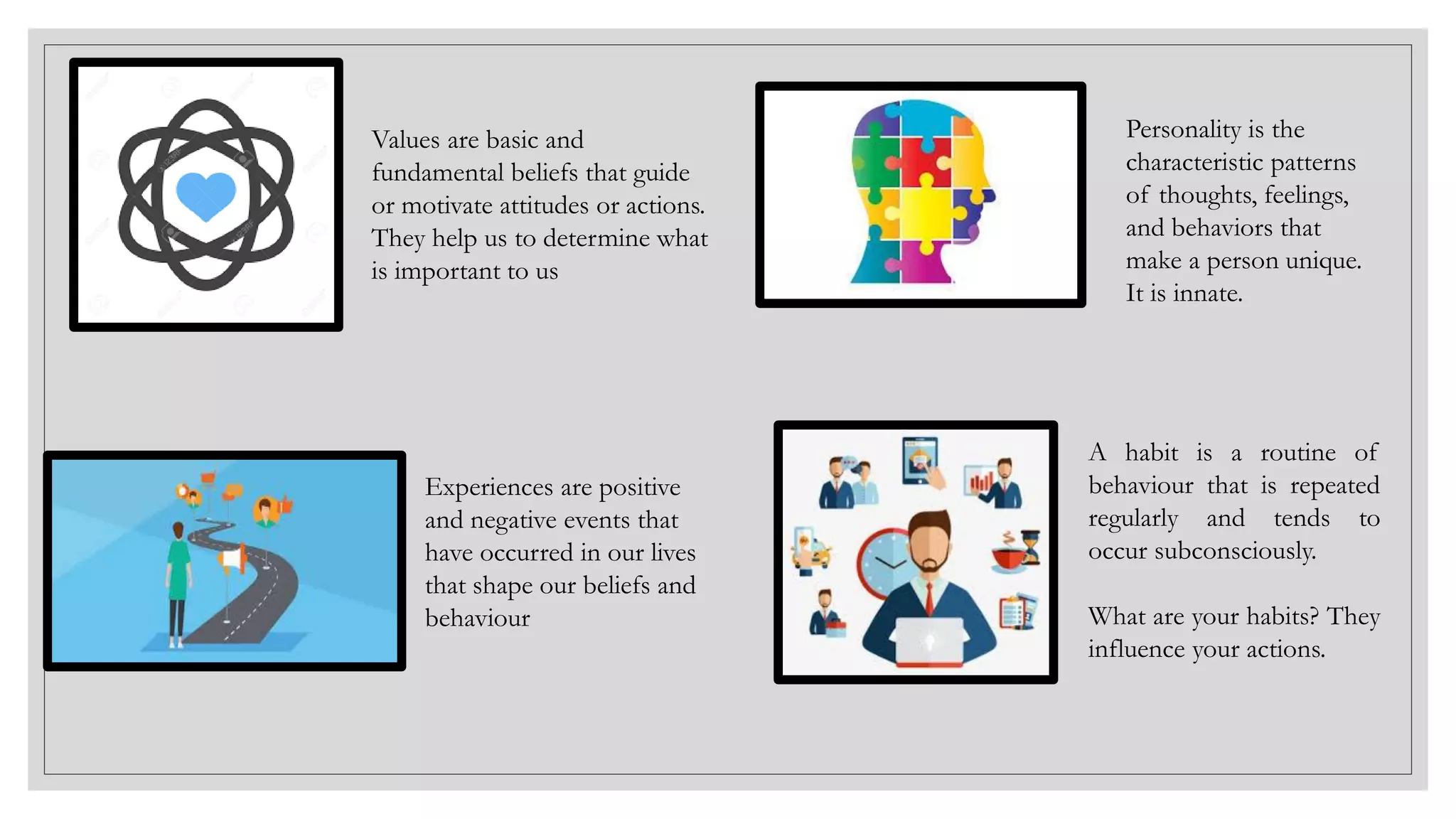
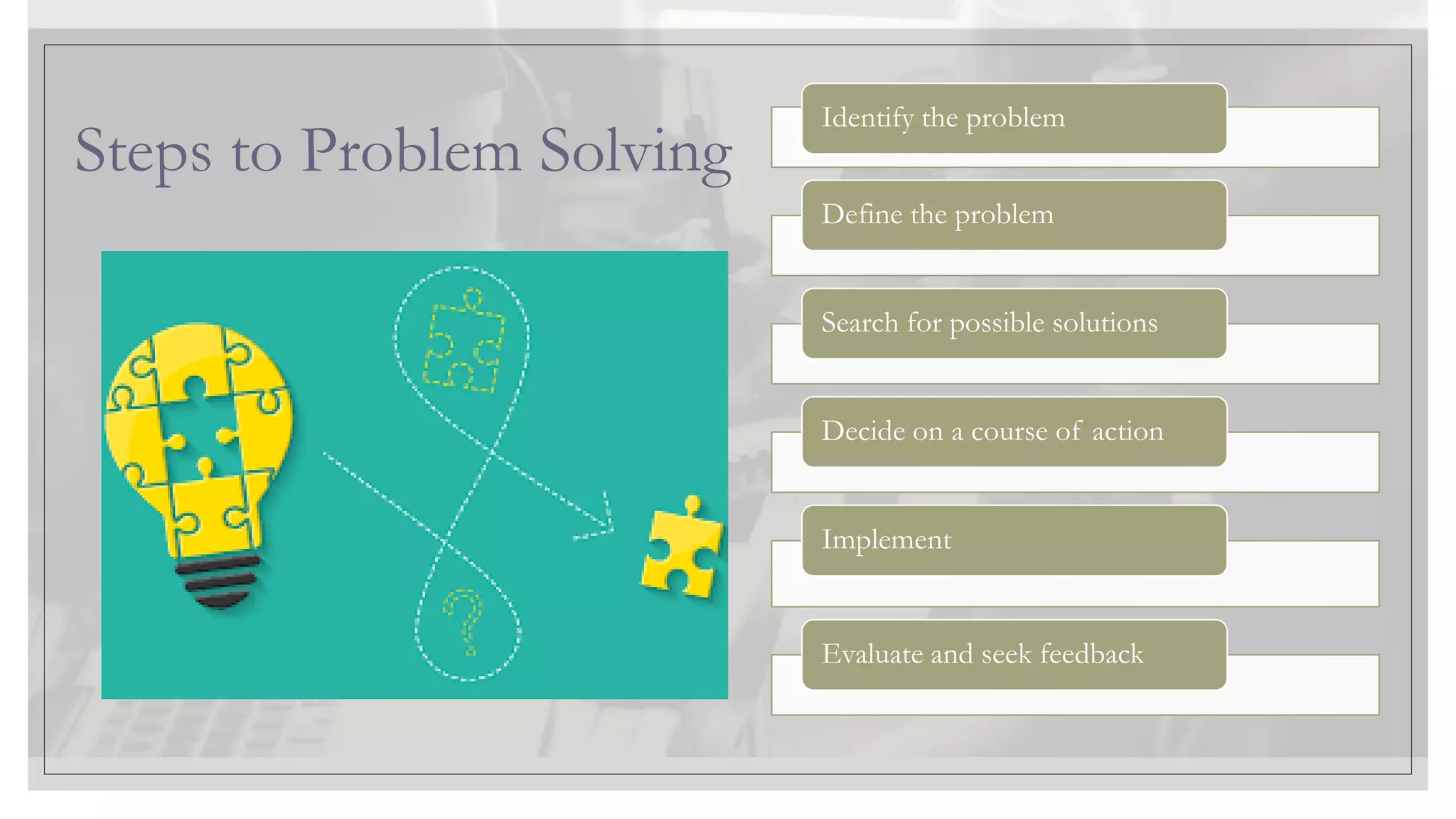
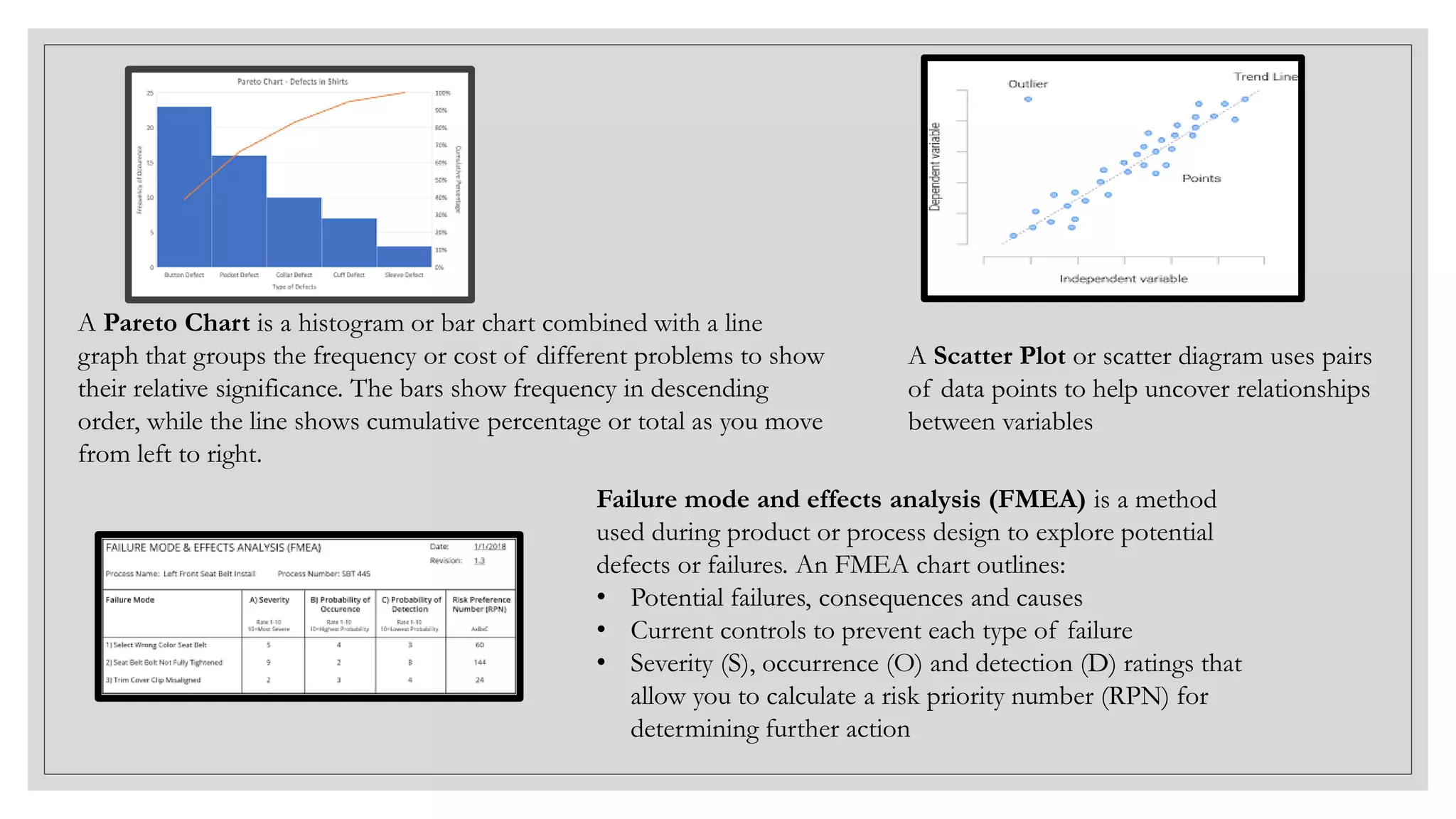
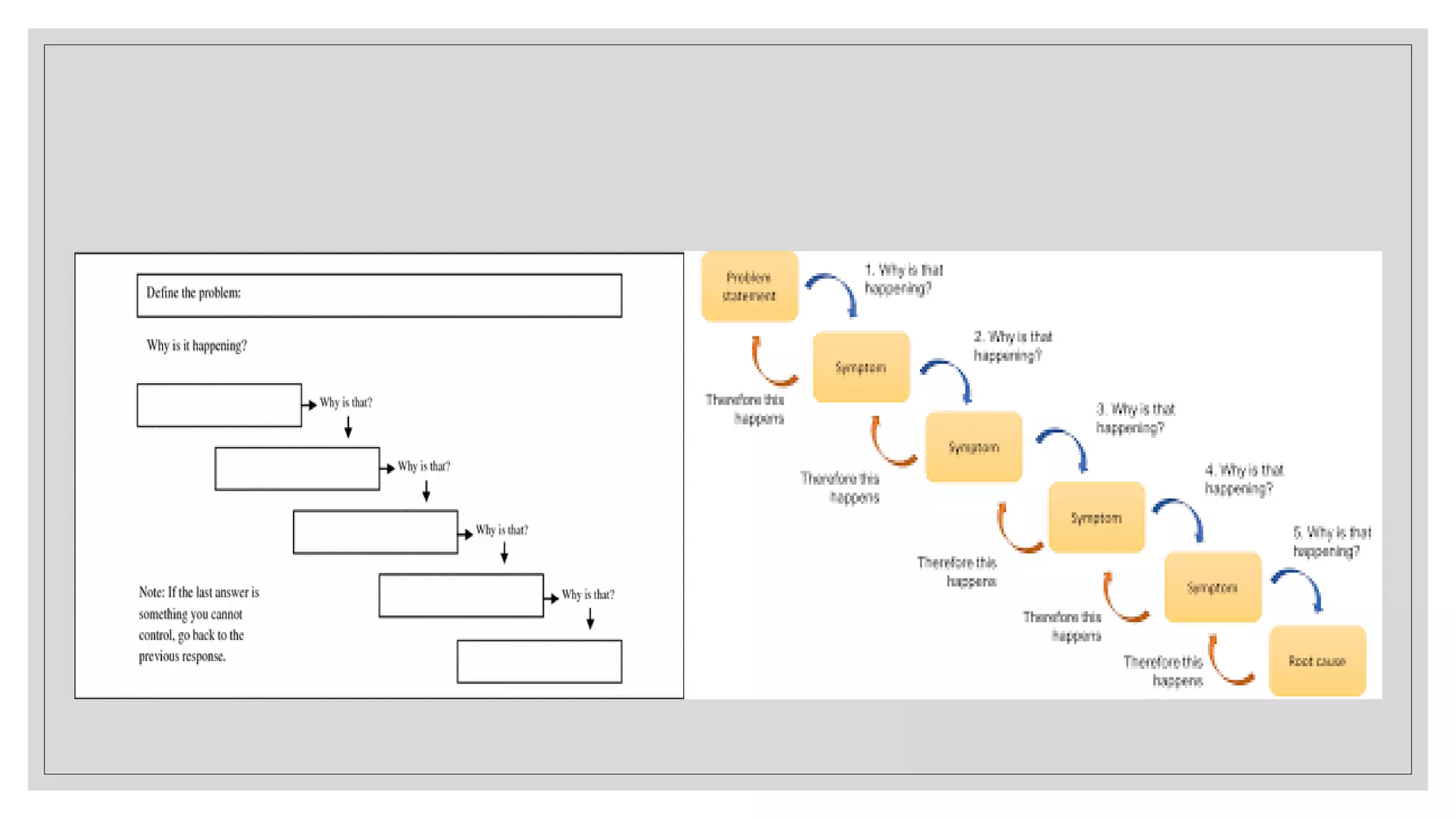
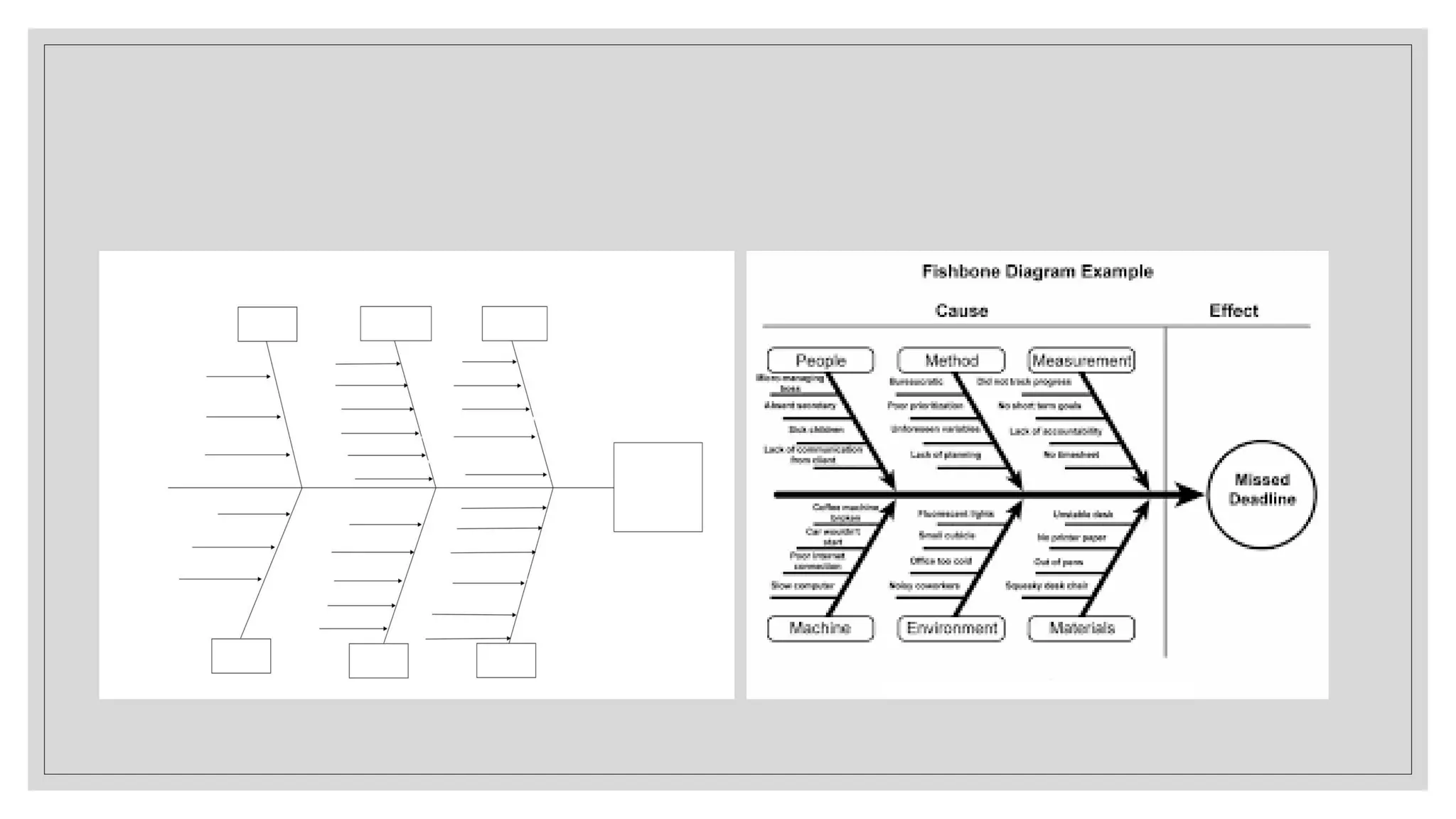
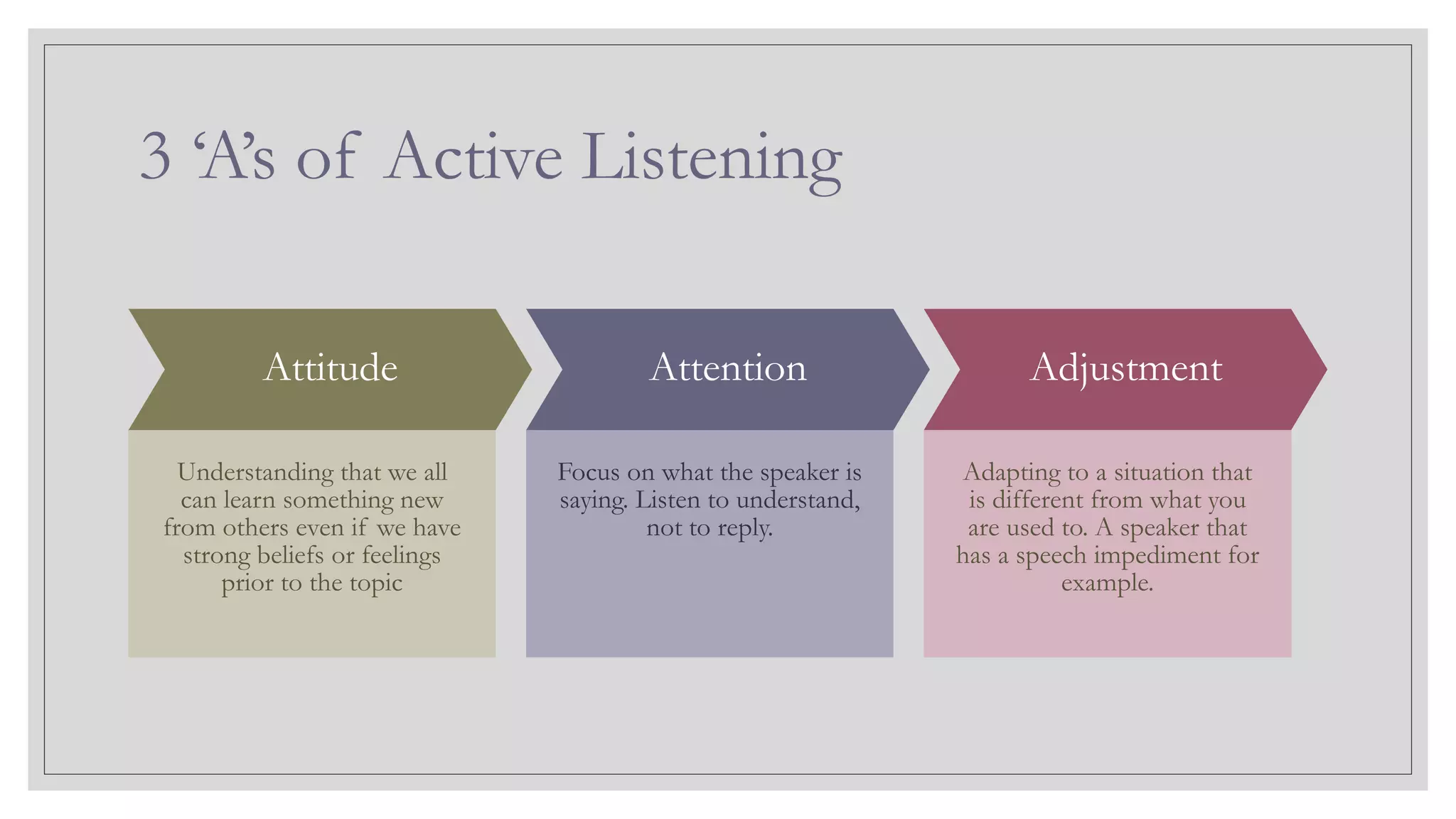
This document provides an overview of a soft skills training series focused on developing employability skills. The series will cover 5 lessons: interpersonal skills, problem solving, listening skills, public speaking, and business etiquette. Soft skills are defined as a combination of personality traits and habits that allow people to work well with others. Problem solving and listening skills will be the focus of two of the lessons. Problem solving techniques like Pareto charts, 5 whys, and fishbone diagrams are introduced. Active listening skills like paraphrasing and nonverbal cues will also be covered. The goal is for participants to improve their soft skills and be better prepared for career success.