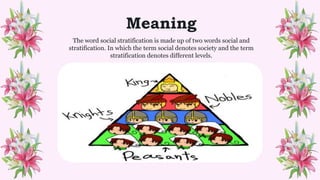
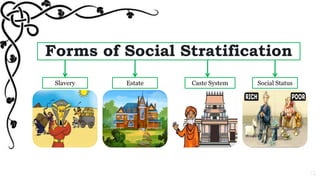
This document defines and discusses social stratification. Social stratification refers to a society dividing its members into rankings based on factors like wealth, class, education, and power. It universally exists in all societies in dividing people into higher and lower social units or classes. The key characteristics of social stratification are that it is a universal social process that divides society into different strata with rankings of superiority and inferiority in a stable, permanent manner. The main forms of social stratification discussed are slavery, estates, caste systems, and social status. Understanding social stratification is important because it lies at the core of sociology and links many social processes by predicting behaviors and life chances based on one's social position.